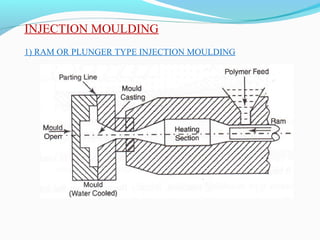
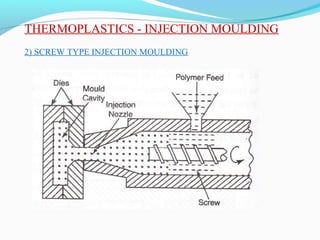
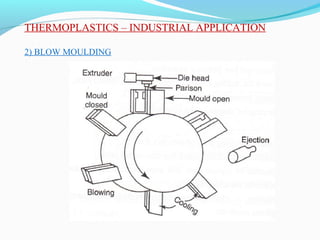
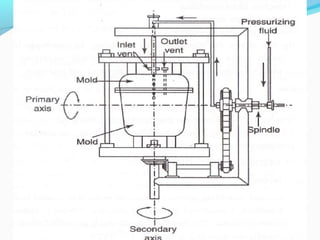
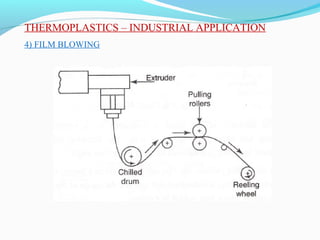
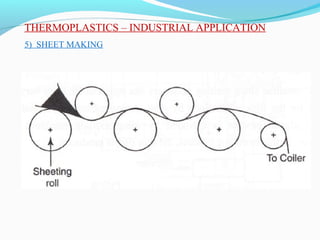
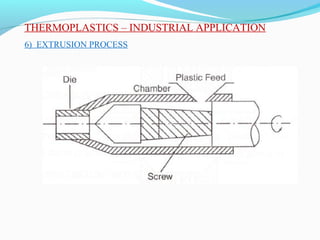
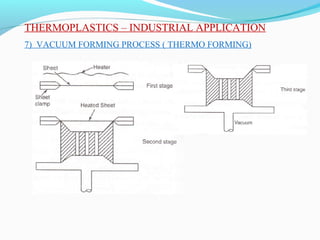
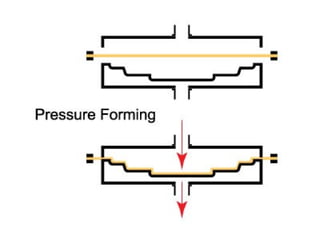
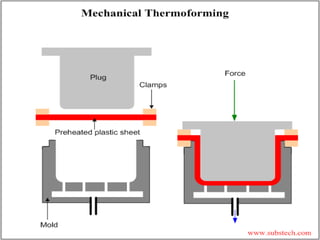
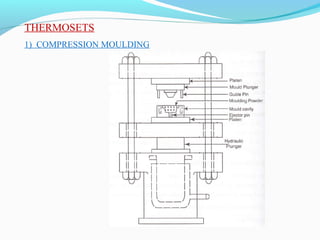
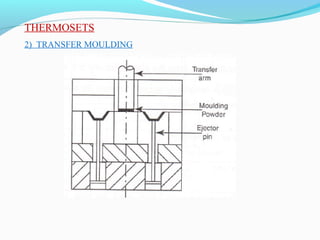
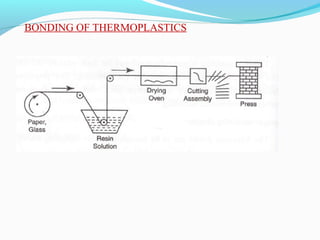
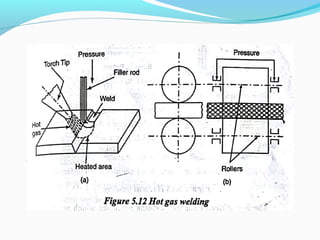
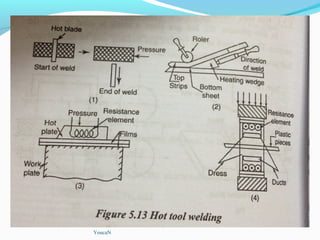
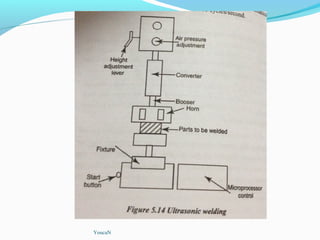
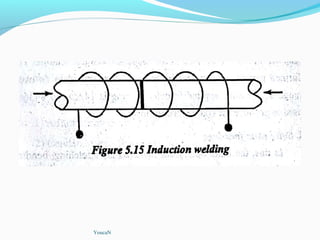
The document discusses various topics related to plastics manufacturing including types of plastics, polymerization processes, properties of plastics, types of resins, thermoplastics vs thermosetting plastics, and common shaping processes for plastics like injection moulding, blow moulding, rotational moulding, extrusion, compression moulding and transfer moulding. Key plastic shaping processes are injection moulding using ram or screw machines, blow moulding, rotational moulding, film blowing, sheet making and extrusion. Common applications of thermosets include compression moulding and transfer moulding.