The document discusses customer-driven marketing strategies, including market segmentation, targeting, differentiation, and positioning. It describes how companies can:
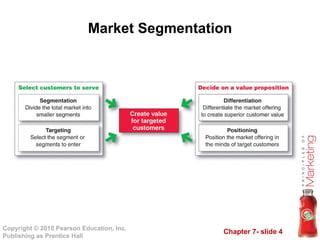
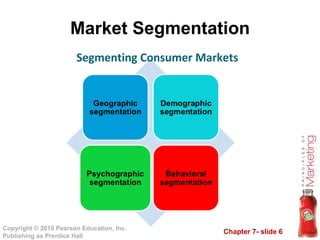
1) Segment markets into distinct groups based on geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors to better target customer needs.
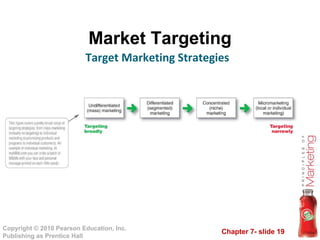
2) Target specific market segments to pursue after evaluating segment size, attractiveness, and fit with company objectives. Strategies include undifferentiated, differentiated, and concentrated marketing.
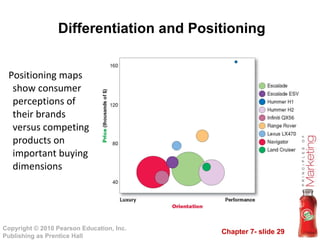
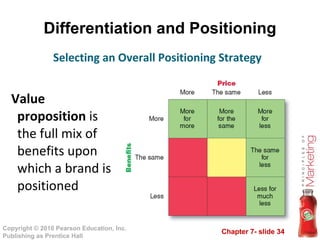
3) Differentiate their products by identifying competitive advantages to build a unique positioning in customers' minds relative to competitors. This involves developing a positioning statement and strategy.