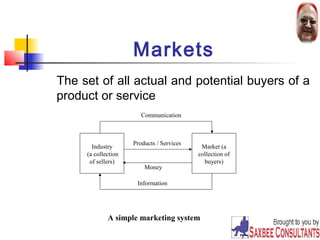
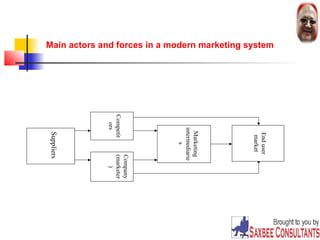
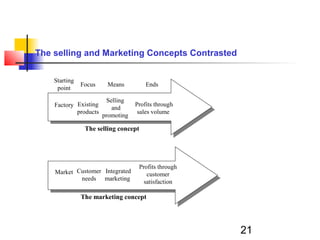
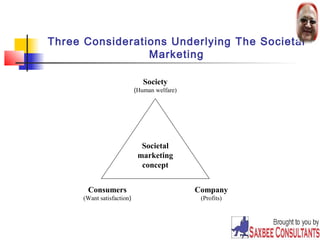
This document provides an overview of marketing concepts. It defines marketing as satisfying customer needs at a profit. The goal of marketing is to attract new customers by promising value and keeping current customers satisfied. Marketing involves understanding customer needs and creating value through products and services exchanged in markets. Firms must practice the marketing concept of customer-orientation to be successful. The document outlines different philosophies like production and selling concepts, and discusses modern challenges like globalization.