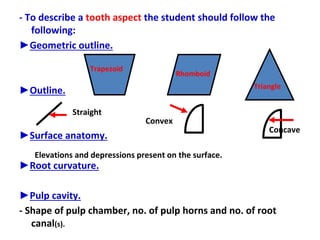
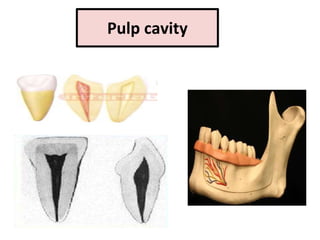
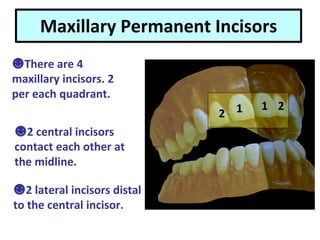
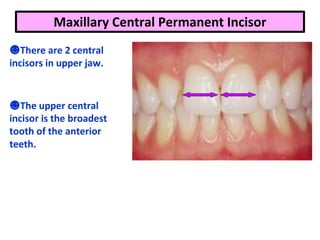
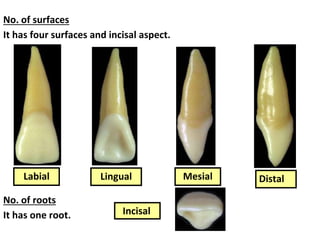
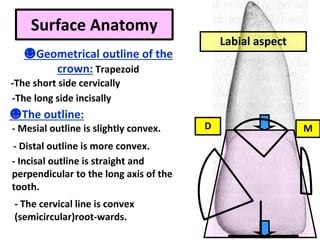
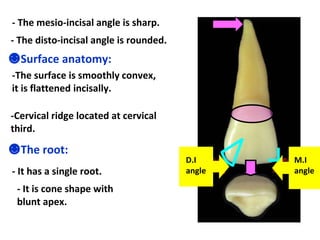
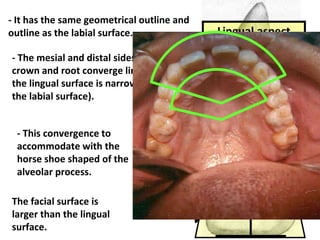
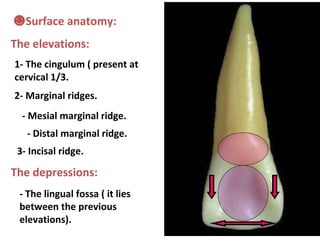
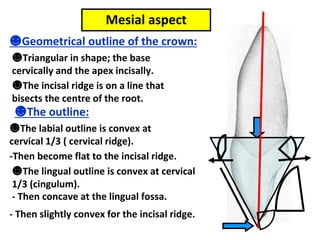
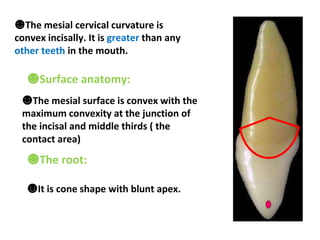
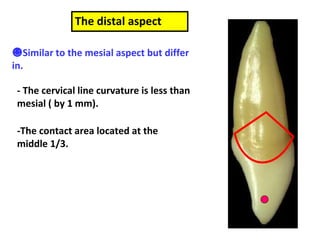
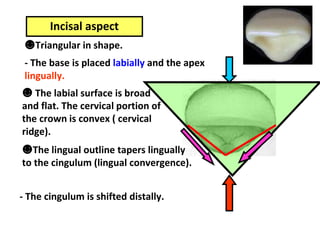
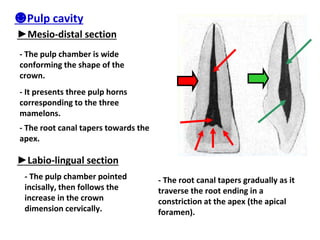
This document describes the anatomy and features of a maxillary permanent central incisor tooth. It discusses the chronology of development, type and function, number of surfaces, lobes and roots. It provides detailed descriptions of the labial, lingual, mesial, distal and incisal aspects of the tooth crown. It outlines the geometric shape, outlines, surface anatomy and root curvature. It also describes the shape of the pulp chamber and root canal.