PHP variables represent data values and are like nouns. Functions represent actions and are like verbs. Operators combine values and functions to form expressions and statements. Control structures like if/else statements and loops structure programs like narratives. The document then discusses regular expressions and creating custom functions in PHP.









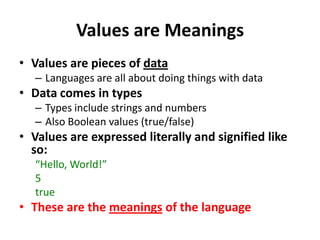




![ExpressionsExpressions are like phrases that combine nouns and verbs5(5 + 10) / 36“Tina” . “ is my cat”;file($url)$fooAll expressions result in a value50.4166666 ...Tina is my cat[the array of the file][whatever $foo was last set to]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdst-3559-02-17-php2-110217141032-phpapp02/85/Mdst-3559-02-17-php2-15-320.jpg)



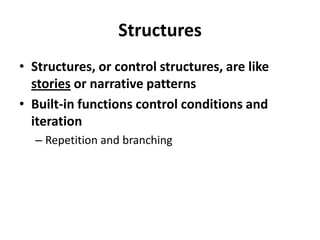





![Regular Expressions. = any character+ = one or more* = 0 or more^ = beginning of the string$ = end of the string[A-Za-z] = character set of all letters() = something to be replaced](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdst-3559-02-17-php2-110217141032-phpapp02/85/Mdst-3559-02-17-php2-25-320.jpg)
