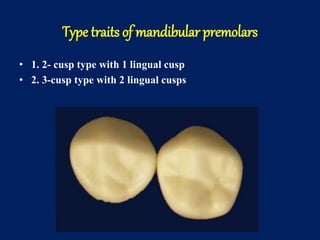
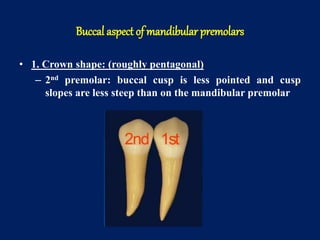
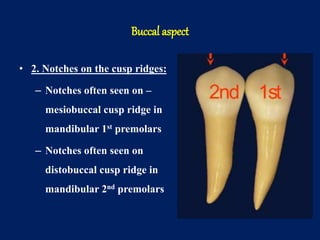
The document details the anatomical characteristics and distinguishing traits of mandibular premolars, focusing on both the first and second premolars' morphology. It describes variations in crown shape, cusp size, contact areas, and occlusal features, highlighting differences between the two types (two-cusp and three-cusp). Key aspects addressed include the shapes, dimensions, and grooving patterns of the occlusal surfaces, as well as root characteristics.