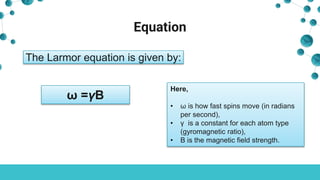
The document discusses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), detailing its inventor, Raymond Vahan Damadian, and how MRI functions using large magnets and radio waves to create detailed body images without radiation. It covers the components of MRI, including superconducting and gradient coils, as well as radiofrequency coils that generate necessary pulses for imaging. Additionally, it contrasts closed and open MRI machines based on their magnetic field strength and image quality.





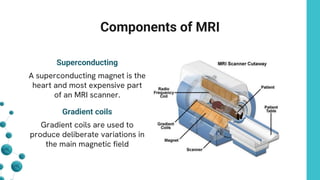
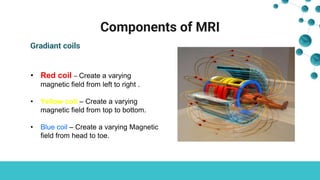
![Components of MRI
RF Coils
• RF coils are the “antenna” of the
MRI system
• They are simply a loop of wire
either circular or rectangular .
[Radiofrequency]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mri-240516053831-d6953aeb/85/Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging-MRI-Presentation-8-320.jpg)