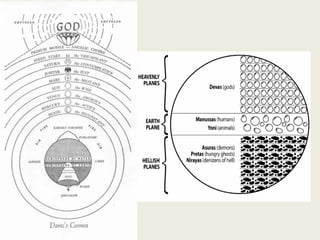
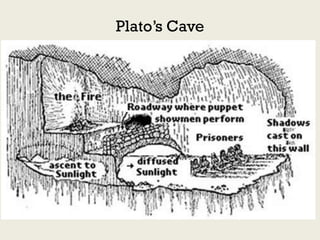
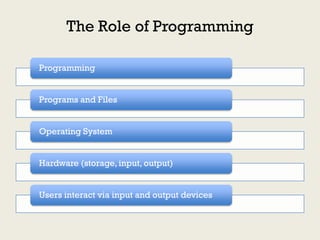
Code functions as a language by representing and creating computational worlds. When writing code, programmers are speaking to computers, which then speak back through the program output. Code uses linguistic structures like variables, values, expressions, and sentences to represent a computational world and direct the computer's operations within that world. Programming involves controlling a new kind of labor by encoding it in a computer language.



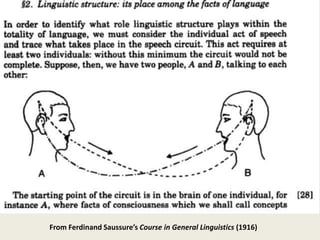




![com⋅put⋅er
/kəm-pyutər/ [kuhm-pyoo-ter]
–noun
1. Also called processor. An electronic device
designed to accept data, perform prescribed
mathematical and logical operations at high
speed, and display the results of these
operations. Compare analog computer, digital
computer.
2. A person who computes; computist.
Origin:
1640–50; compute + -er 1 ; cf. MF computeur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdst3705-2012-01-22-code-as-language-130128090724-phpapp02/85/Mdst3705-2012-01-22-code-as-language-11-320.jpg)