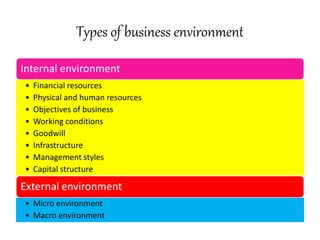
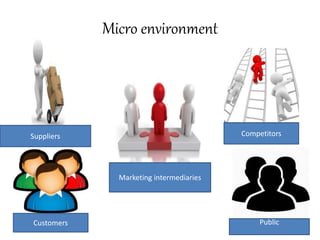
The document discusses the business environment and its various components. It describes the internal environment including resources, objectives, and management. It also analyzes the external/macro environment including political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors. Specific examples are provided to illustrate how these environmental factors impact business decisions and operations in areas like product offerings, market entry, and agricultural practices.