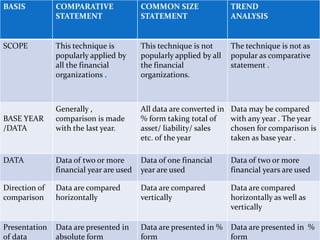
This document discusses financial statement analysis. It defines financial statements as presenting a periodic view of a company's financial progress and status. Financial statements are used by shareholders, creditors, stock exchanges, bankers, management, investors, and governments. Financial statement analysis studies the relationships between financial factors disclosed in statements and trends over time. It can be done externally by outsiders without company access or internally by management. The objectives are to understand the company, identify strengths and weaknesses, check fund movements, measure efficiency, and assess growth potential for comparison. Limitations include relying on user intentions, ignoring qualitative factors, and only using historical data. Common techniques discussed are comparative statements, common size statements, and trend analysis.