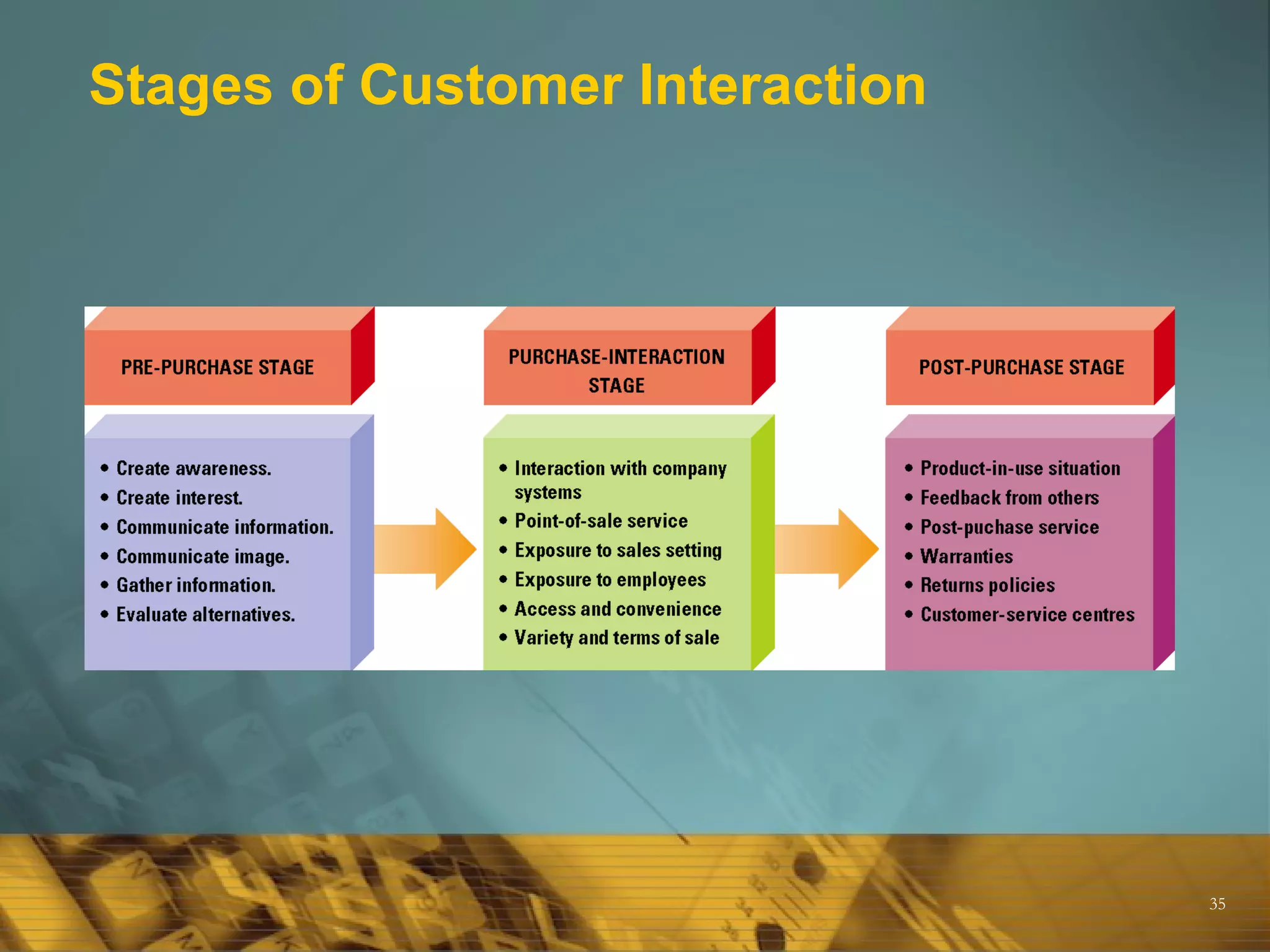
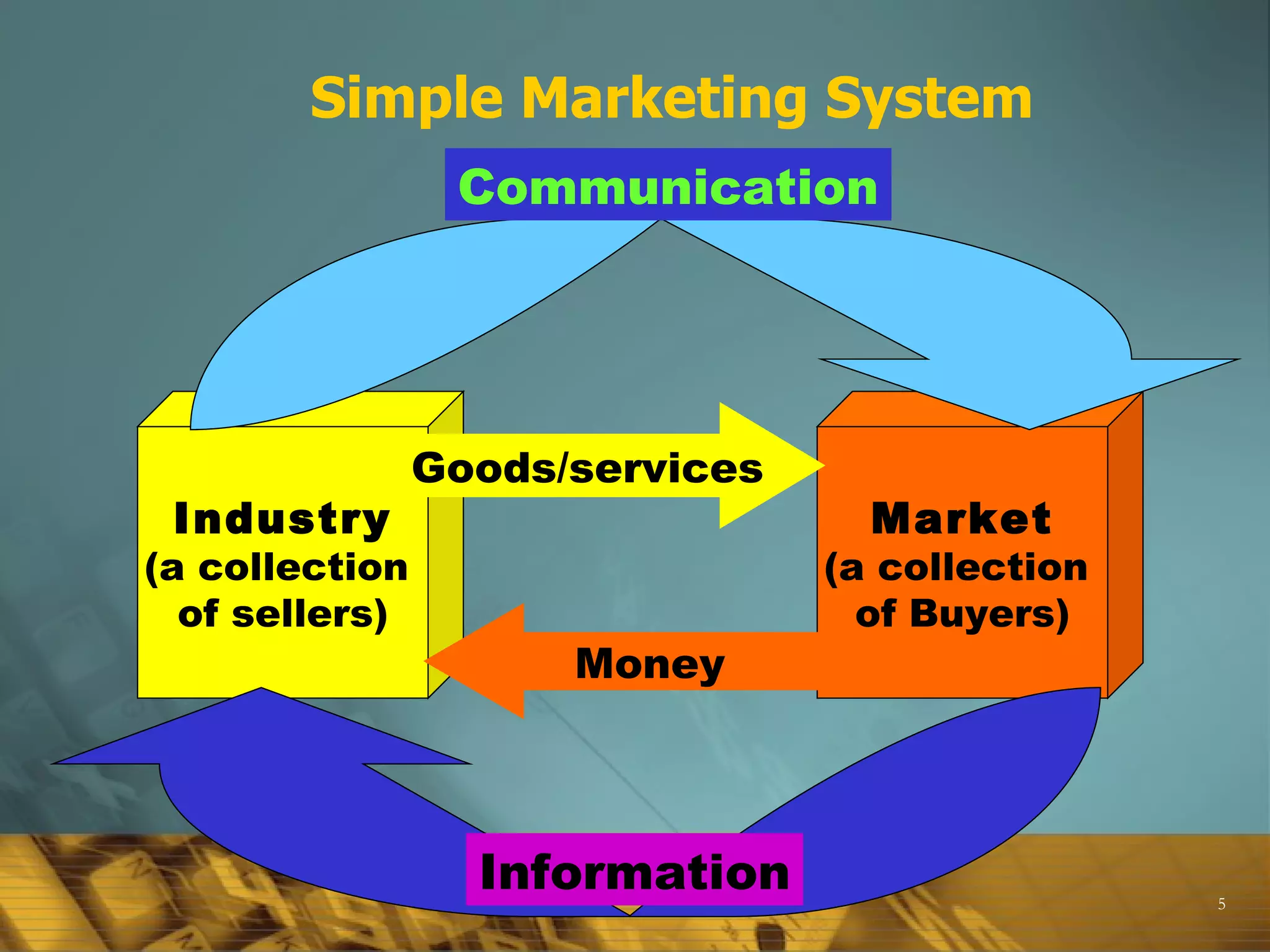
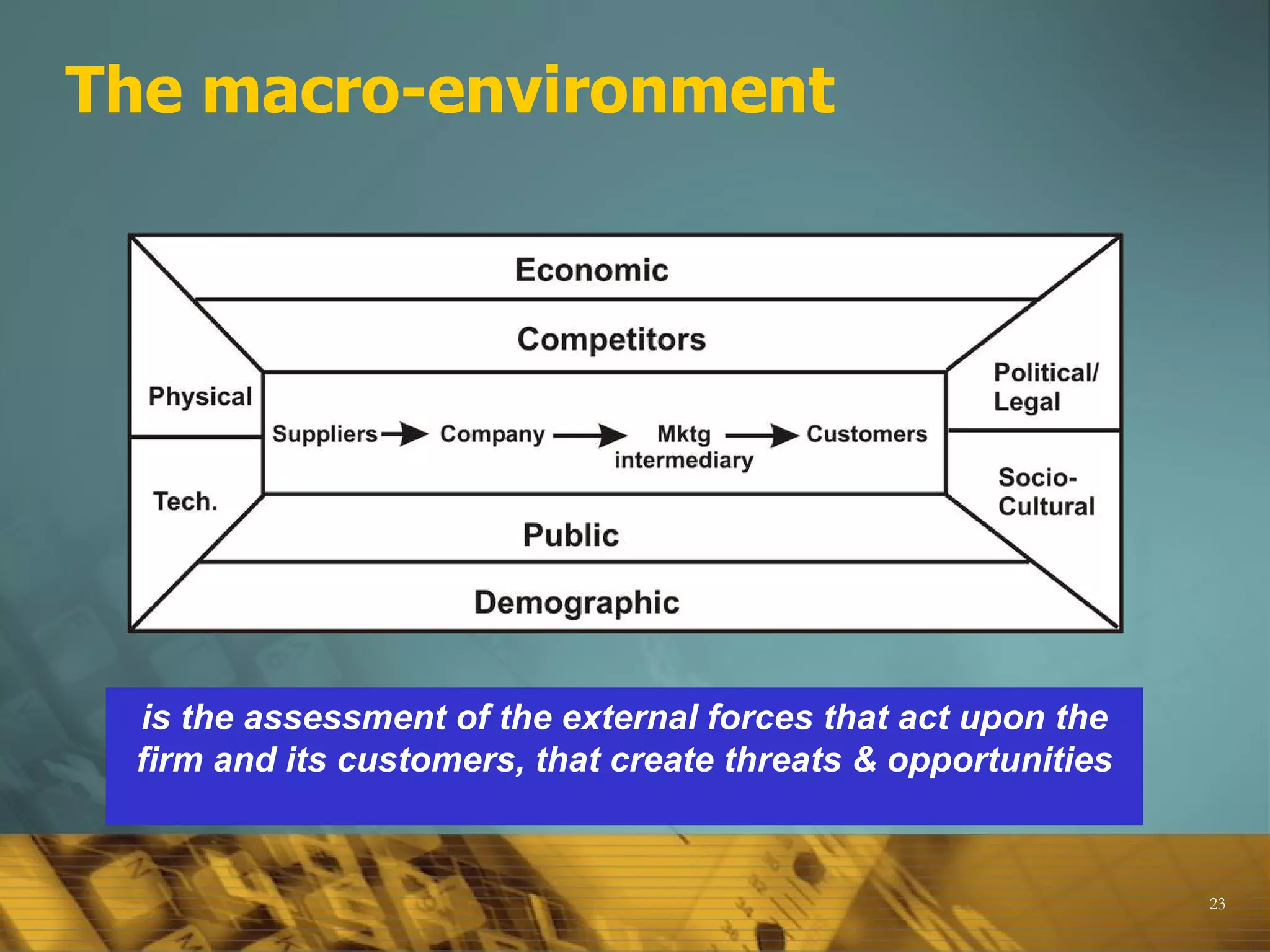
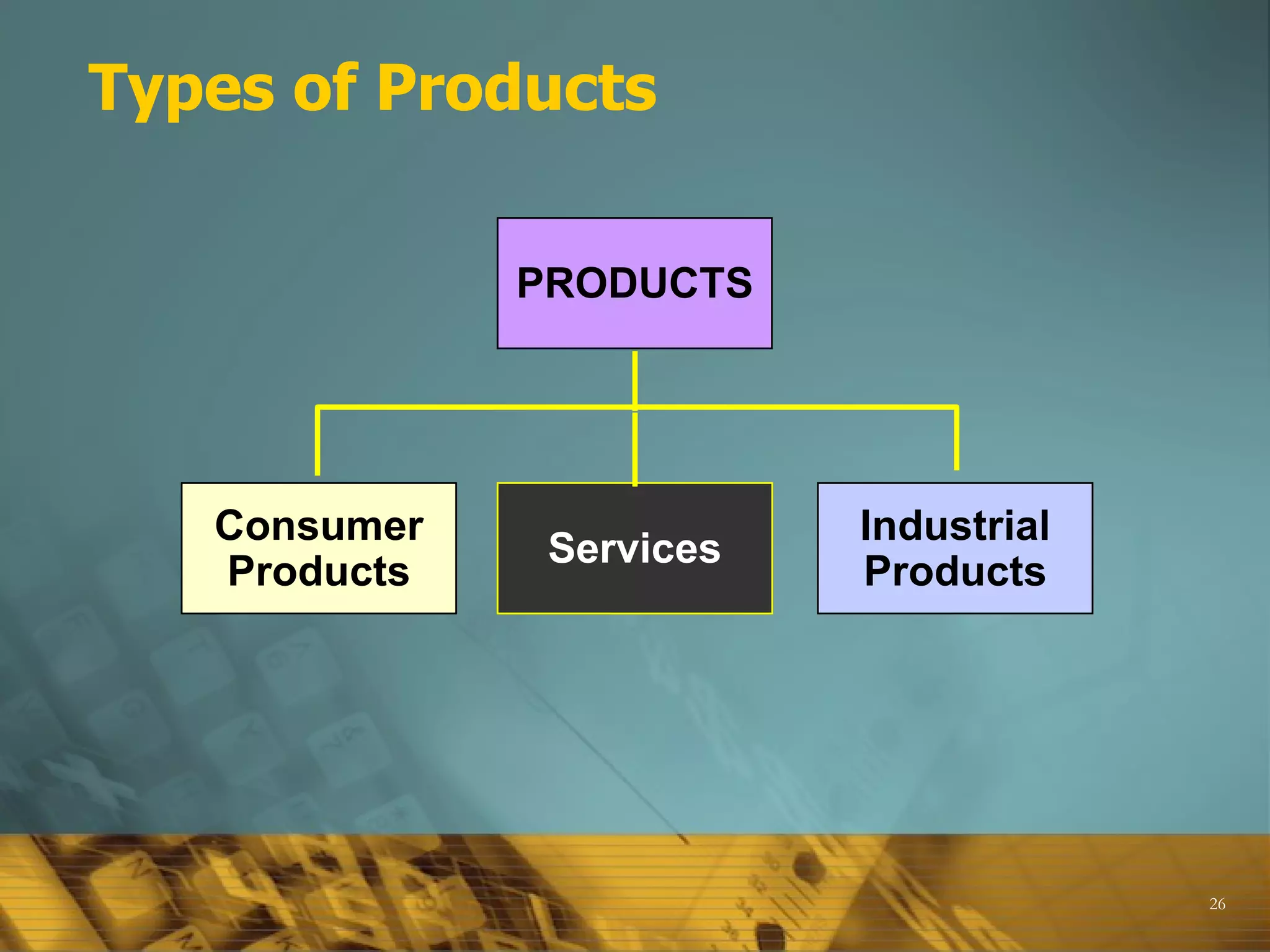
The document provides an overview of key marketing concepts and terms, including definitions of marketing, the marketing mix (4Ps and 4Cs), differences between sales and marketing, the scope of what can be marketed, core concepts like customer needs and wants, and factors that influence marketing strategy like the external environment. It also discusses topics like target markets, the marketing plan, the marketing process, product types and product mix, customers and understanding customer value.





