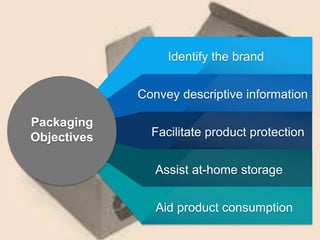
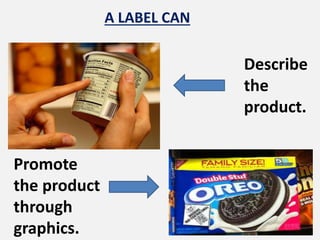
The document outlines product strategy, classifications, and differentiation, emphasizing various product levels and their characteristics such as durability, tangibility, and consumer classifications. It discusses the importance of design, customer service elements, and co-branding strategies, highlighting their impact on marketing effectiveness and consumer perception. Additionally, it covers packaging, labeling, and warranty aspects as vital components of product strategy.