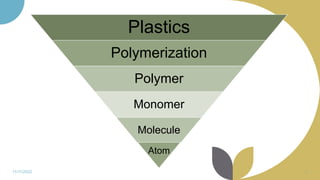
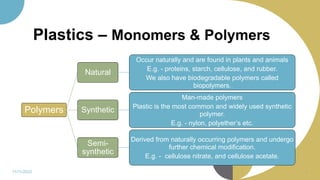
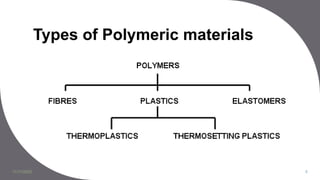
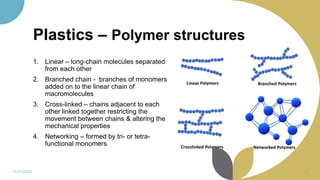
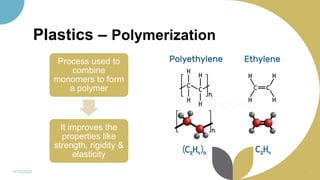
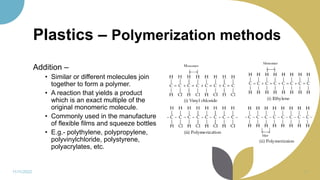
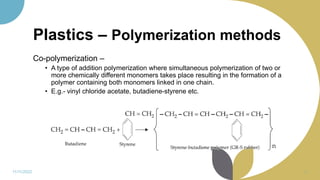
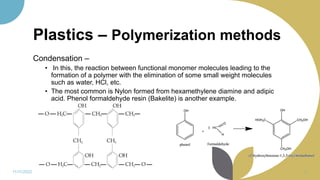
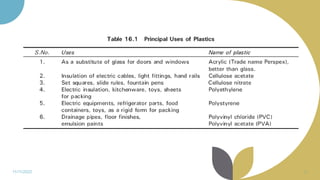
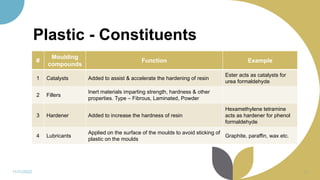
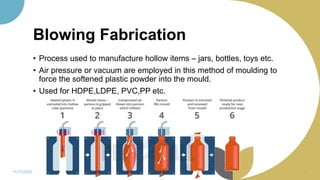
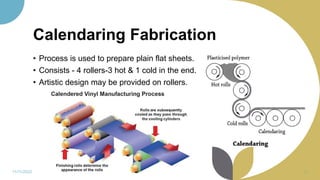
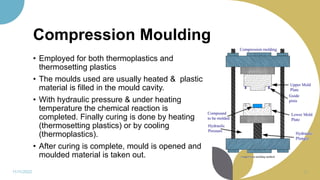
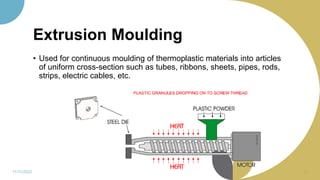
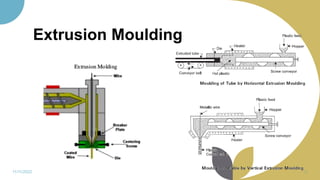
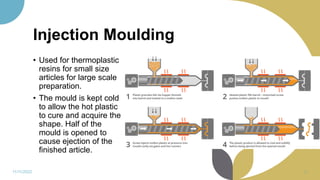
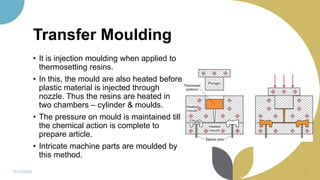
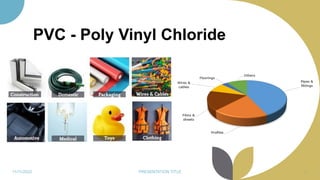
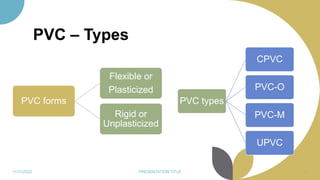
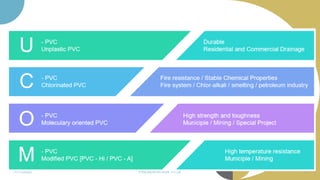
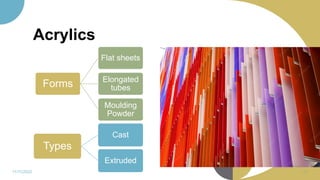
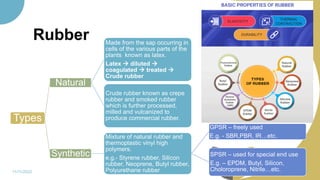
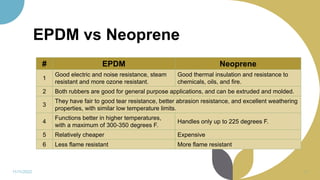
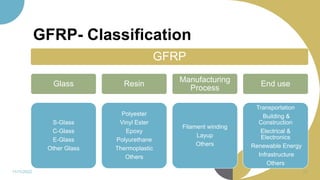
The document discusses plastics and polymers. It begins by defining plastics and polymers, noting they are made up of chains of monomers linked together. It then describes the different types of polymers like natural, synthetic, and semi-synthetic. It explains the polymerization process and different methods like addition, condensation, and co-polymerization. The document also discusses key plastic types like thermoplastics and thermosets. It provides a timeline of important developments in the plastics industry. In summary, the document provides an overview of plastics and polymers, including their composition, production methods, types, and history.