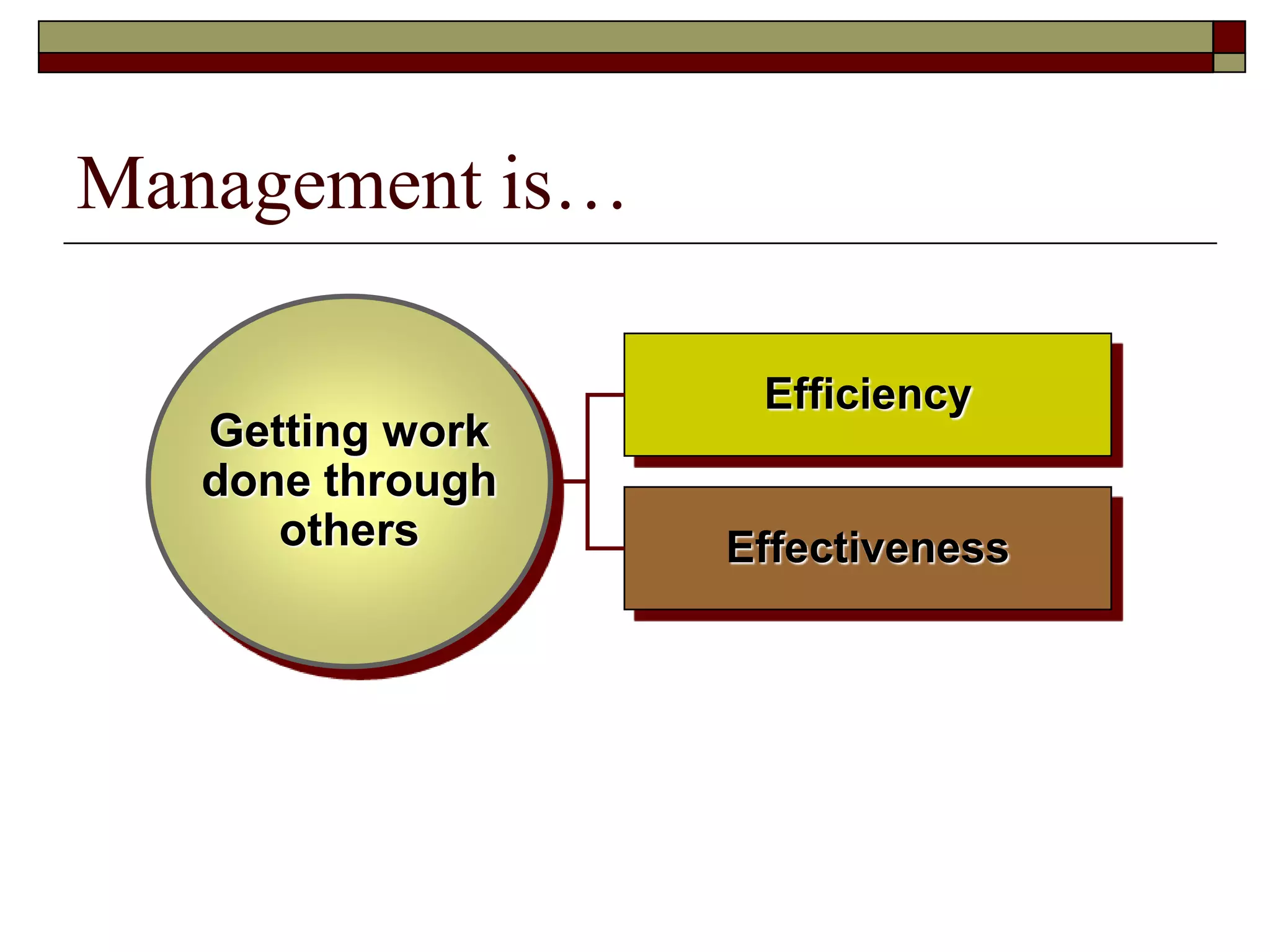
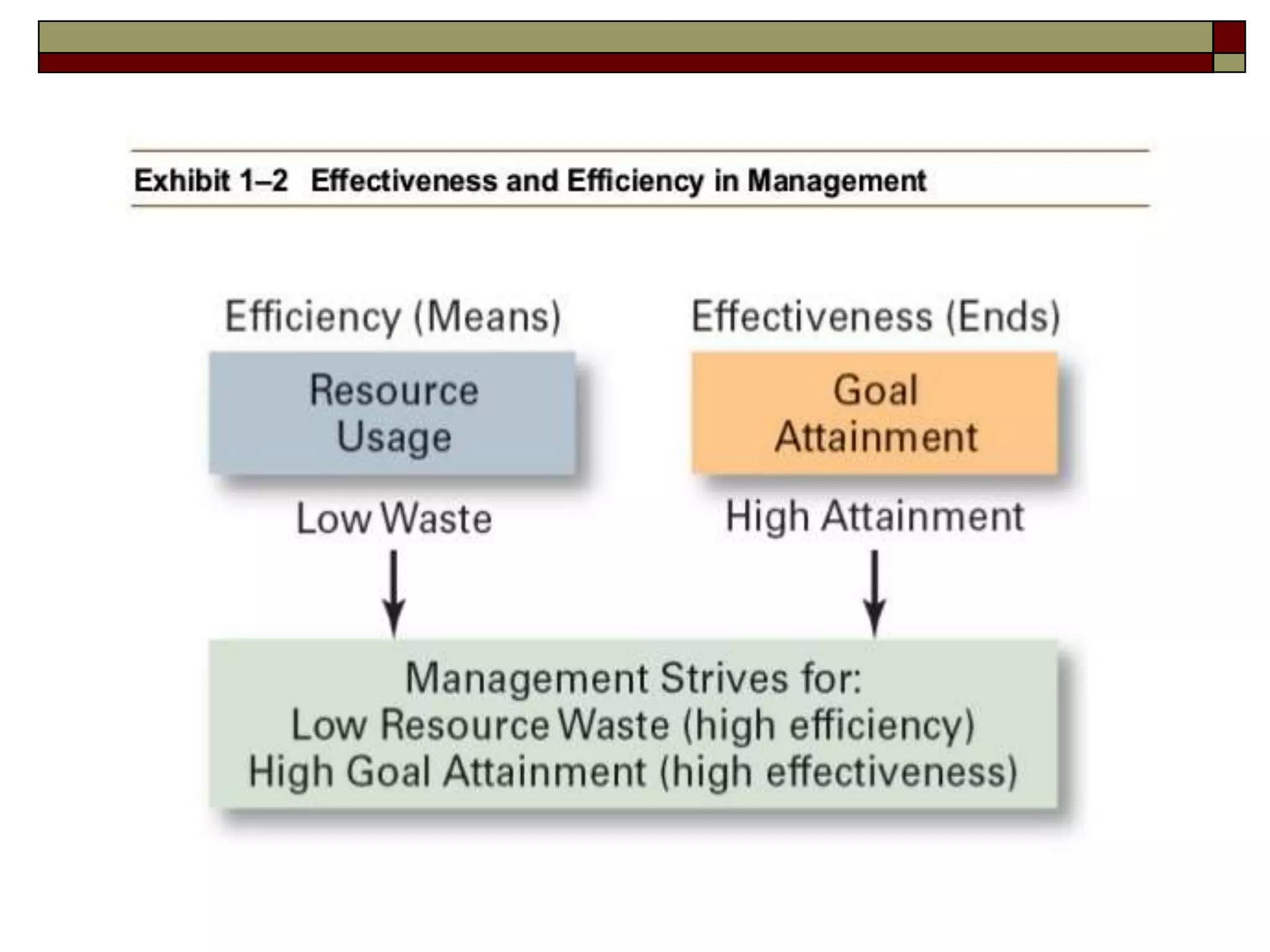
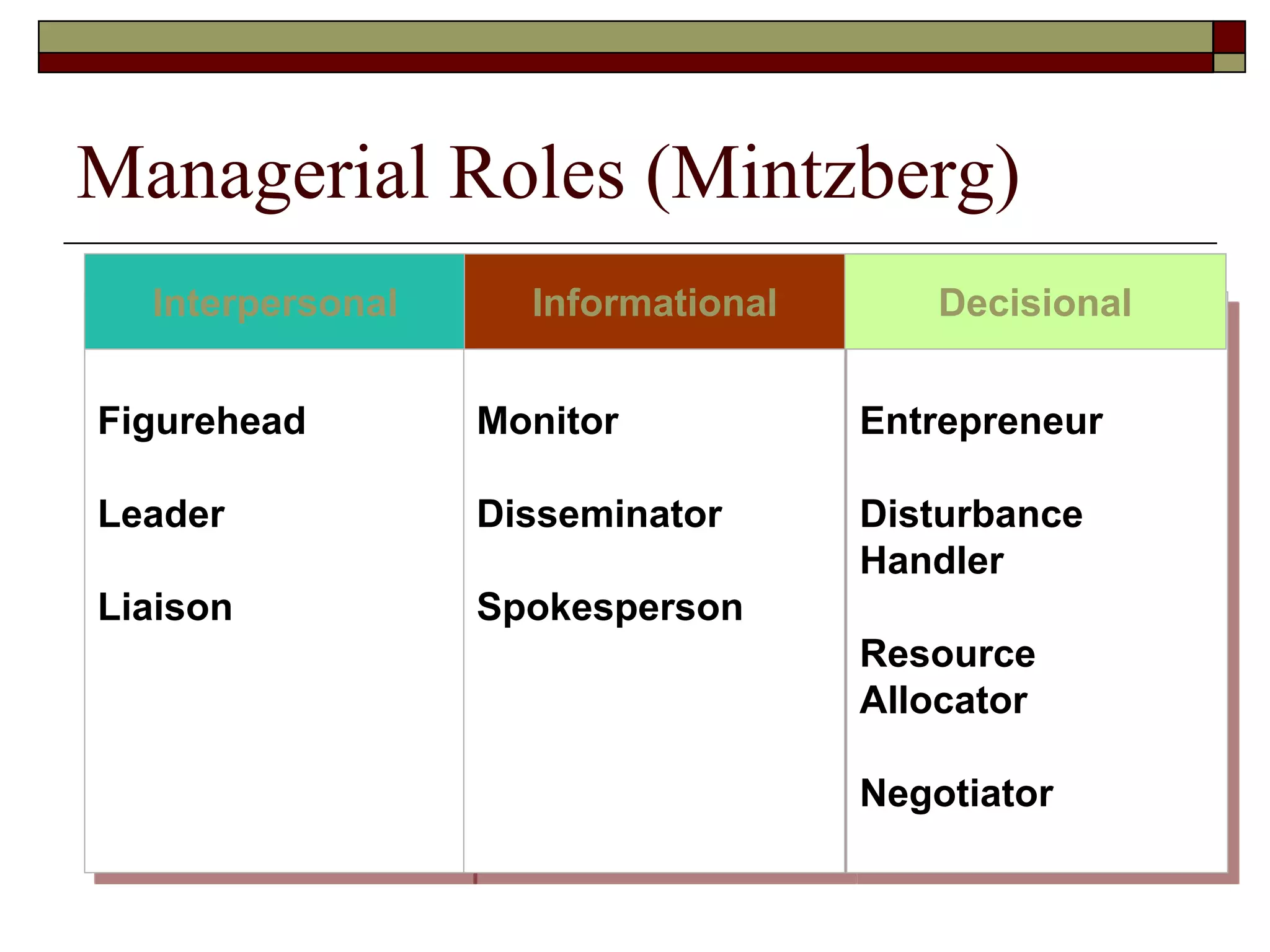
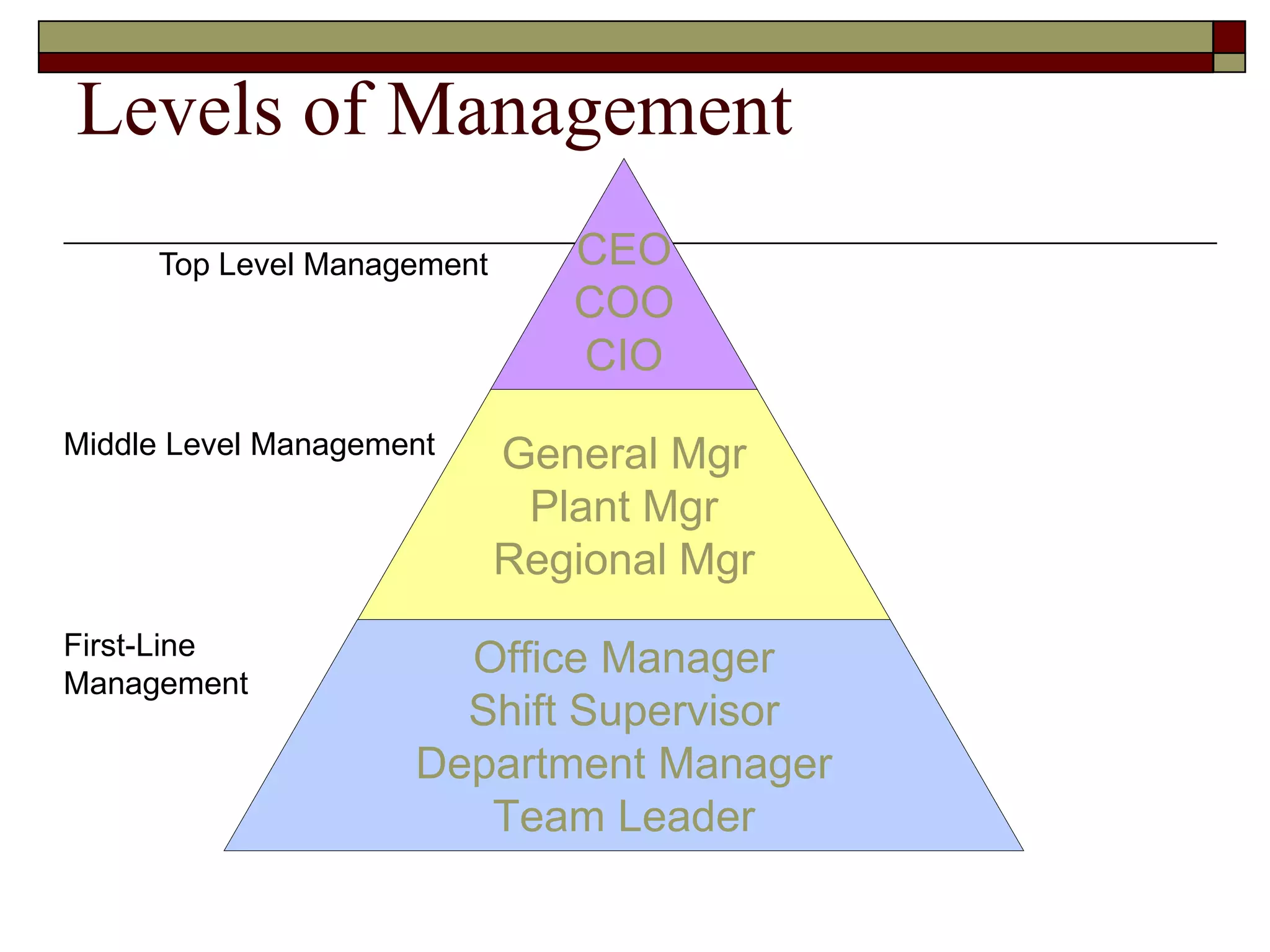
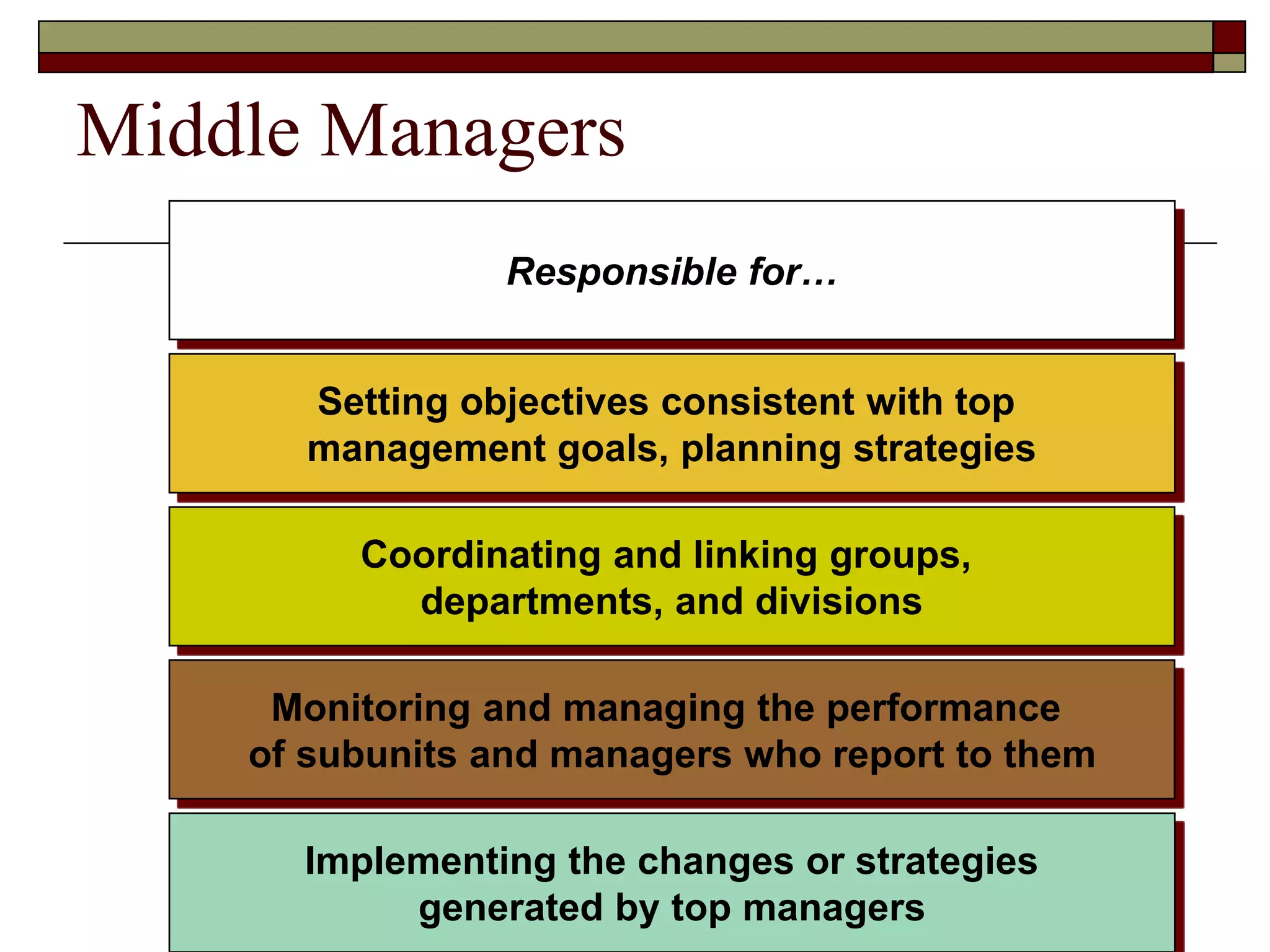
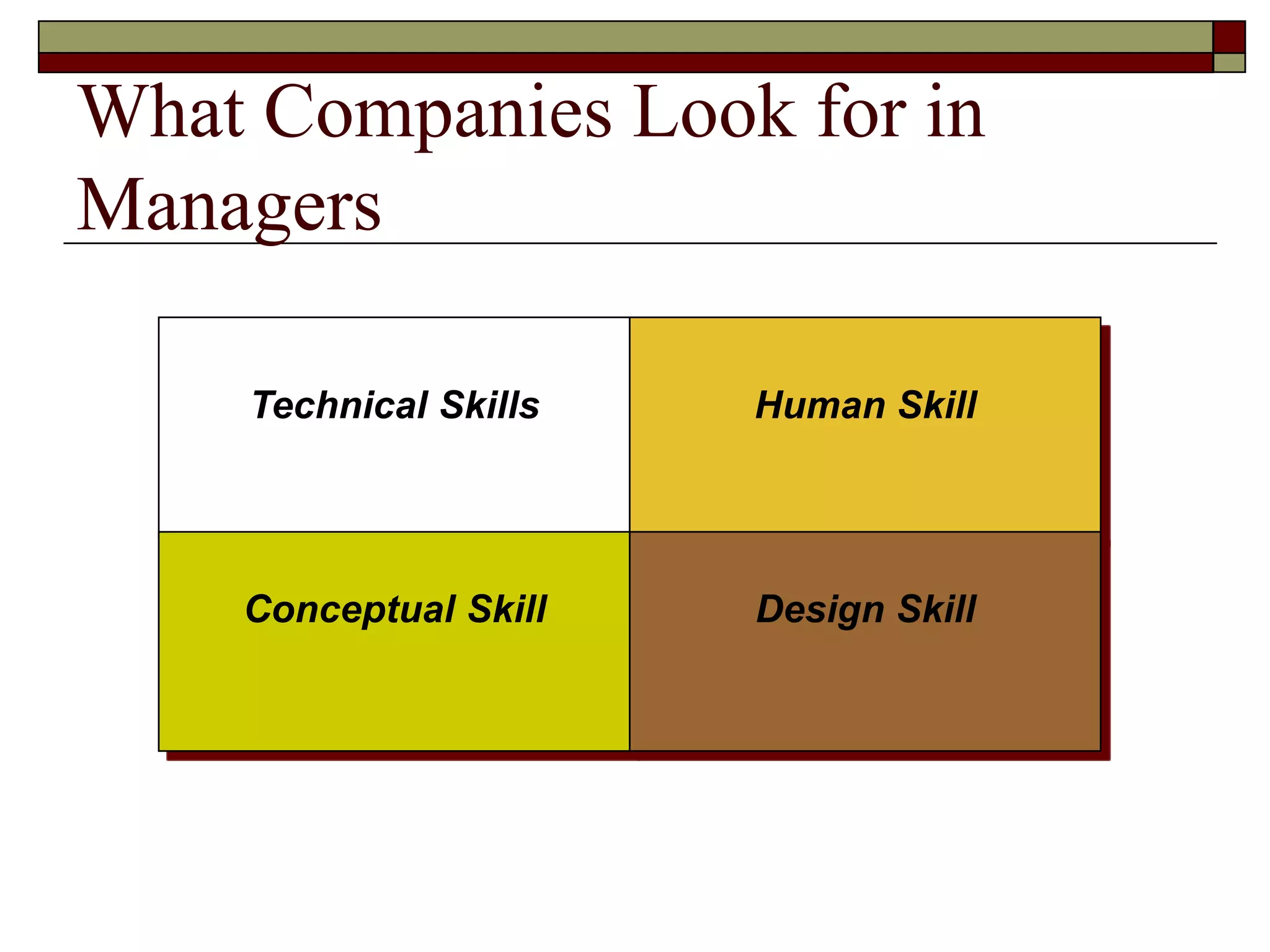
