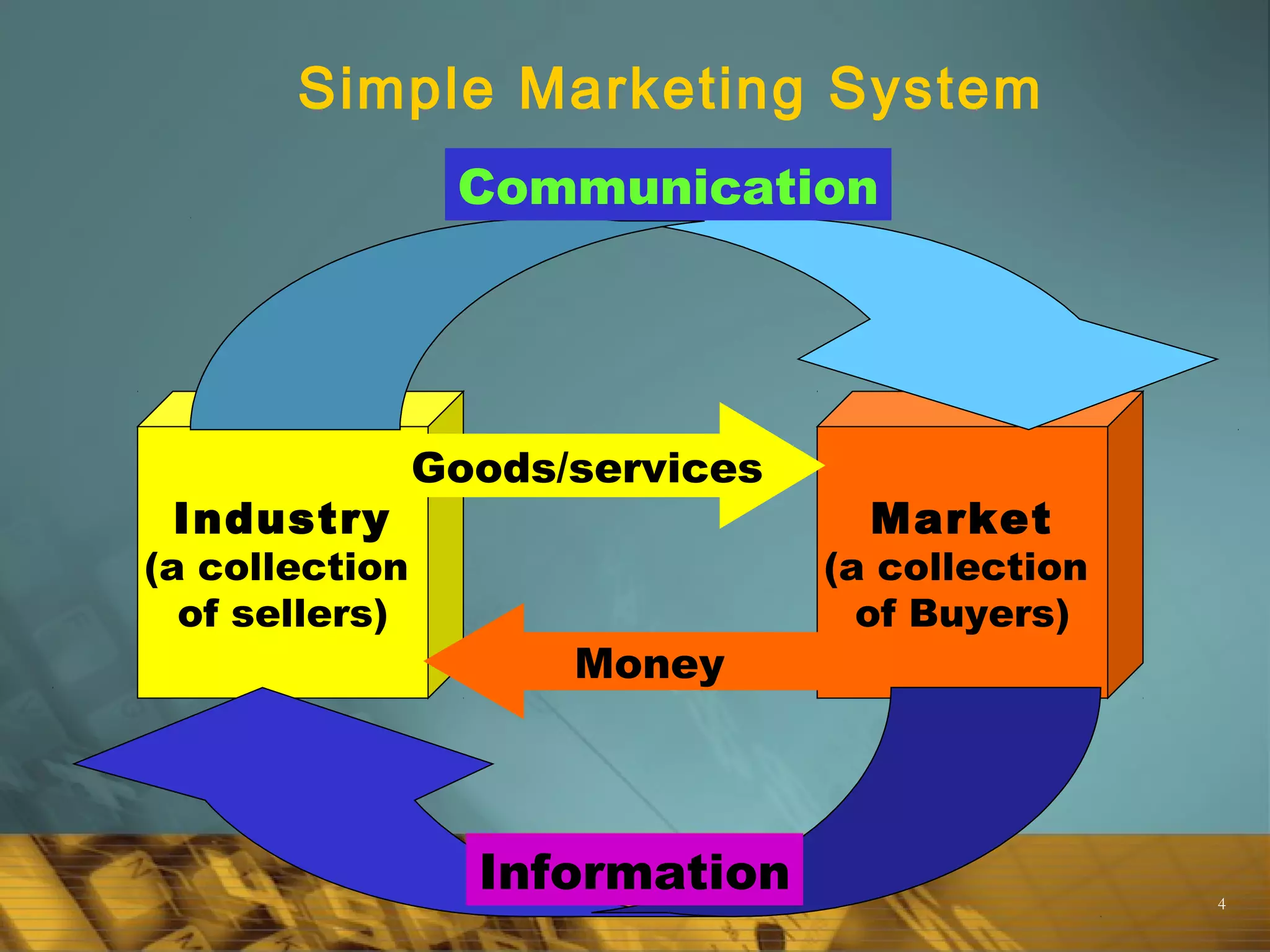
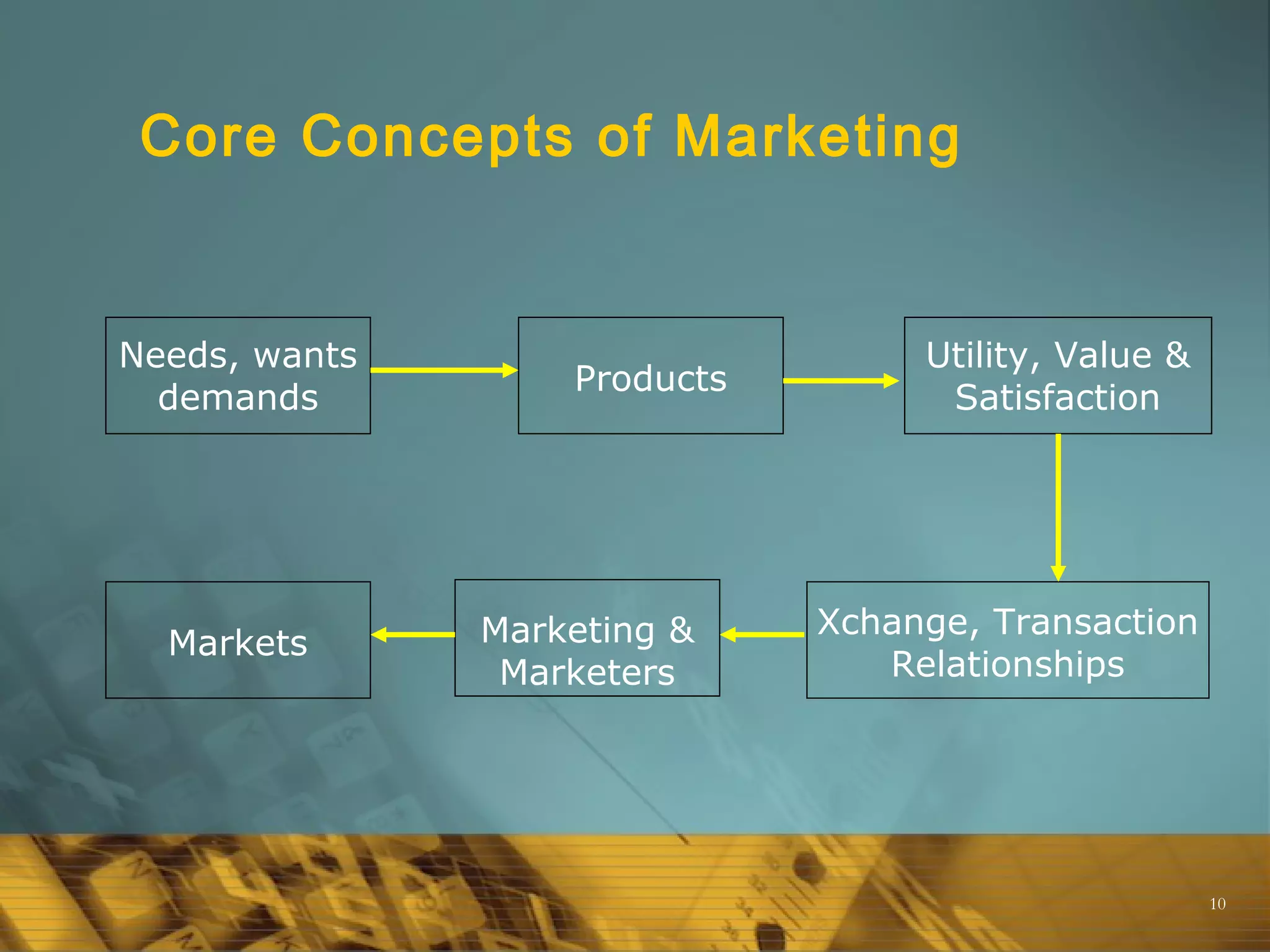
Marketing involves planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of goods and services. It is the process of understanding customer needs and satisfying them through exchanges that benefit both customers and organizations. Marketing aims to understand problems from the customer's perspective in order to provide solutions that customers perceive as valuable. The goal is to make selling unnecessary by creating value for and building relationships with customers.

































