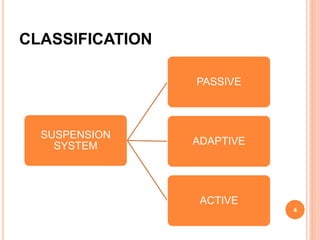
The document outlines the magic body control suspension system, an advanced electronically controlled system developed by Mercedes-Benz. It explains its components, functionality, driving modes, and compares its performance to conventional systems, emphasizing its merits and demerits. Key features include real-time monitoring of road conditions via a stereo camera and independent control of shock absorbers to enhance ride comfort and stability.