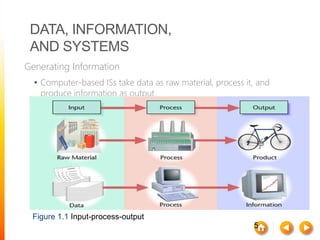
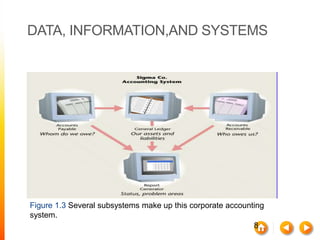
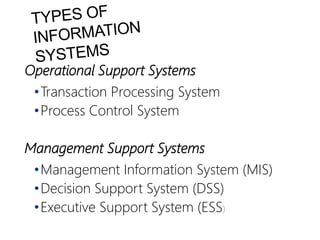
This document discusses information systems and their components. It defines key terms like data, information, and systems. It explains how data is collected and manipulated to generate useful information. It also describes the main components of information systems like hardware, software, networks, and data management. Different types of information systems that support business operations and management are discussed. The document also covers some ethical and societal issues related to information technology.