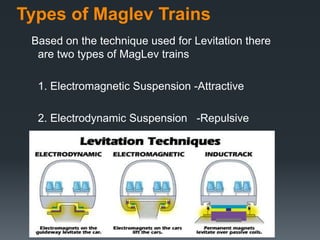
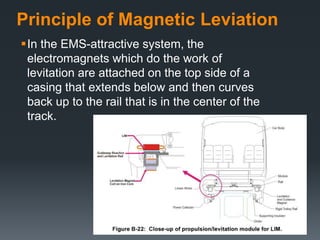
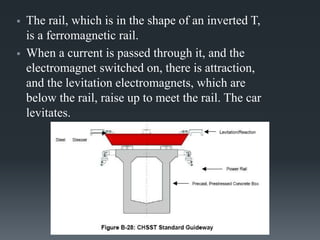
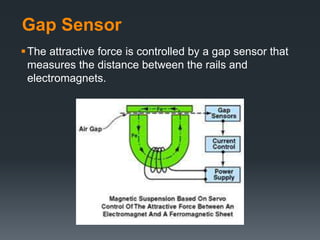
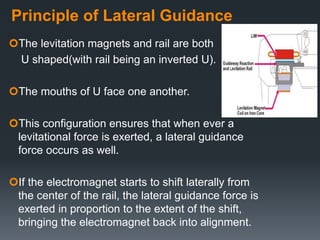
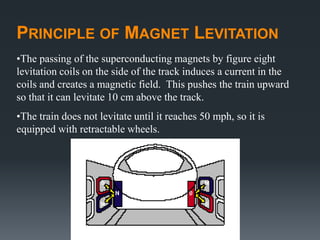
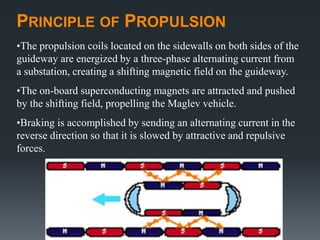
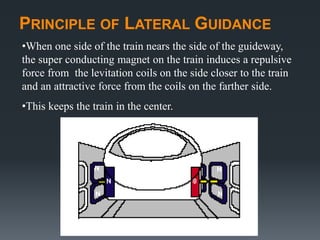
This document provides an introduction to magnetic levitation, or maglev, which uses magnetic fields to levitate objects without physical contact. It discusses two main types of maglev trains - electromagnetic suspension systems that use attractive forces, and electrodynamic suspension systems using superconductors and repulsive forces. The key principles of levitation, propulsion, and lateral guidance for maglev trains are described for both systems. Advantages of maglev transportation include lower energy usage and greater safety compared to other modes of transportation.