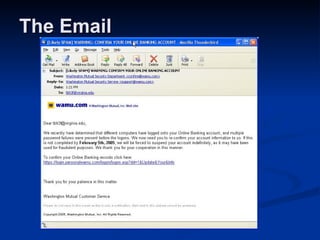
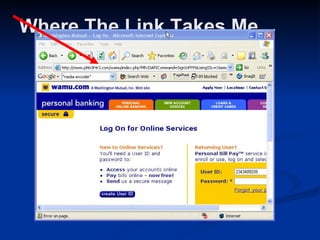
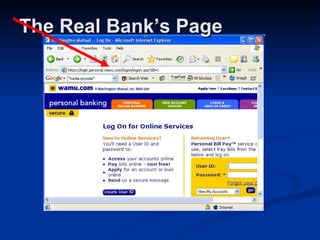
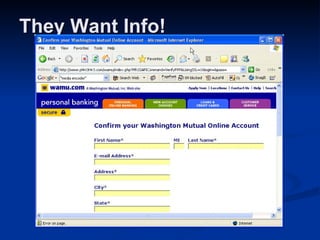
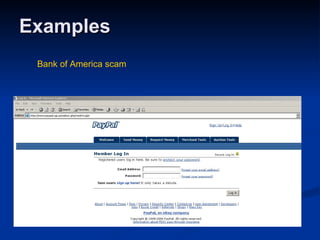
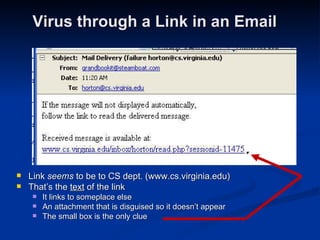
Malware can take many forms such as viruses, worms, trojan horses, adware, and spyware. Viruses and worms are programs that can copy themselves and spread from computer to computer, sometimes causing harm. Adware displays advertisements, and spyware tracks personal information without consent. Phishing scams try to steal personal details through fraudulent emails or websites. Users should use antivirus software, avoid suspicious emails/attachments, and practice safe password habits to protect against malware threats.