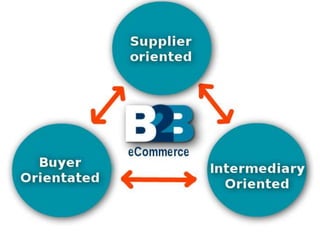
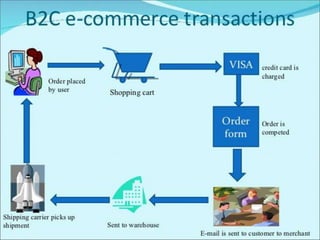
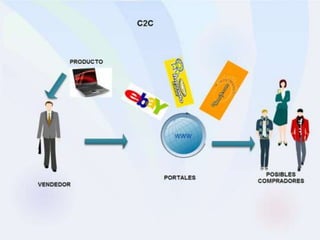
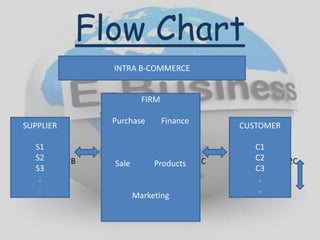
E-business refers to carrying out business activities through the internet. It allows organizations to conduct day-to-day operations using internet technologies internally and externally. The major types of e-business are B2B (business to business), B2C (business to customer), C2C (customer to customer), and intra-business commerce. E-business provides opportunities like low costs and global reach but also faces security risks and requires resources like qualified staff and payment systems. While e-business has limitations like low personal touch, it is becoming more interactive and is the future of business despite constraints.