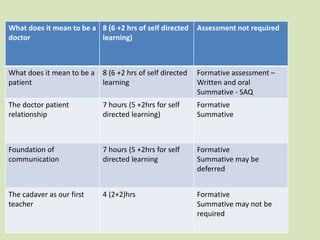
The document outlines the AETCOM initiative aimed at enhancing the curriculum for Indian medical graduates by emphasizing key competencies such as communication, ethics, and lifelong learning. It includes structured modules for each professional year, detailing the roles and responsibilities of a clinician, leader, and communicator within the healthcare system. Additionally, it addresses the hidden curriculum and proposes formal assessments to ensure competency acquisition and the development of professional attitudes.