This document discusses key marketing concepts including:
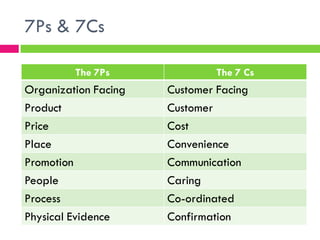
1) The 4 Ps of marketing - product, price, promotion, and place which are elements an organization controls to satisfy customers.
2) Extended marketing concepts including people, physical evidence, and process which represent the human element, tangible experiences, and operational procedures of marketing.
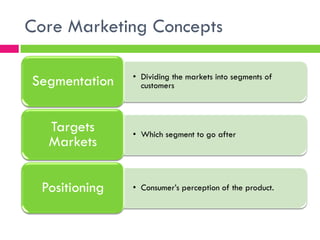
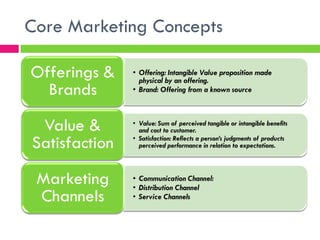
3) Core concepts like segmentation, targeting, positioning, branding, and the supply chain which are fundamental to understanding customer needs and delivering value.
The document provides an overview of fundamental marketing principles for developing strategies that satisfy customer wants and communicate an organization's offerings.