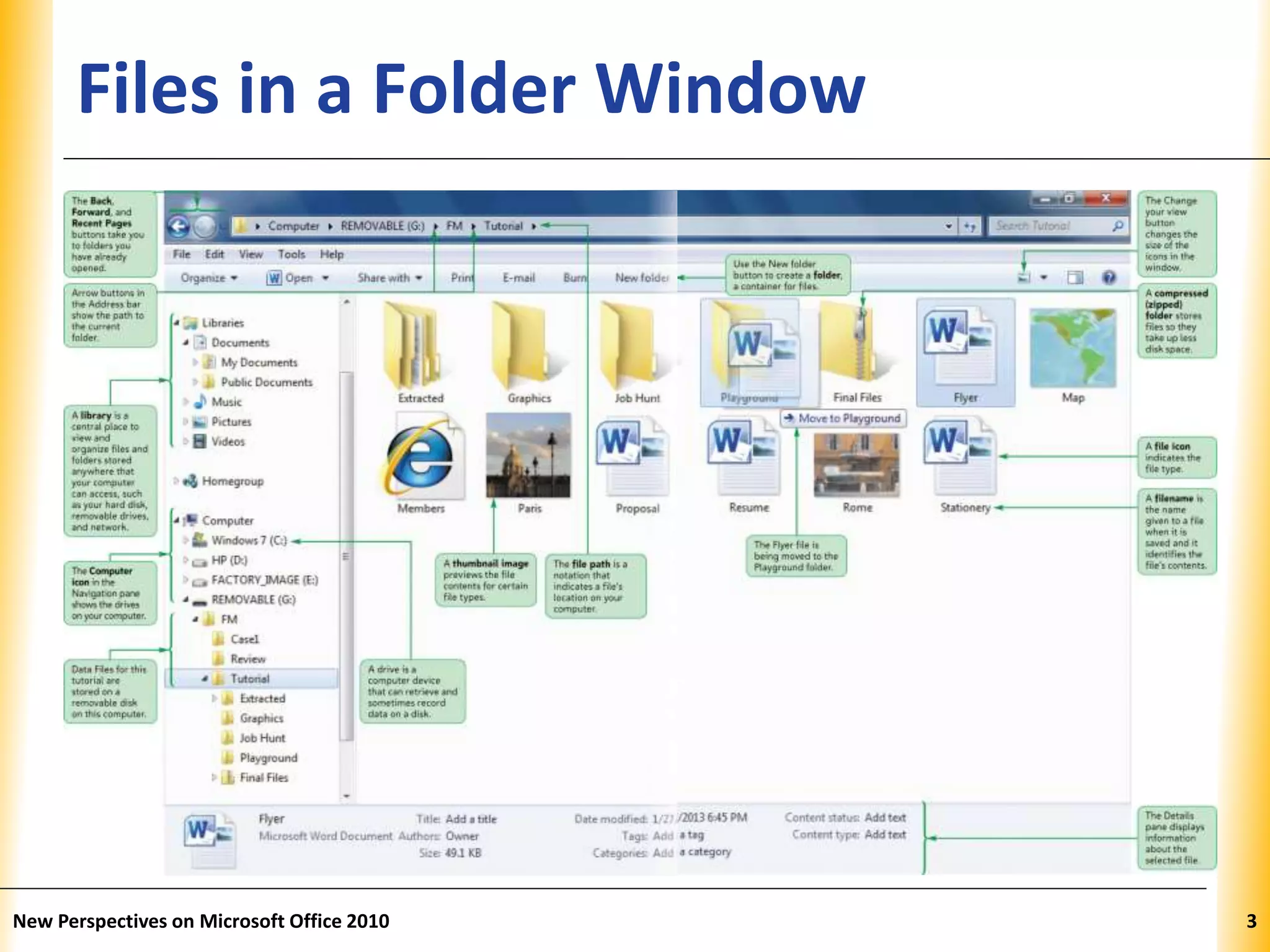
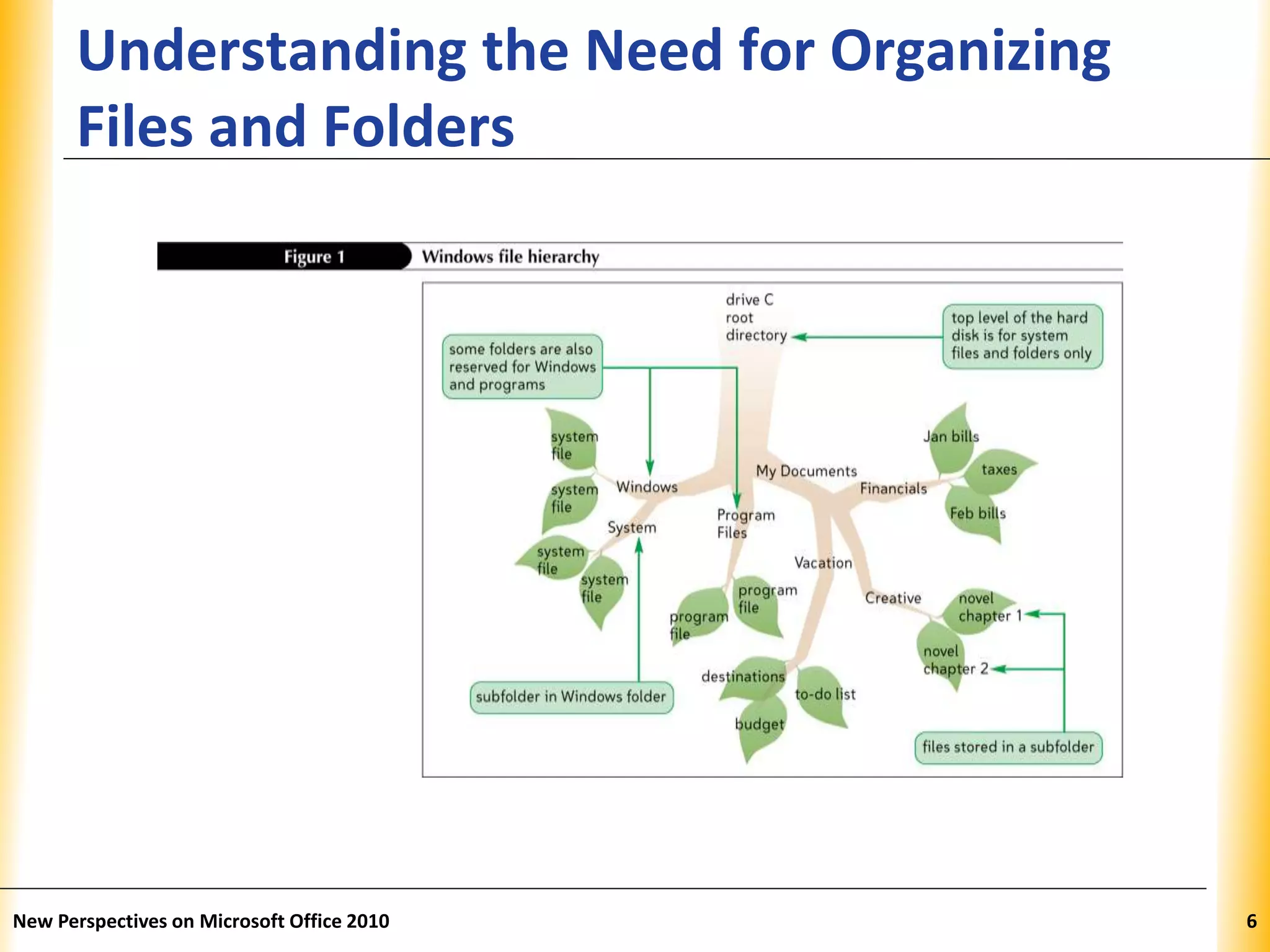
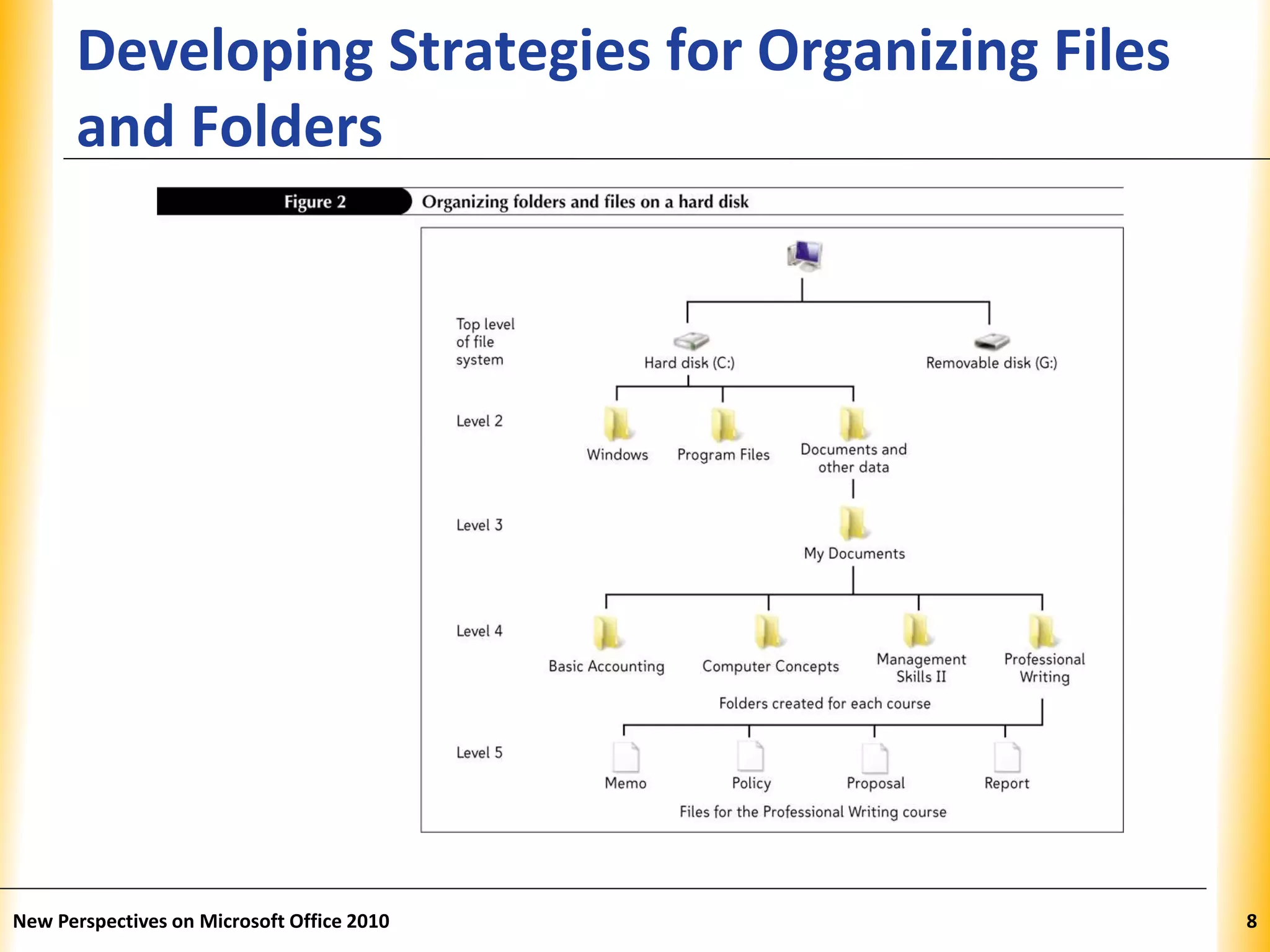
