Syndactyly Hand
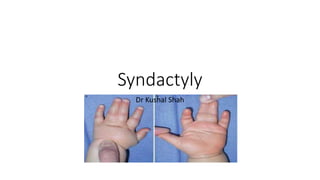
- 5. Definition and embryology • Its a variable fusion of the soft tissue or skeletal elements or both of adjacent digits, and it occurs when the normal processes of digital separation and web space formation fail to some degree.( figure 1) • Normally digits form as condensations of mesoderm within the terminal paddle of the embryonic upper limb. Spaces form between the fingers in a distal to proximal direction to the level of the normal we space by a process of regulated apoptosis which is dependent on the apical ectodermal ridge ( AER) and the molecular signaling • The normal web space slopes 45 degrees in a dorsal to palmar direction from the metacarpal heads to the midproximal phalanx (Figure 2). • The second and fourth webs are wider than the third web, allowing greater abduction of the index and small fingers. • The first web space is a broader diamond-shaped expanse of skin composed of the glabrous skin of the palm and thinner mobile skin dorsally
- 6. Etiology • Are fairly common and often run in families • Occur in about one out of every 2,500-3,000 newborns • Affect boys more often than girls( 2:1) • Affect whites more often than blacks or Asians • Bilateral about 50 % of the time • Can occur alone or as part of a genetic syndrome, such as Apert syndrome • Can sometimes be seen prior to birth by ultrasound
- 7. Ray involvement • 50% long-ring finger • 30% ring-small finger • 15% index-long finger • 5% thumb-index finger
- 8. type
- 9. Pre op evaluation • which web space(s) is involved • the extent of the syndactyly • the involvement of the nail • and the presence of other anomalies. • Lack of differential motion between the digits may indicate bony fusion or an extra digit, or both, concealed within the conjoined digits. • Examine entire upper limb, the contralateral hand, the chest wall, and the feet. • Radiographs may reveal skeletal fusion, a concealed extra digit (synpolydactyly), or other bony or articular deformities. • Further imaging with ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging can be useful in determining the flexor tendon and Vascular anatomy in complex cases
- 10. Management • Syndactyly can have cosmetic, functional, or developmental impacts on the growing child. • The appearance of the hand is altered, more so with complete complicated forms of syndactyly. • Syndactyly of the first web space hampers grasp and the development of pinch. • