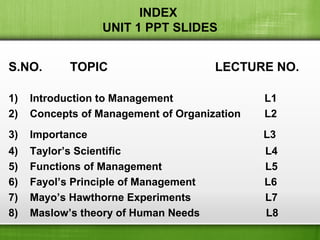
This document provides an introduction to management concepts. It defines management, outlines its nature and features. It discusses the importance of management and covers early management theories like Taylor's scientific management theory, Fayol's 14 principles of management, and Mayo's Hawthorne experiments. It also covers human needs theories like Maslow's hierarchy of needs and McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y. The document is structured as a course on management with 8 topics covered in 8 lectures.