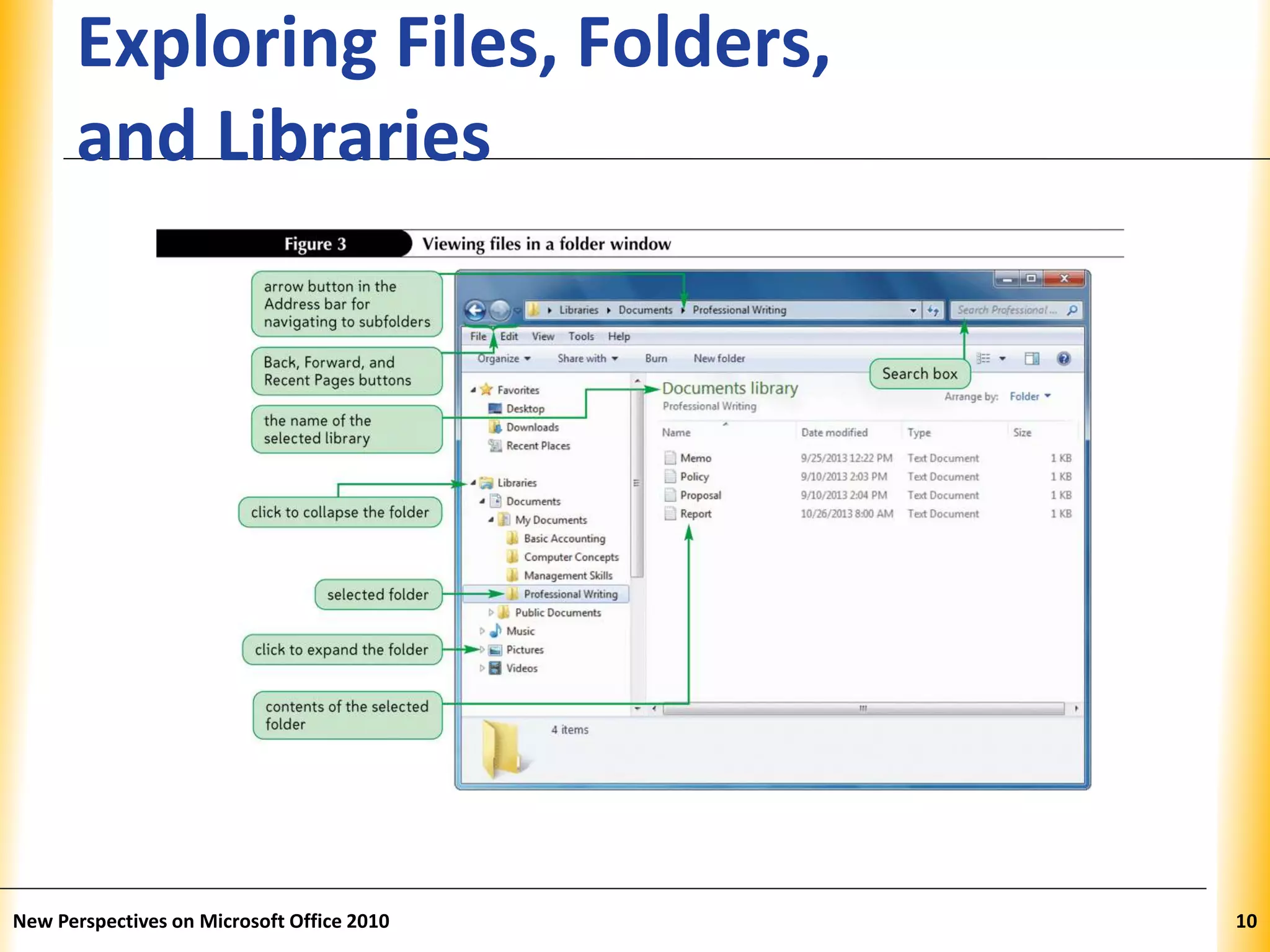
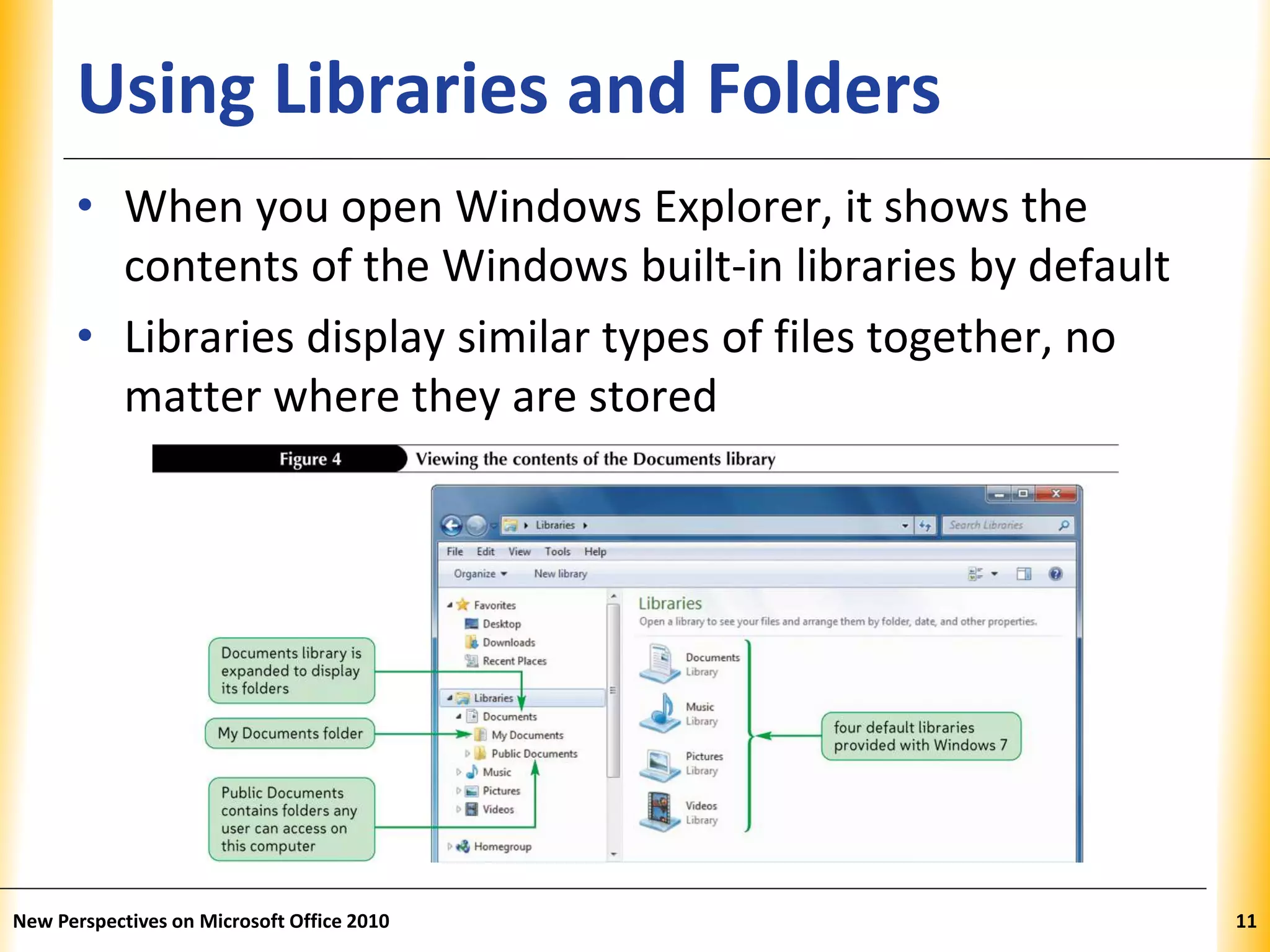
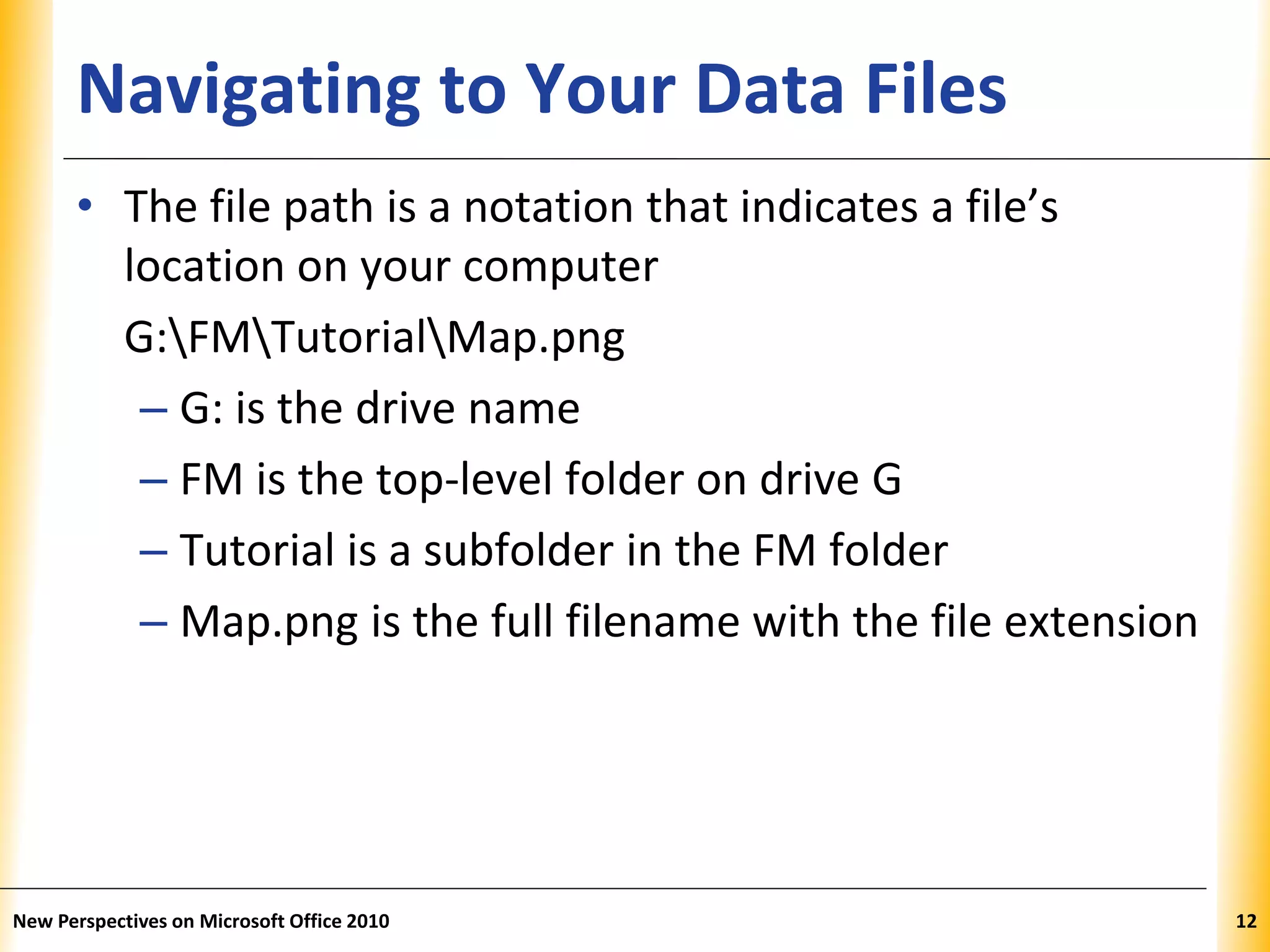
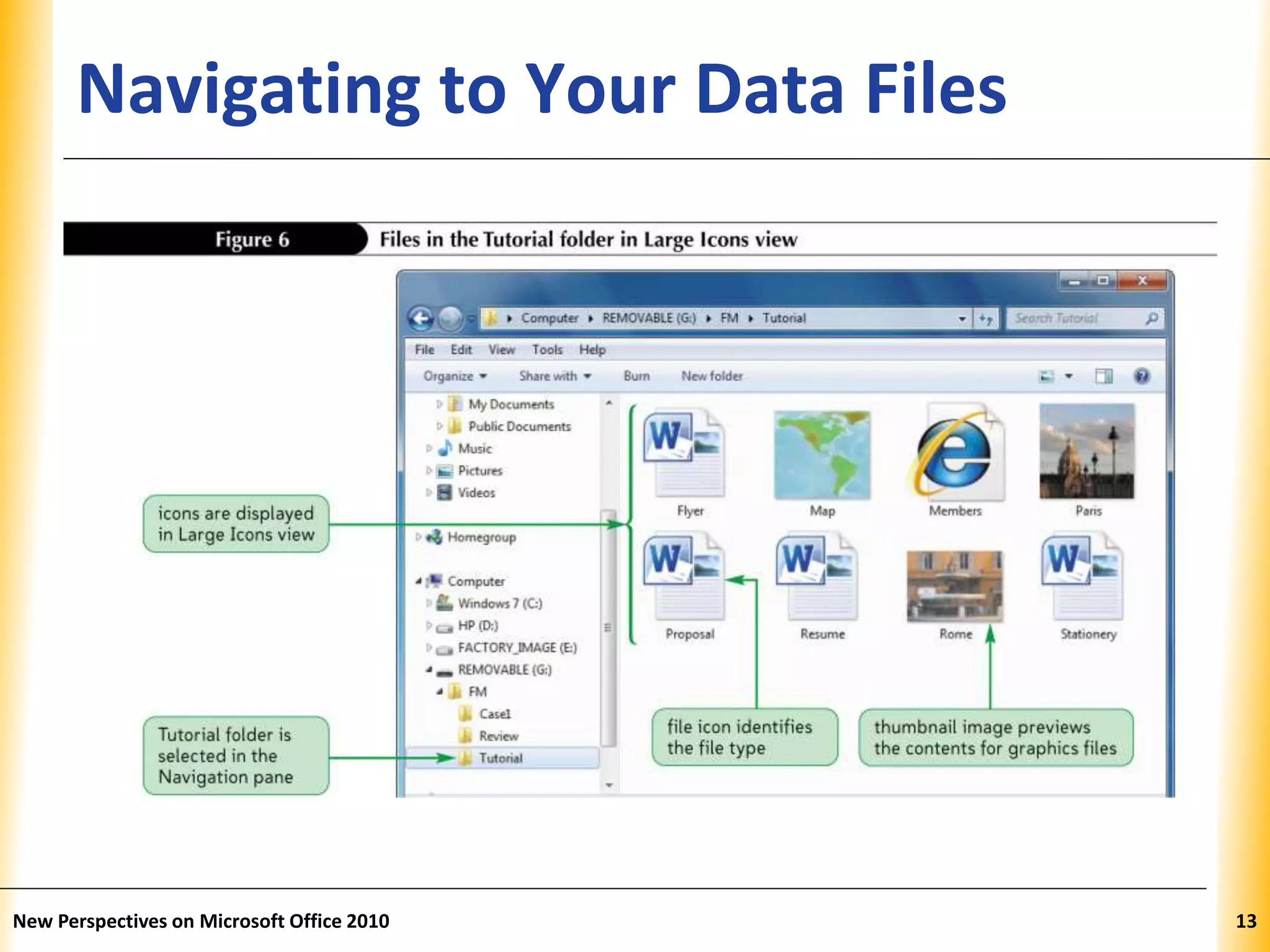
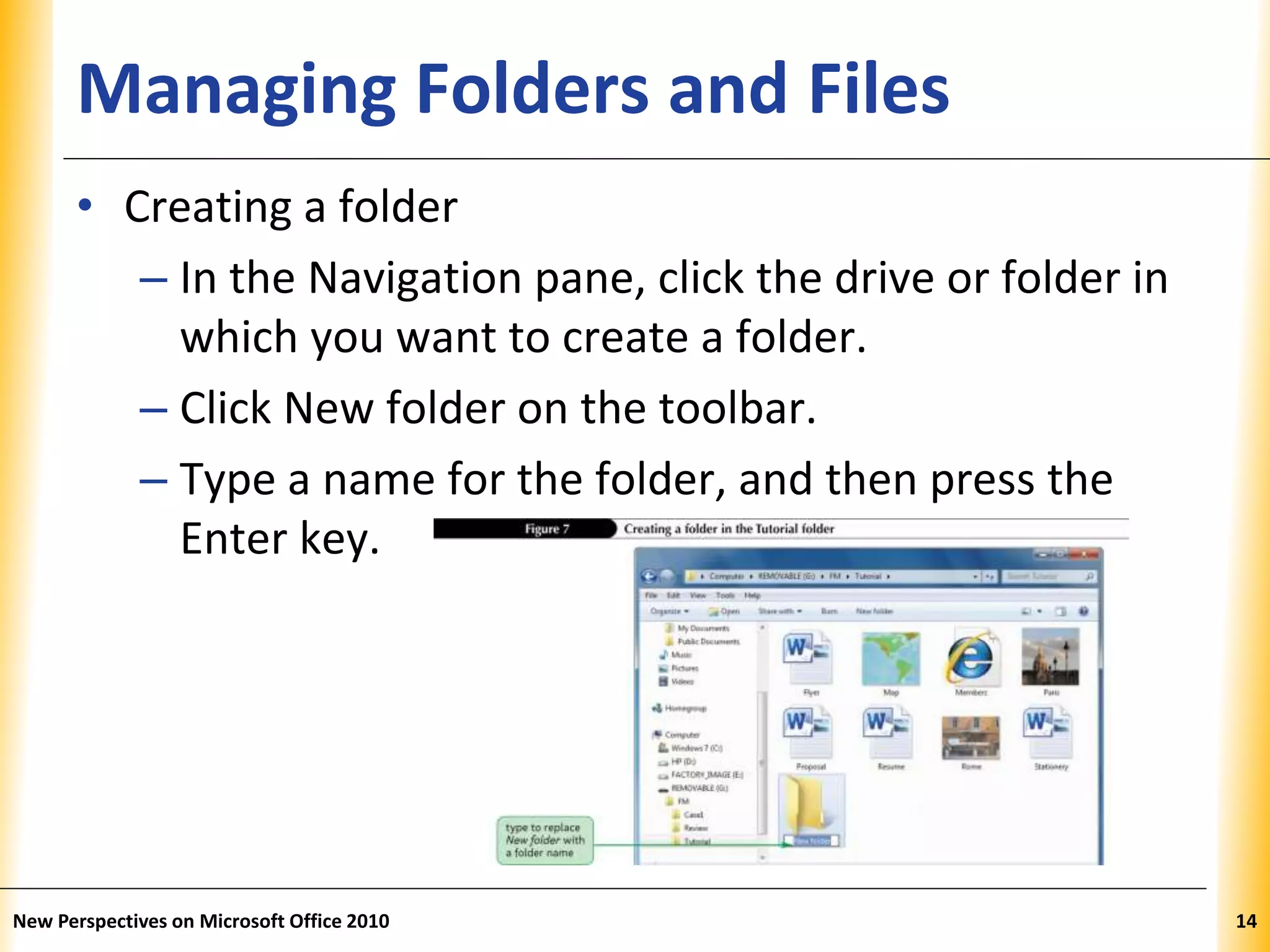