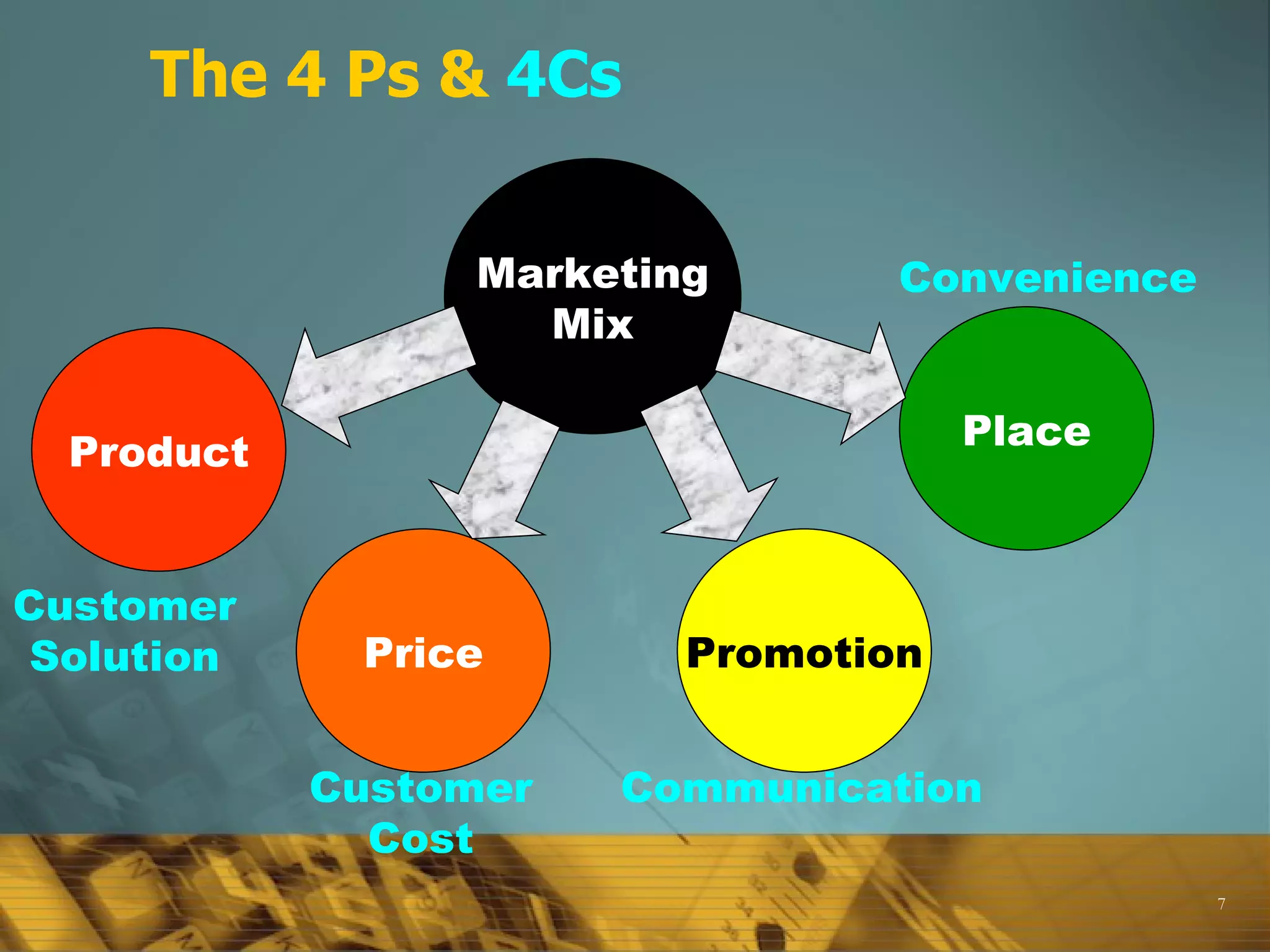















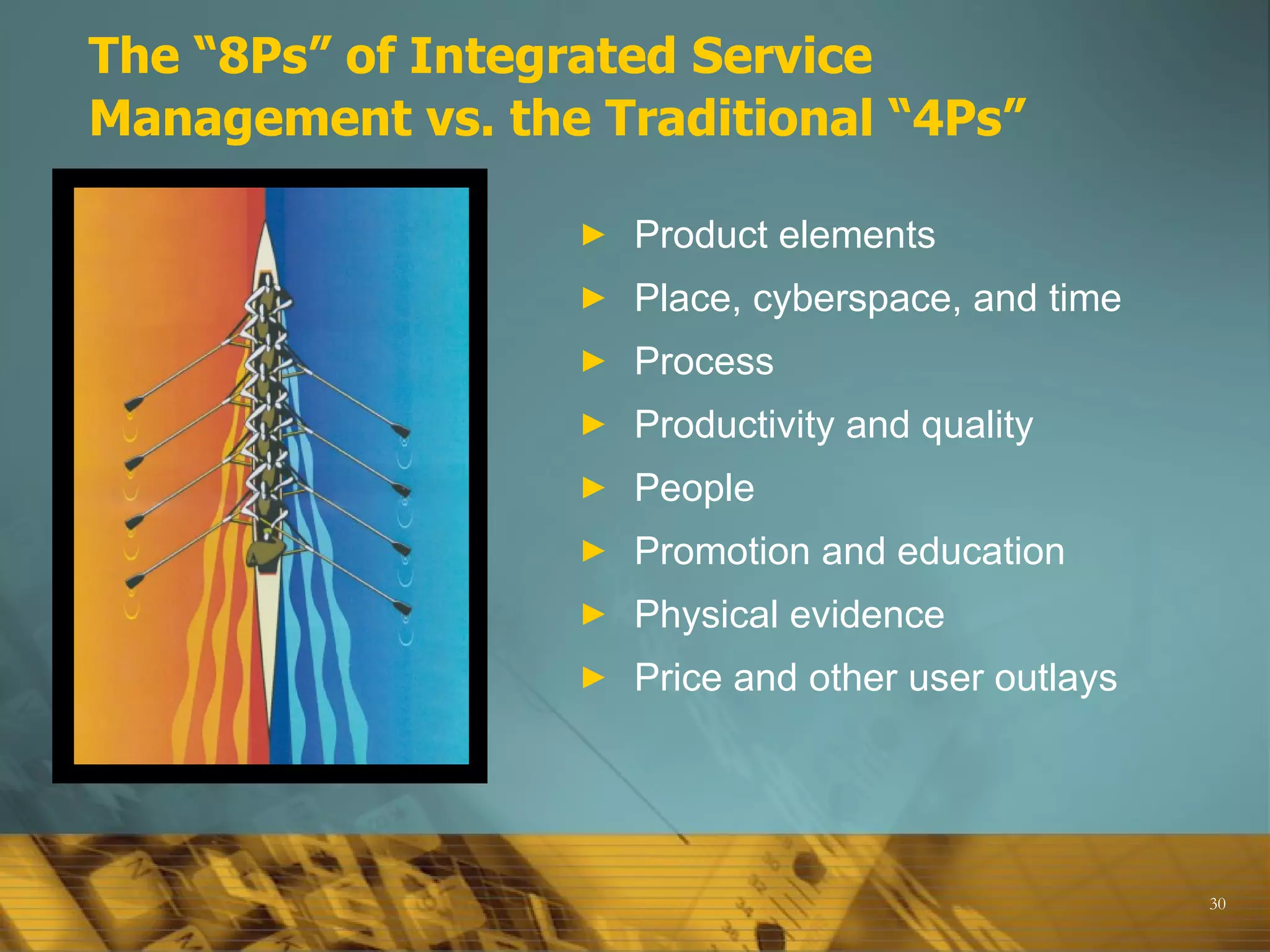
![The Marketing Mix The conventional view of the marketing mix consisted of four components (4 Ps): Product, Price, Place/ distribution and Promotion . Generally acknowledged that this is too narrow today; now includes , P rocesses , P roductivity [technology ] P eople [employees], P hysical evidence Marketers today are focused on virtually all aspects of the firm’s operations that have the potential to affect the relationship with customers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01-marketingconcepts-110403204735-phpapp01/75/01-marketing-concepts-29-2048.jpg)