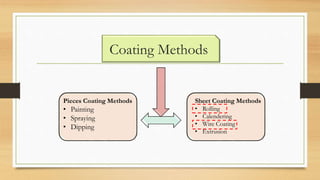
This document discusses polymer coating materials (PCM). It defines monomers and polymers, and classifications of polymers including thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, and thermoplastic elastomers. It describes the characteristics and advantages of polymers, examples of polymer coatings, and common coating methods like painting, spraying, dipping, rolling, calendaring, wire coating, and extrusion. Specific polymer coatings discussed include acrylics, alkyds, polyurethanes, phenolics, nylon, and fluorocarbons; and their applications.