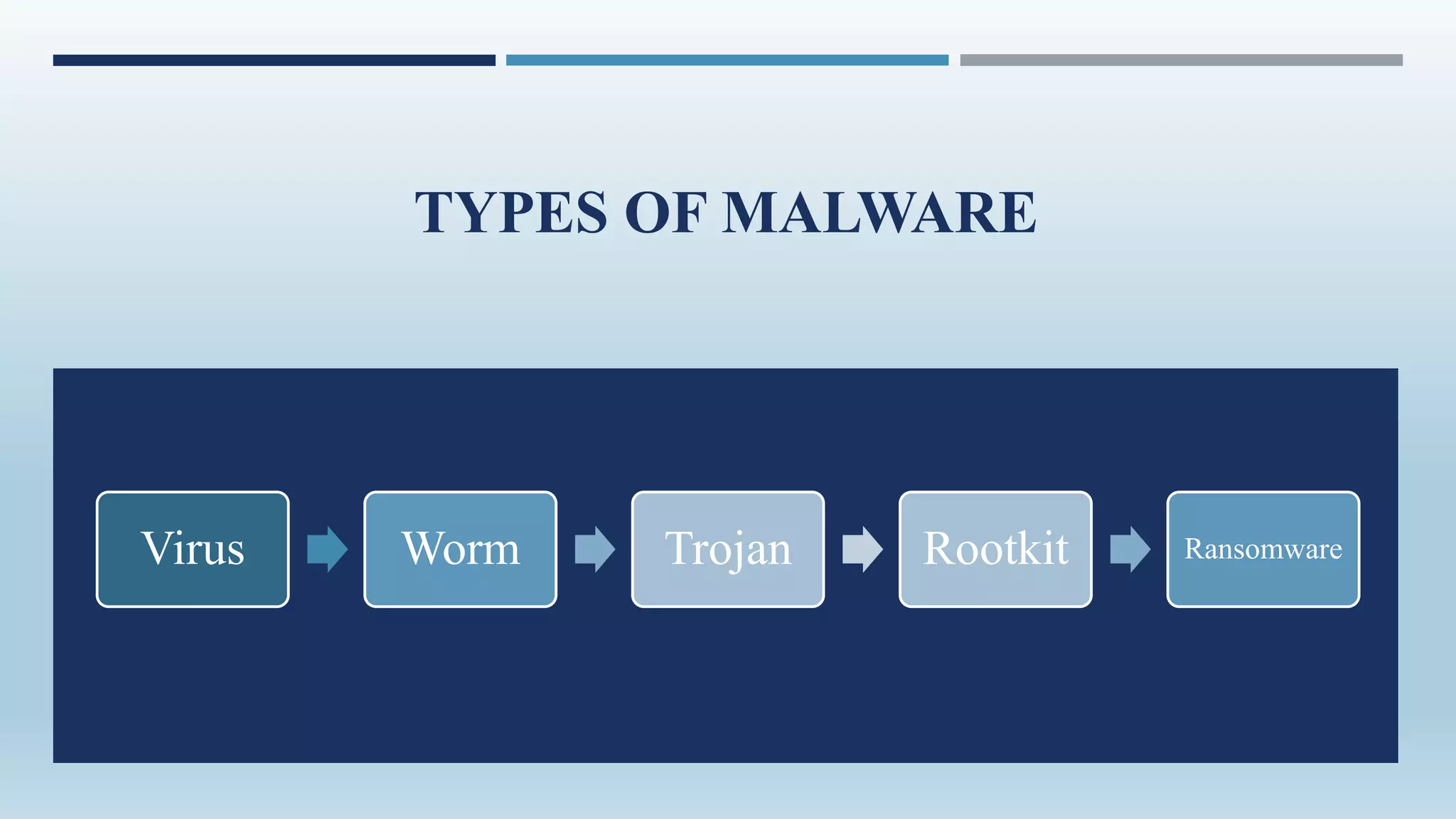
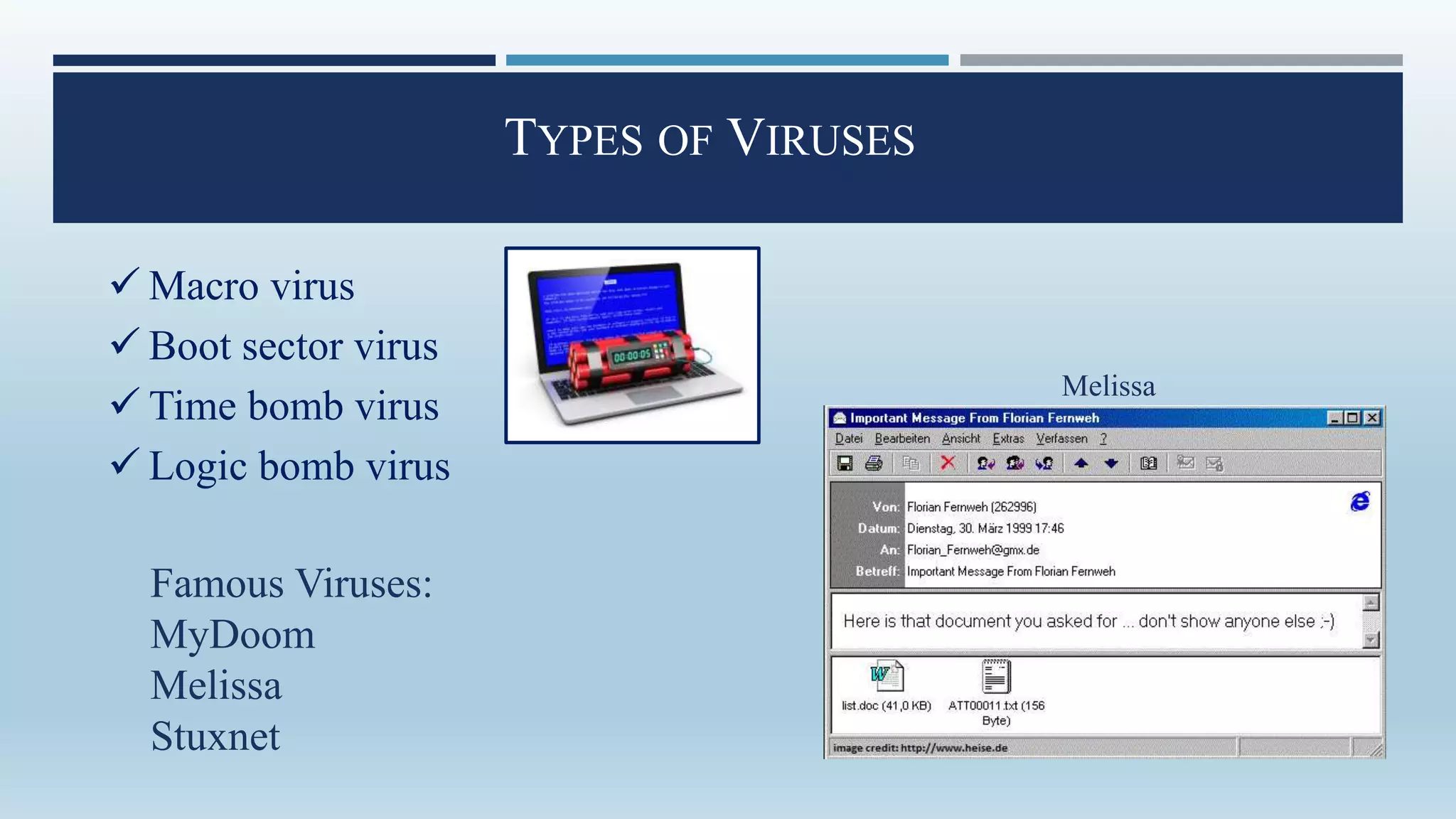
Malware, short for 'malicious software', encompasses programs designed to damage or exploit computer systems, including viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware. Initially created for fun in the 1970s and 1980s, its prevalence surged in the early 2000s, with significant impacts on personal and governmental data. Protection against malware involves personal vigilance and robust antivirus software, along with legal frameworks like India's Information Technology Act addressing malware-related offenses.