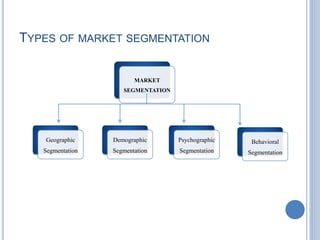
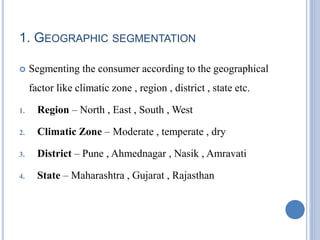
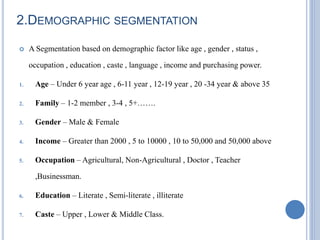
This document defines market segmentation and describes the four main types: geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral. Market segmentation involves dividing the overall heterogeneous market into submarkets based on characteristics that are important to targeting customers. Geographic segmentation divides the market based on location factors. Demographic segmentation uses variables like age, income, gender, occupation. Psychographic segmentation considers personality traits and attitudes. Behavioral segmentation analyzes purchasing behaviors and benefits sought. The advantages of segmentation include tailoring products/services to specific targets and identifying new profitable segments. Disadvantages include higher costs for developing individual marketing strategies and messages for each segment.