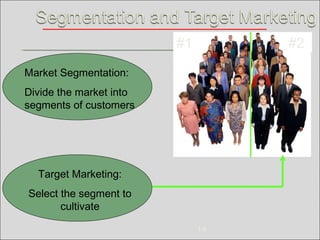
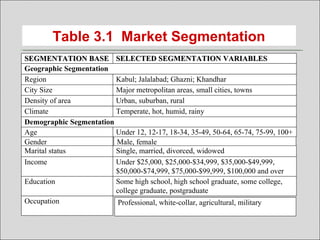
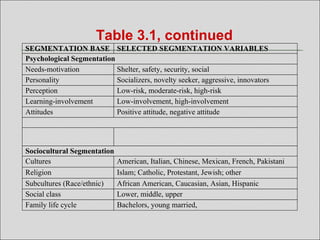
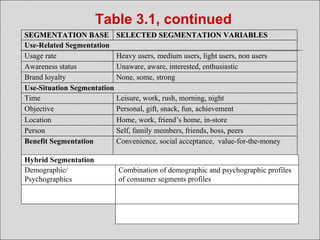
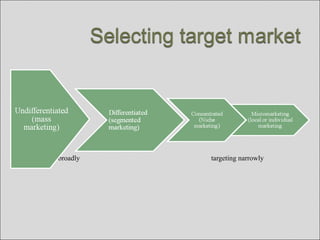
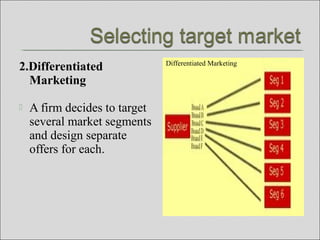
The document discusses market segmentation, targeting, and positioning. It defines market segmentation as dividing a market into smaller groups with similar characteristics that may require separate products or marketing mixes. It also defines target marketing as selecting a category of customers to focus on. The document then discusses different ways to segment consumer and business markets, including by geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors. It also discusses evaluating market segments and different targeting strategies like undifferentiated, differentiated, concentrated, micromarketing, and individual marketing.