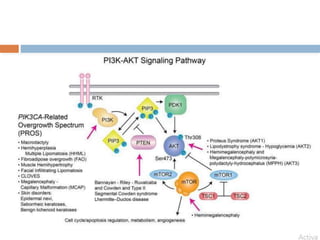
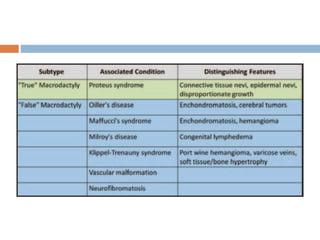
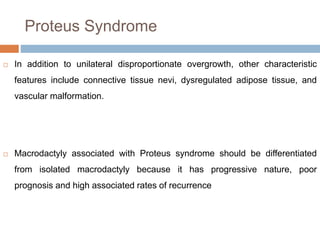
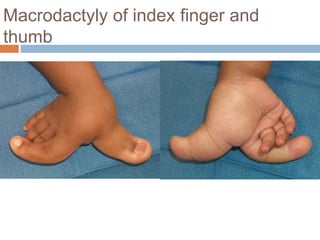
1) Macrodactyly is an overgrowth of one or more fingers, most often the index finger. It can involve enlargement of skin, bone, nerves, and other tissues.
2) The cause is unknown but may involve abnormal nerve or blood supply. Recent evidence suggests a genetic mutation can cause abnormal growth regulation.
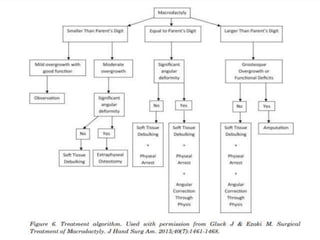
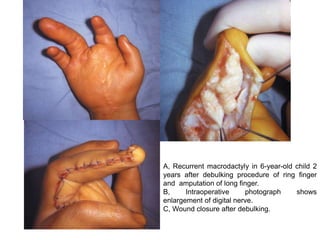
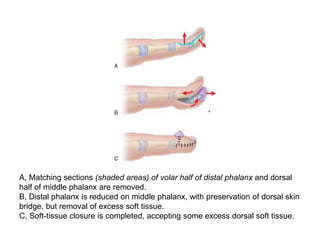
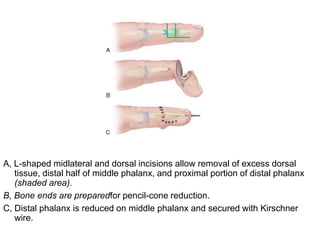
3) Treatment involves surgical procedures like debulking excess tissue or shortening the enlarged bones to improve appearance and function.