![40
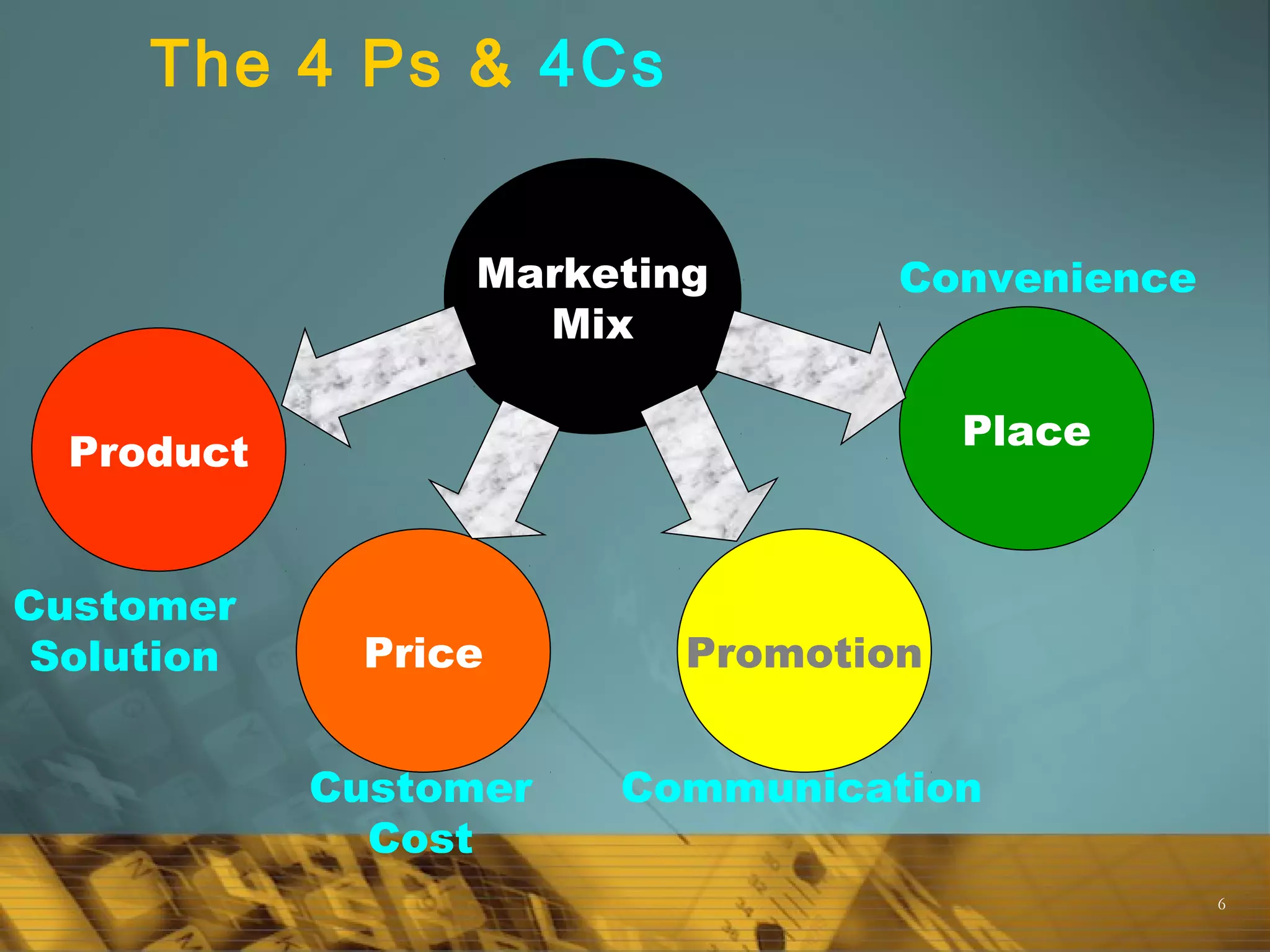
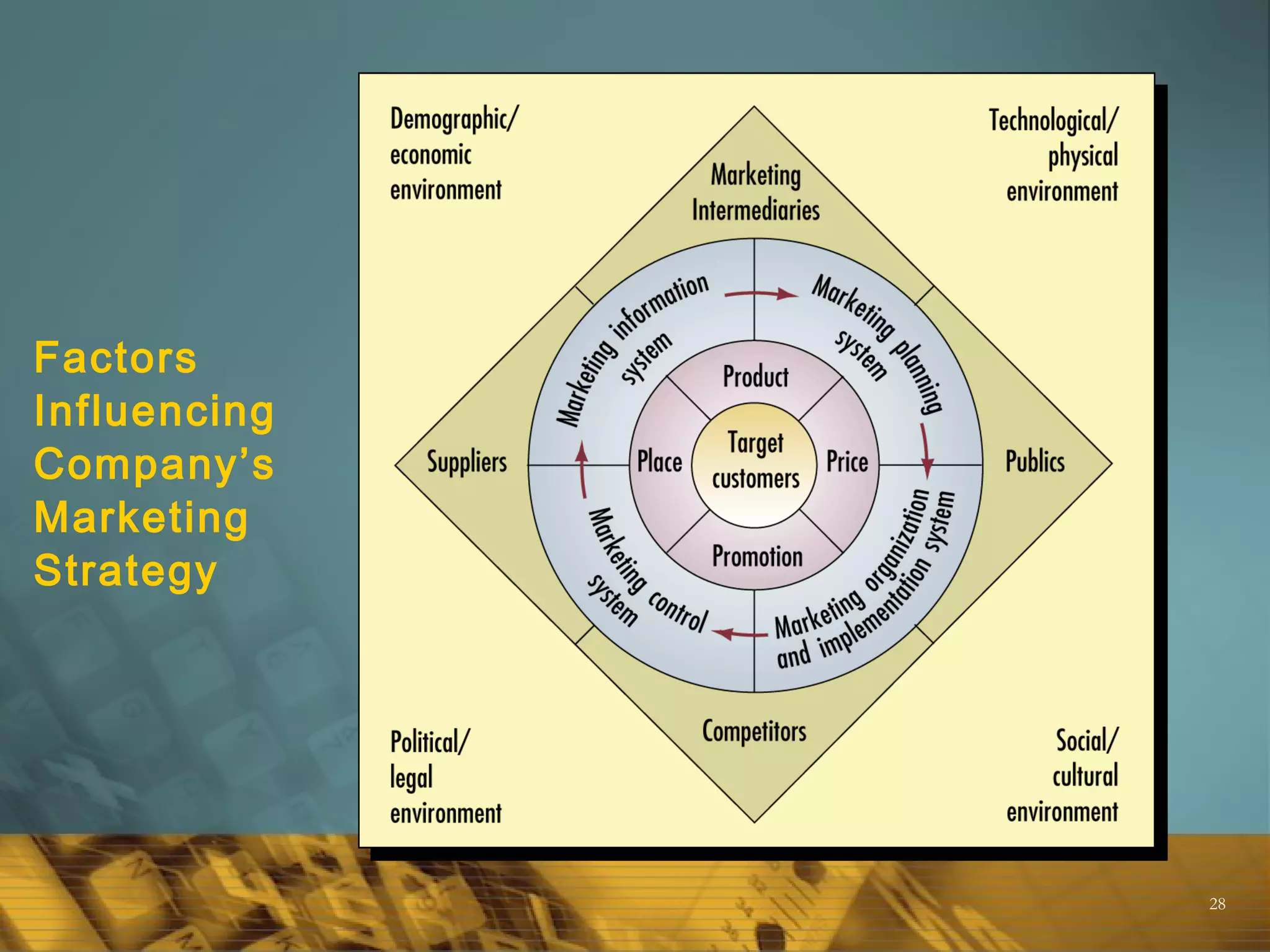
The Marketing Mix
The conventional view of the marketing mix consisted of
four components (4 Ps): Product, Price, Place/
distribution and Promotion.
Generally acknowledged that this is too narrow today;
now includes , Processes, Productivity [technology ]
People [employees], Physical evidence
Marketers today are focused on virtually all aspects of
the firm’s operations that have the potential to affect
the relationship with customers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/marketinganditsfundamentals-160507135645/75/Marketing-and-its-fundamentals-39-2048.jpg)
















