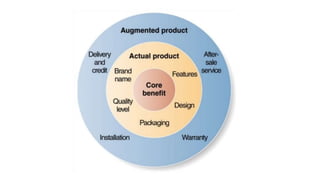
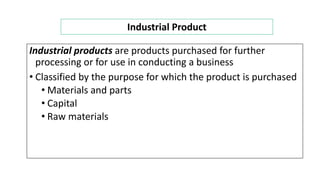
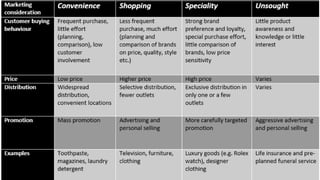
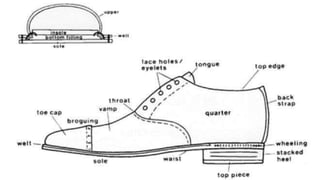
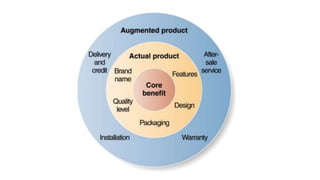
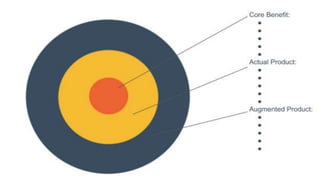
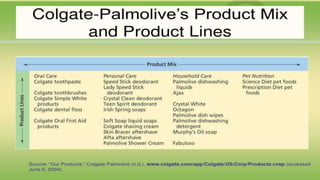
The document discusses key concepts in product and brand building, emphasizing the significance of understanding core customer value, actual products, and augmented products. It differentiates between consumer and industrial products, outlining various classifications such as convenience, shopping, specialty, and unsought products, as well as individual, product line, and product mix decisions from a marketer's perspective. Key elements include product quality, features, branding, packaging, and labeling, all contributing to customer value and satisfaction.