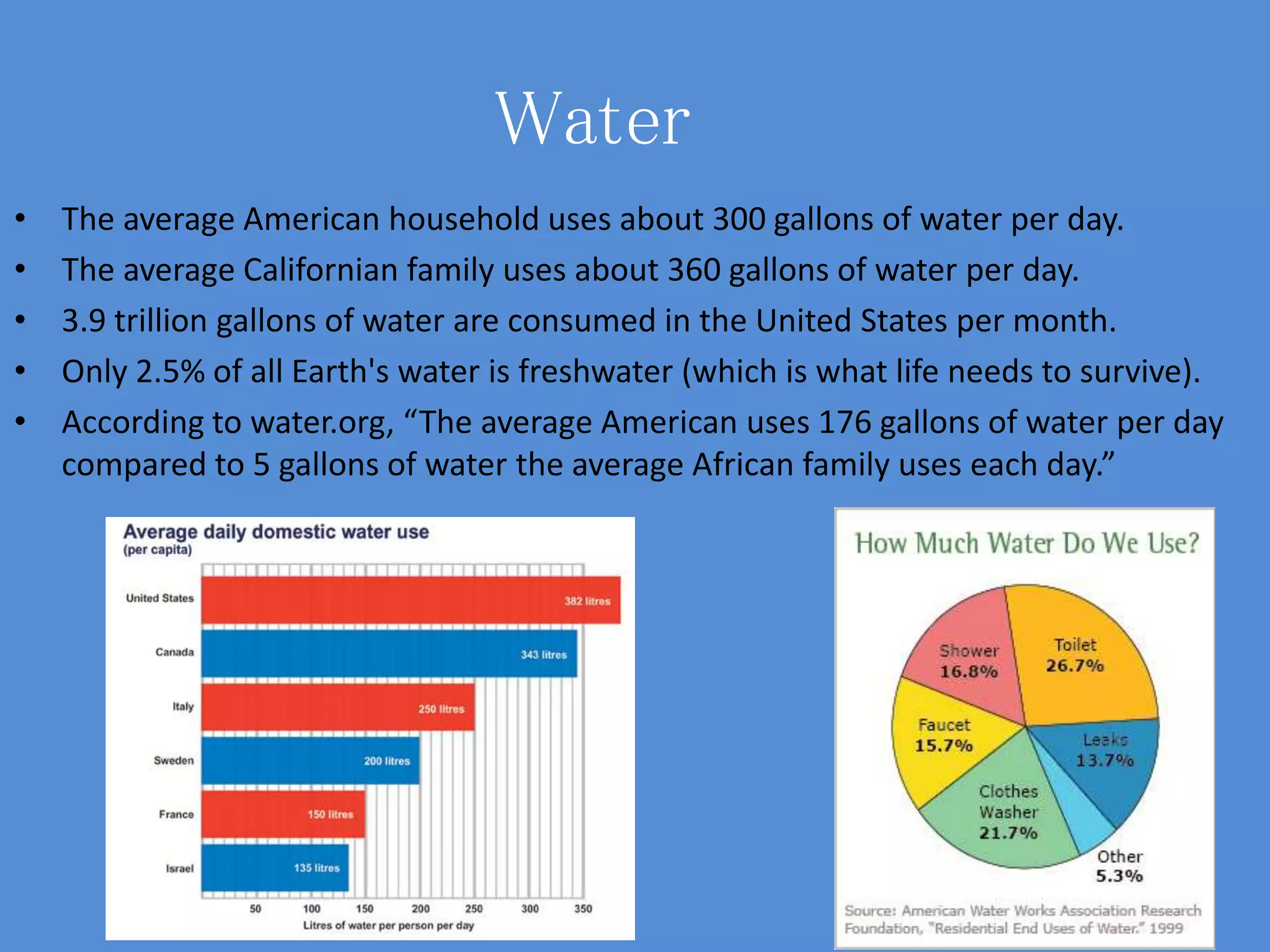
Natural resources discussed in the document include water, fossil fuels, natural gases, forests, and soil. Some key points:
- The average US household uses 300 gallons of water per day while the average Californian family uses 360 gallons.
- Fossil fuels such as gasoline, heating oil and diesel provide energy for transportation, heating and manufacturing. The US relies heavily on fossil fuels.
- Forests and soil are important natural resources but are threatened by unsustainable harvesting and pollution. Forests regulate climate and rainfall while soil supports biodiversity and agriculture.