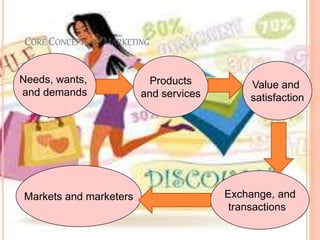
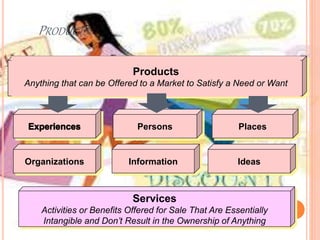
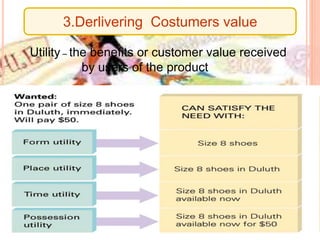
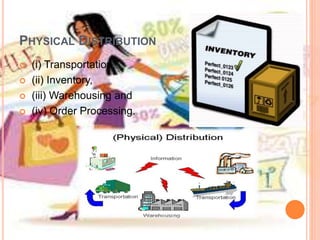
This document outlines core concepts of marketing including needs, wants, demands, products, services, value, satisfaction, exchange, transactions, markets, and marketers. It defines these terms and discusses how consumers choose among products based on comparing value and satisfaction. The functions of marketing are also summarized, including marketing research, product development, buying/assembling, selling, transportation, storage, standardization, branding, packaging, pricing, financing, promotion, customer service, and more. Finally, the importance of marketing for firms, consumers, and society is highlighted.