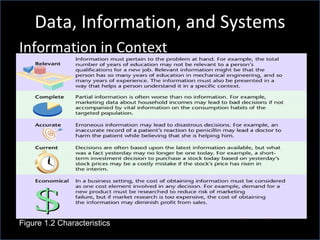
The document discusses classic management functions, components of a management information system (MIS), and how information and communication technologies relate to management. It describes the five classic management functions as planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. It explains that an MIS takes data as input, processes it, and produces useful information as output using computer-based systems. It also discusses how information systems help managers focus on goals and operations by taking a systems thinking approach.