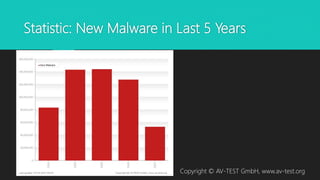
Malware comes in many forms and poses increasing threats. The document discusses the basics of how malware works, including propagation techniques to spread, payloads to damage systems, and self-defense mechanisms. It also covers common malware classes like viruses, worms and Trojans. Examples are given of real malware outbreaks like WannaCry and Petya to show how quickly they can spread. Defense strategies include using antivirus software, keeping systems updated, and maintaining backups.