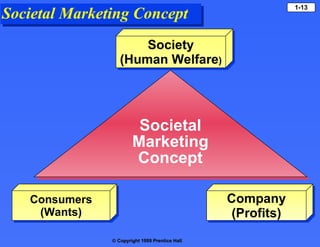
The document provides an overview of key marketing concepts:
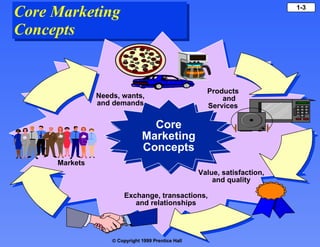
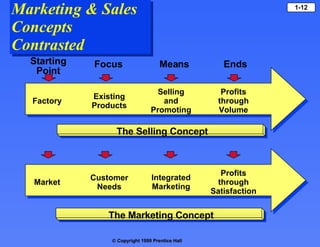
- Marketing involves creating and exchanging products of value to satisfy customer needs and wants, with the goal of profitably delivering customer satisfaction.
- Core concepts include products/services, value/satisfaction, exchange/transactions, needs/wants, and markets.
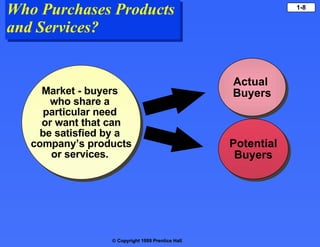
- Marketers must understand what motivates consumers by addressing their needs, wants, and demands. They must also provide products/services that satisfy these needs and wants.
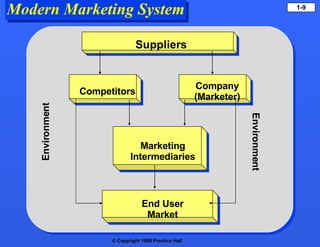
- Modern marketing involves attracting and retaining customers through relationships and exchanges to achieve organizational goals.