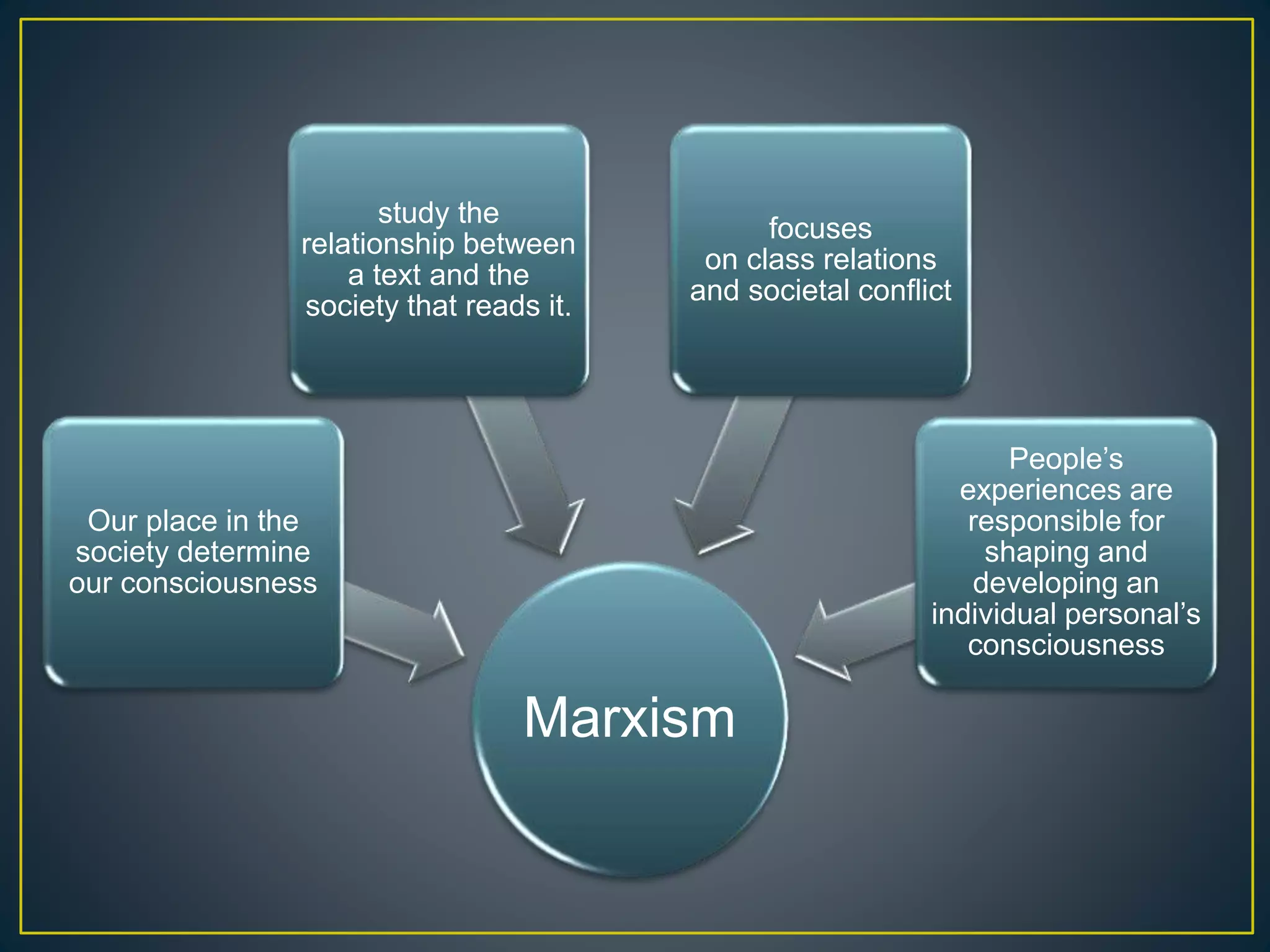
1. Marxism is both a literary theory and social/economic philosophy that views society and history through the lens of class struggle.
2. Key aspects of Marxism include the belief that a society's economic base determines its ideological superstructure, including cultural works, and that the bourgeoisie exploits the proletariat.
3. Marxist literary criticism examines how a text reflects the author's ideology and society's class relations through elements like characterizations and treatment of social forces. The critic's goal is to uncover how the text exposes oppression of the working classes.