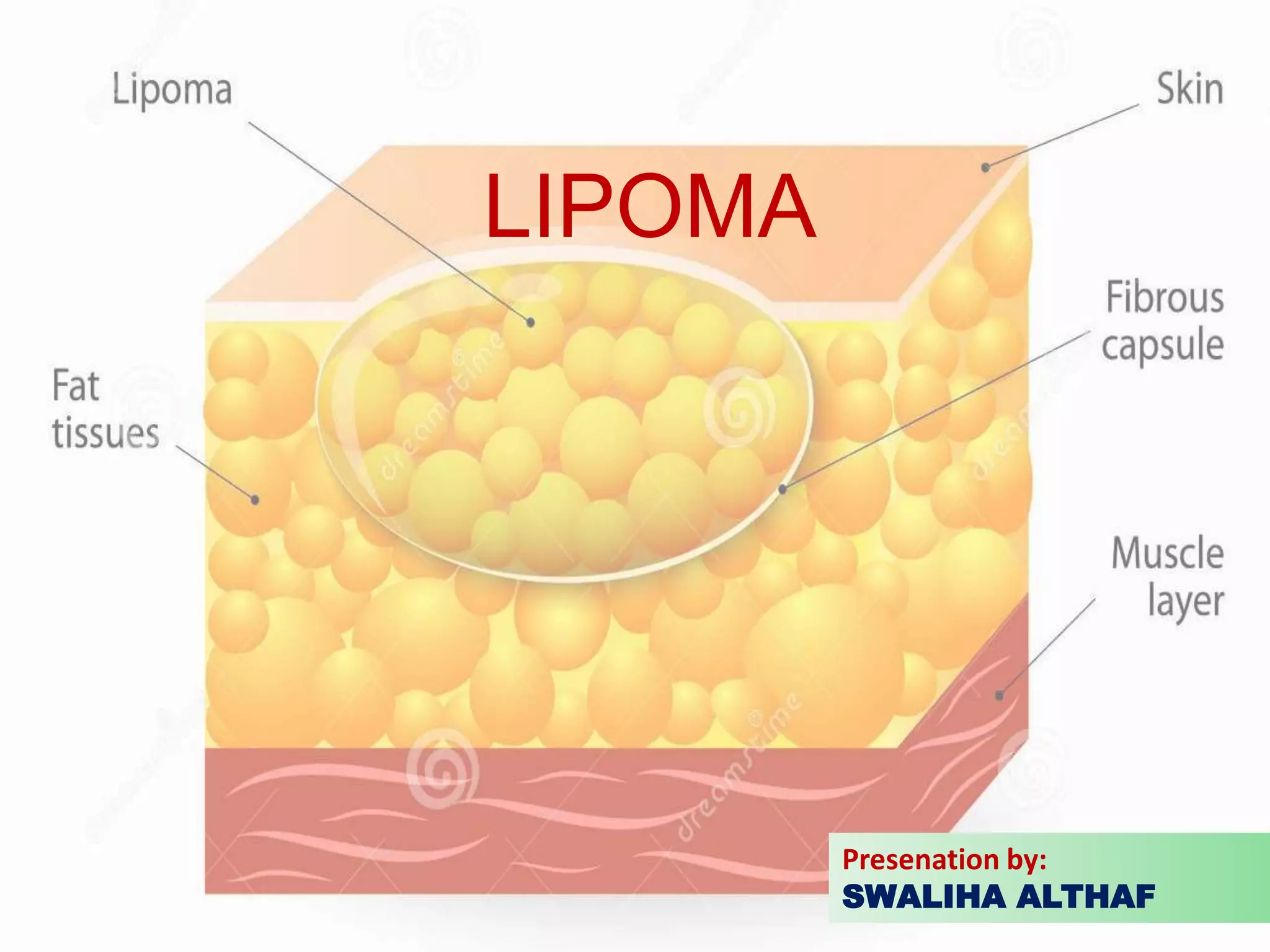
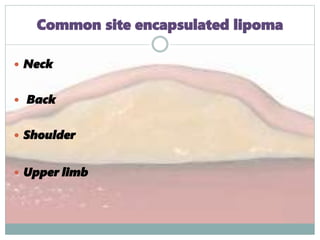
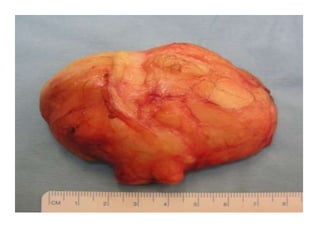
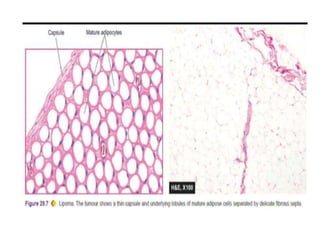
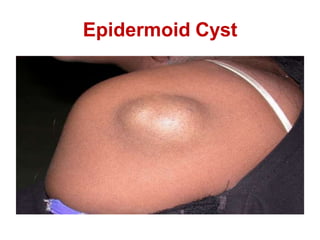
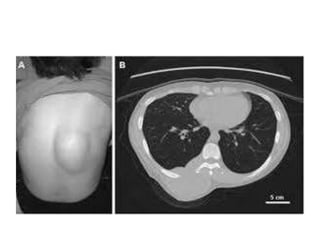
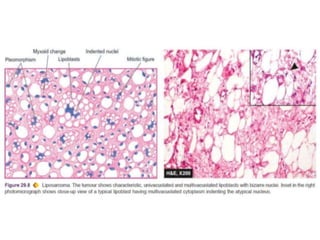
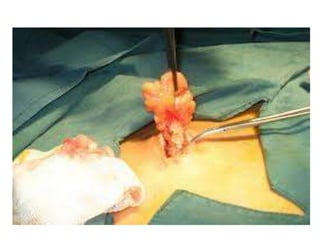
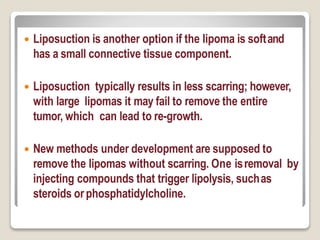
Lipomas are benign soft tissue tumors composed of adipose tissue enclosed in a connective tissue capsule. They are the most common soft tissue tumor and typically present as localized, mobile, soft, non-tender lumps under the skin. Lipomas can occur anywhere on the body but are most common on the neck, back, and shoulders. While lipomas usually do not require treatment, surgical excision is recommended if they are painful, restrict movement, or grow very large in order to confirm benign histology. Surgical removal is typically via simple excision, which effectively cures most cases with few recurrences.