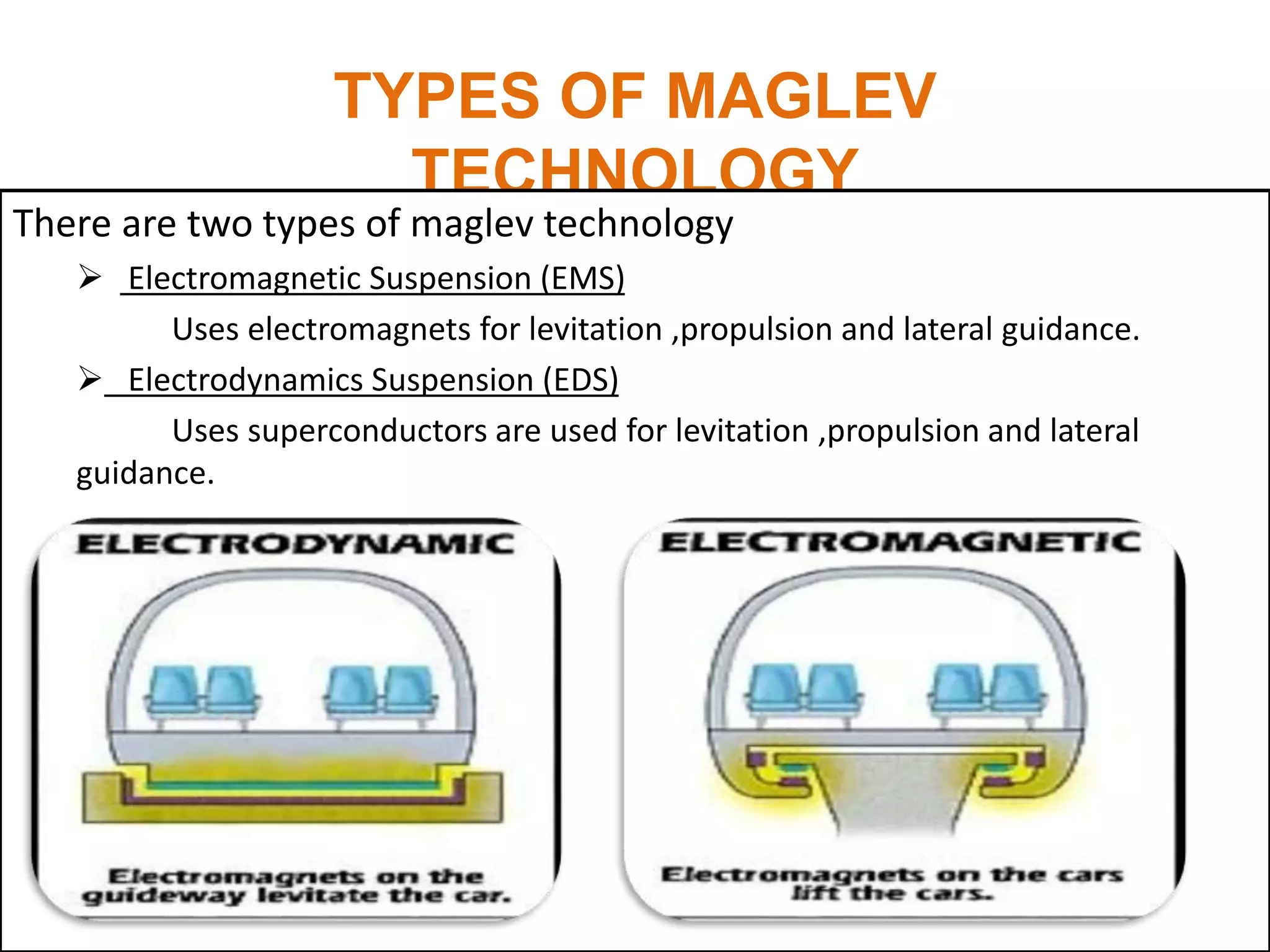
The document discusses maglev (magnetic levitation) technology used in trains, which allows for frictionless travel by using electromagnetic forces for levitation, propulsion, and lateral guidance. It details two types of maglev technology: electromagnetic suspension (EMS) and electrodynamic suspension (EDS), and also introduces ultra-high-speed tube trains that operate in a vacuum to enhance speed beyond traditional limits. Despite its advantages, challenges such as speed limitations due to air resistance and potential passenger safety issues in tube trains are acknowledged.