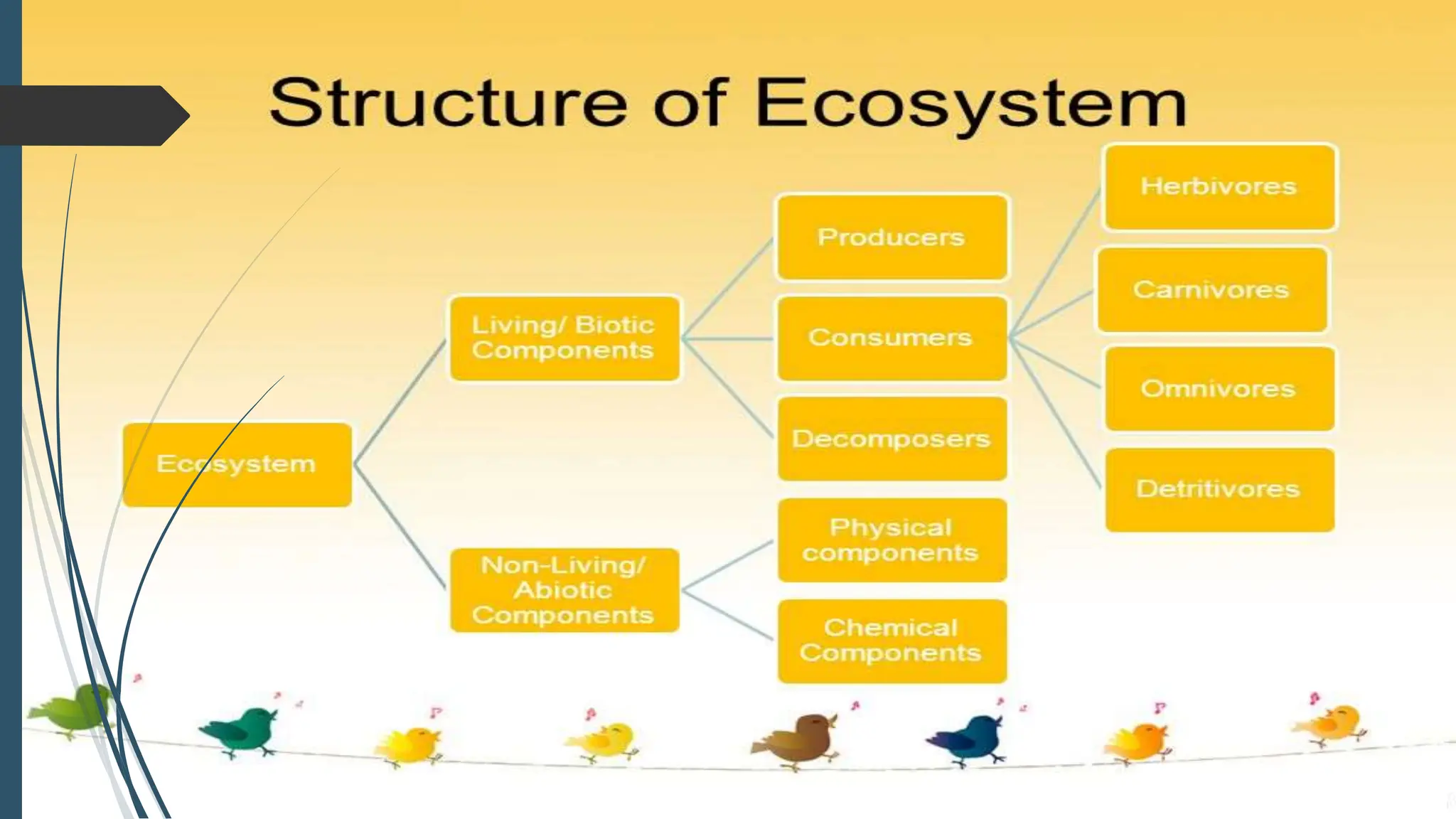
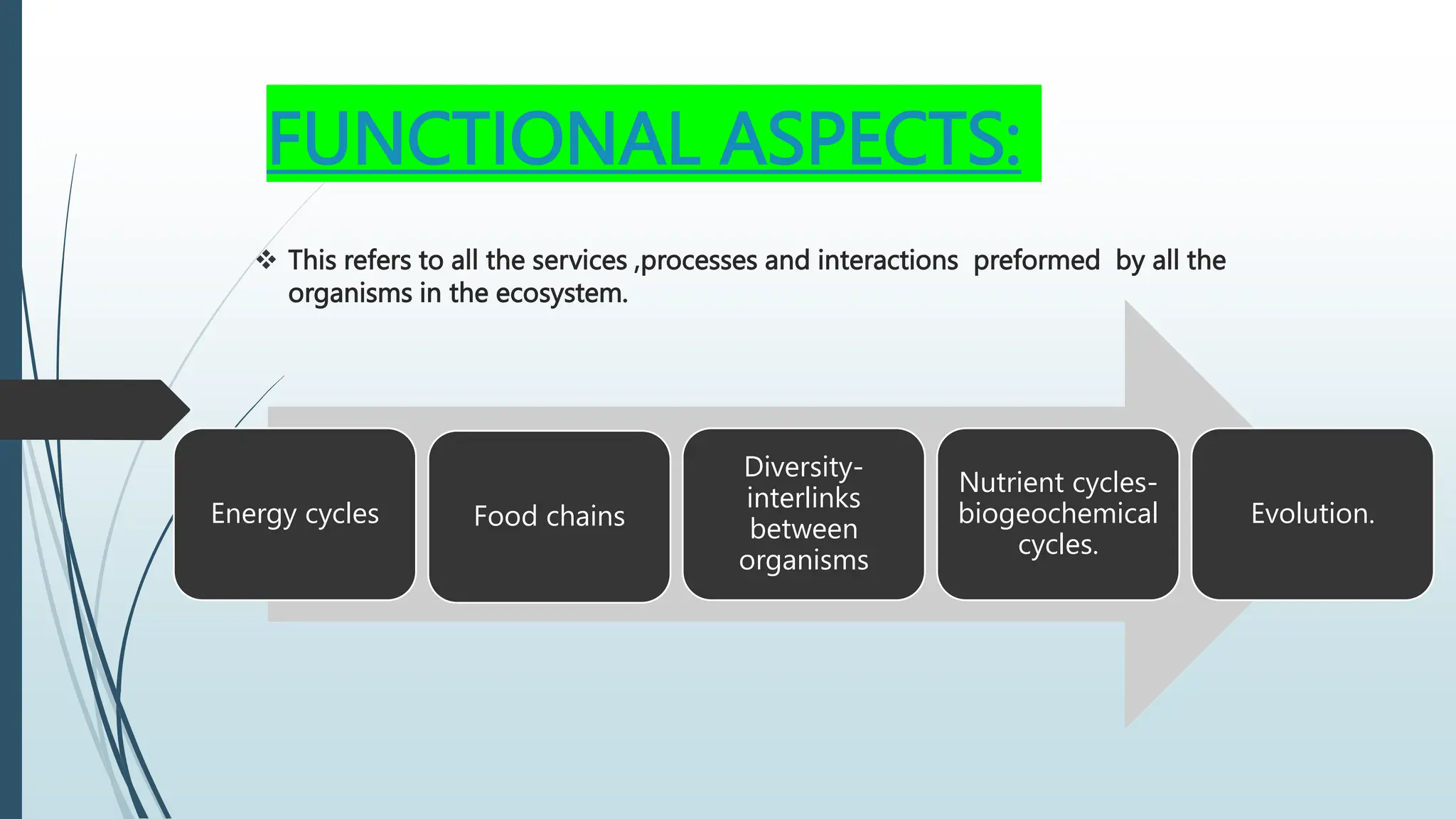
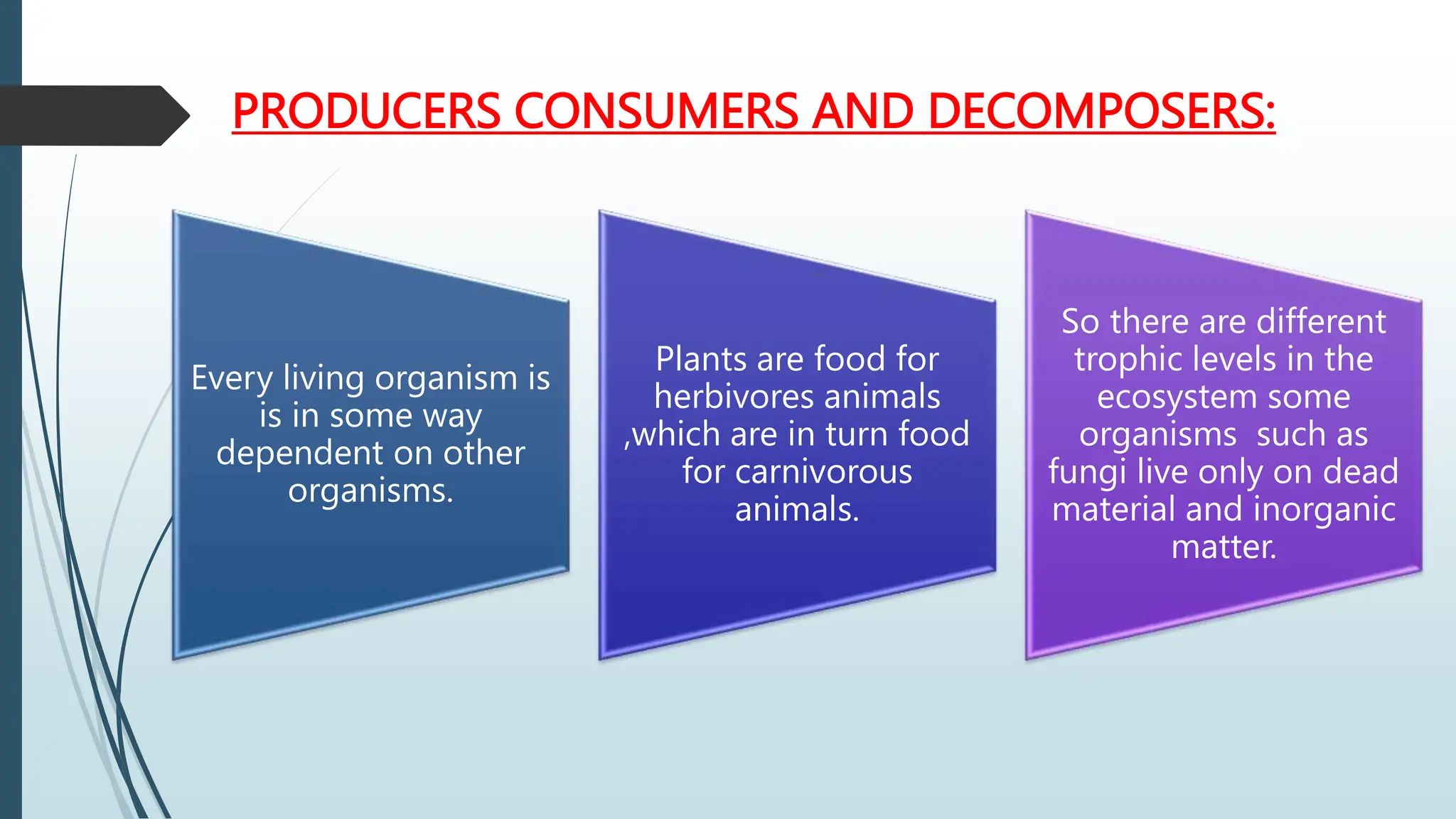
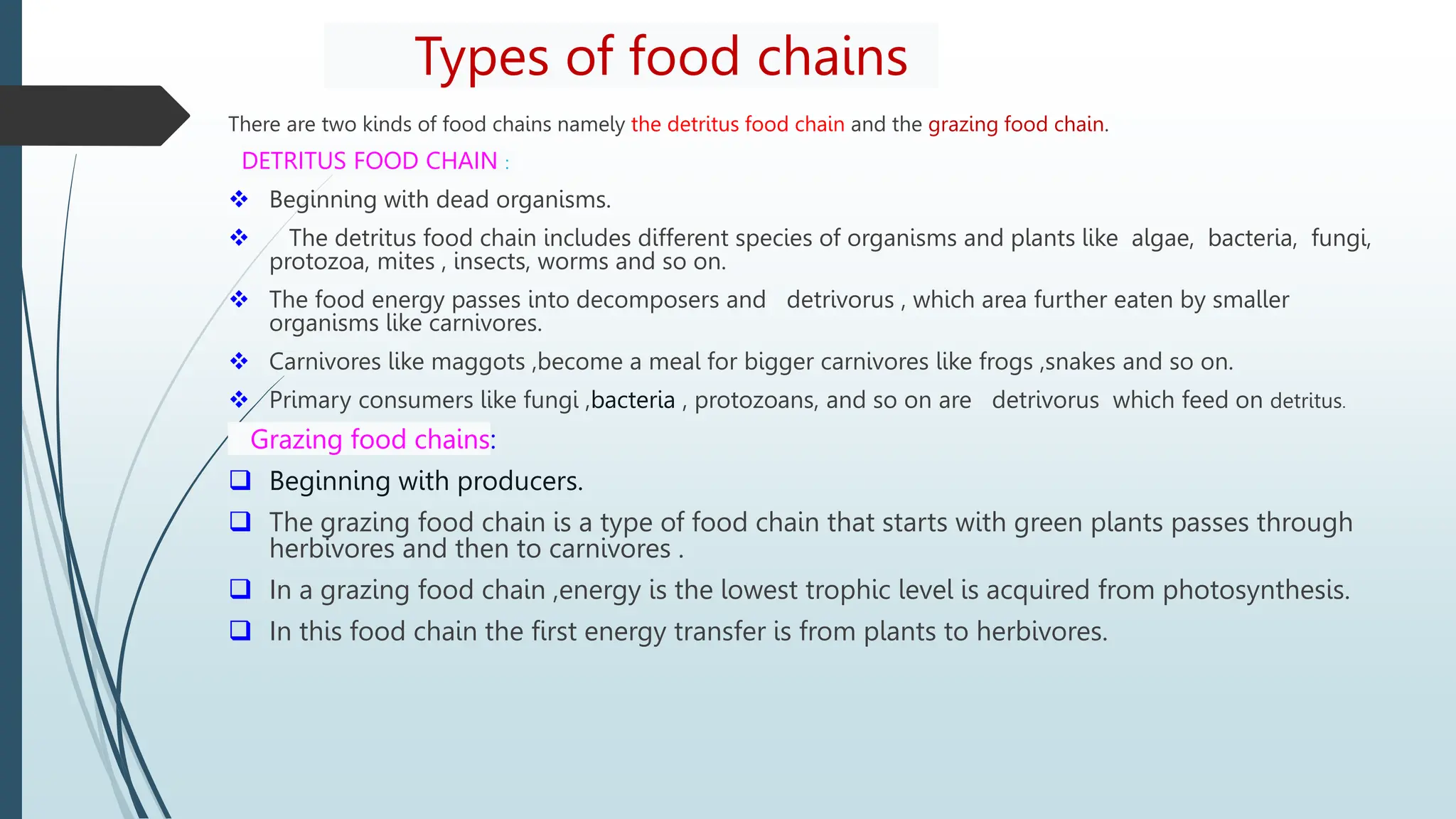
An ecosystem is a region with a recognizable landscape such as a forest, grassland, desert, or coastal area. The ecosystem is controlled by climatic conditions like sunlight, temperature, and rainfall. It includes both living organisms that depend on each other and non-living components like soil, air, and water. Resources in an ecosystem like light, nutrients, water, and habitat can be consumed by one organism and become unavailable to others. Key resources for plants include sunlight, nutrients, water, and space to grow, while animals rely on food and water.