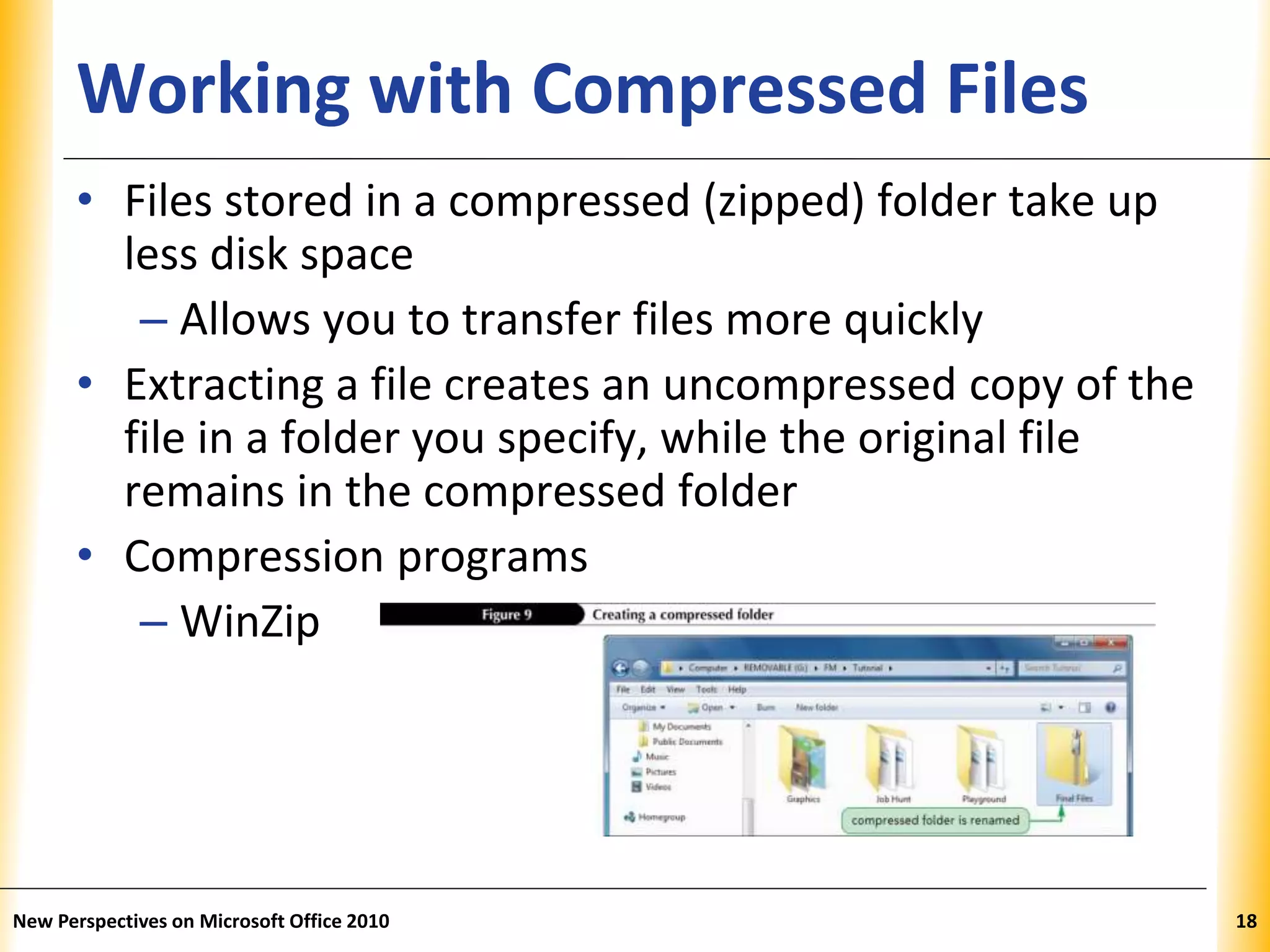
This document discusses file management strategies in Microsoft Office 2010, including organizing files and folders, exploring files and folders using Windows Explorer and libraries, navigating folder locations, and managing files by creating, moving, copying, renaming, deleting, and compressing files. Key topics covered are setting up file organization strategies based on storage medium, understanding folder hierarchies, using libraries to group similar file types, and managing compressed zip files to reduce file sizes.