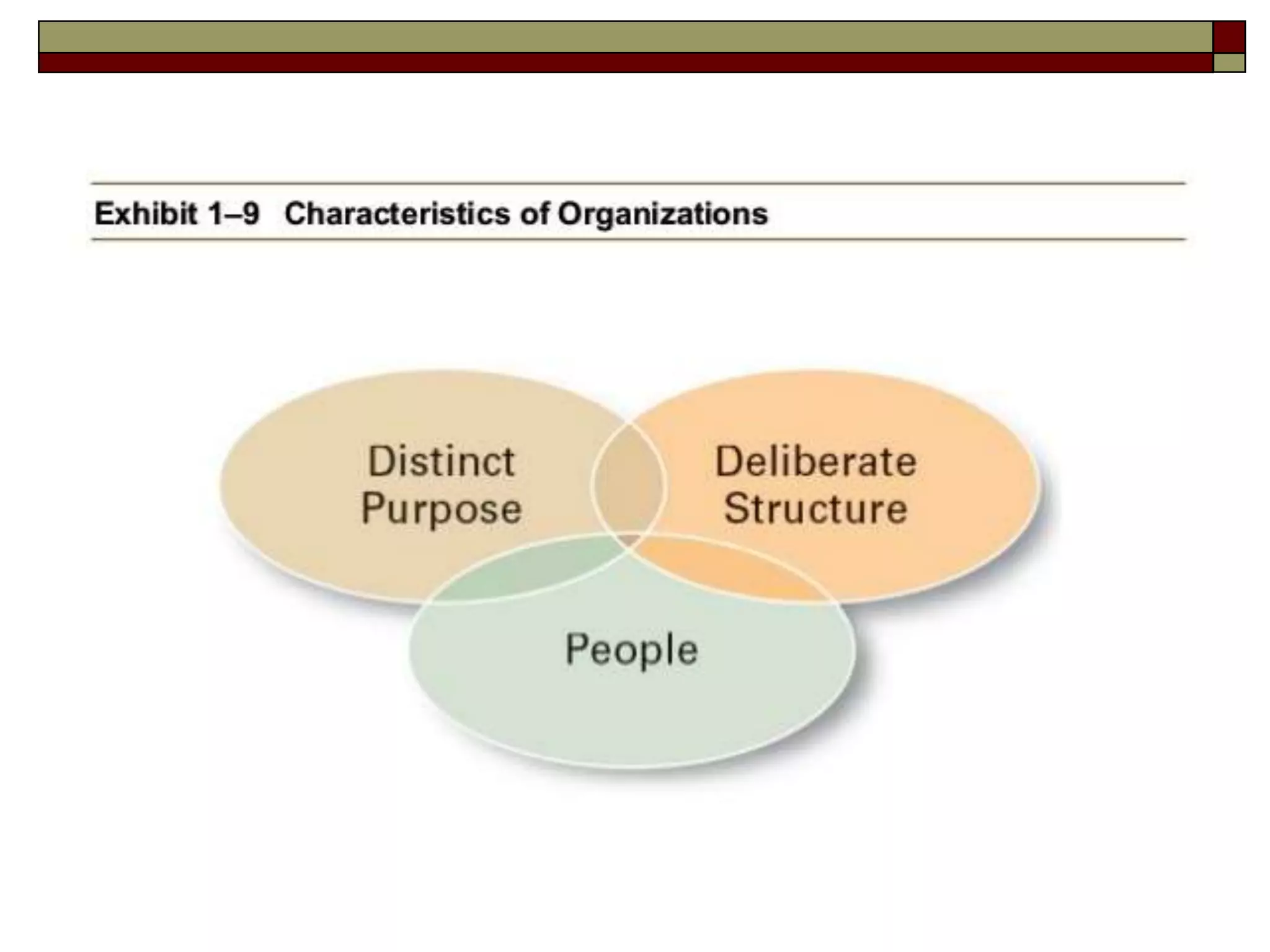
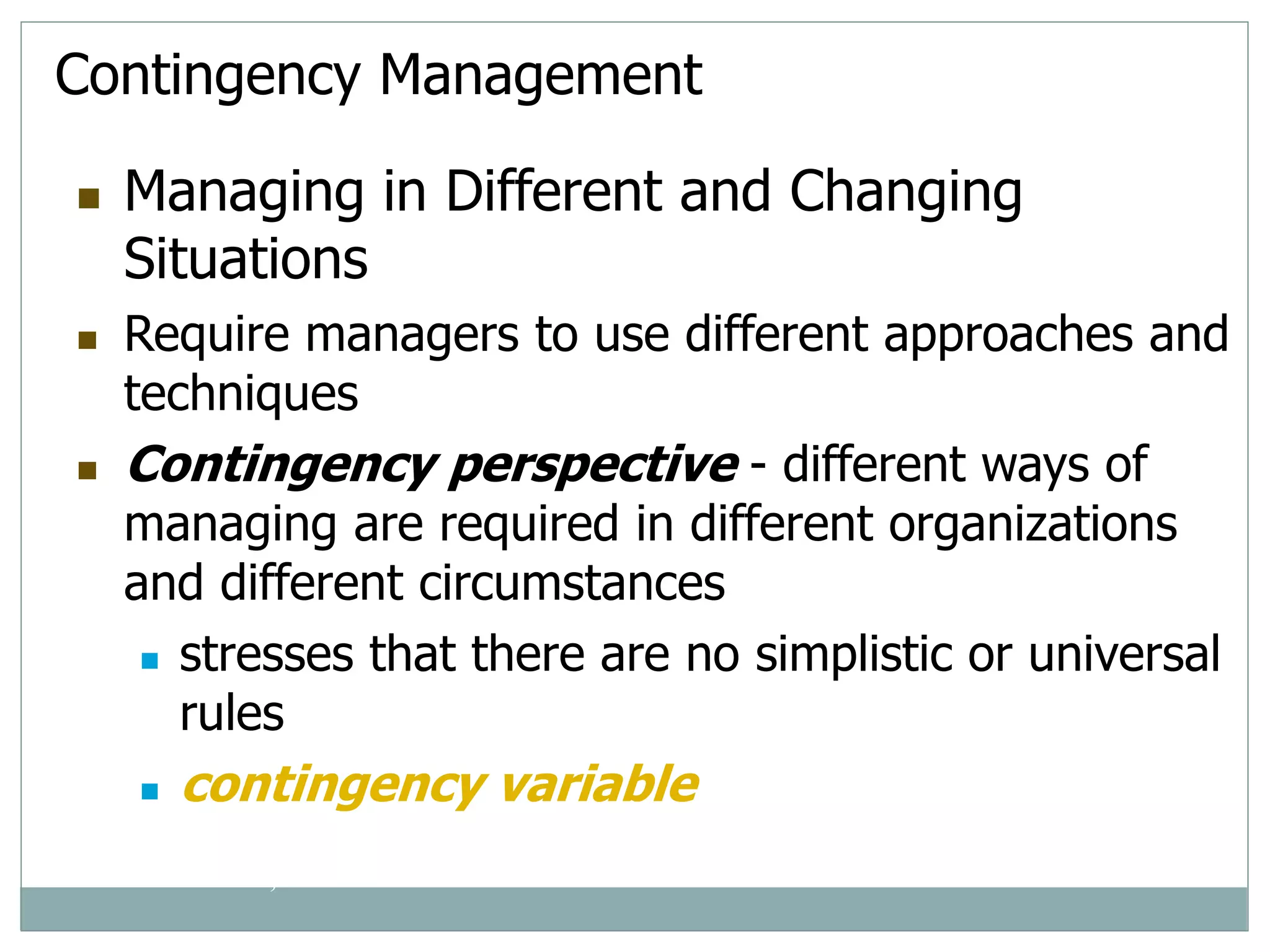
Management involves coordinating work through other people to achieve organizational goals efficiently and effectively. There are three levels of management: top management sets strategy, middle management implements strategy, and first-line management oversees entry-level employees. Early management theorists like Taylor, Fayol, and Weber developed classical approaches to management focusing on specialization, authority, and bureaucracy. Behavioral theorists like Hawthorne highlighted the importance of human factors, while McGregor's Theory X and Y distinguished coercive vs. empowering management styles. Contemporary approaches include Ouchi's Theory Z emphasizing culture and contingency theory adapting to changing situations.