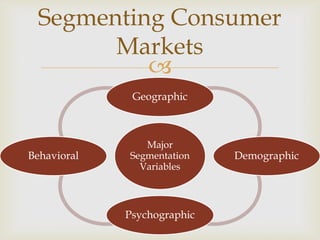
This document discusses various ways to segment consumer and business markets. There are four major types of segmentation: geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral. Geographic segmentation divides markets into geographic units. Demographic segmentation divides markets based on variables like age, gender, income. Psychographic segmentation divides based on psychological factors like personality traits and lifestyle values. Behavioral segmentation divides based on factors like customer benefits sought, brand loyalty, and usage rates. Effective segmentation criteria should be measurable, substantial in size, accessible to target, allow for differentiation of needs, and be actionable for marketing strategies.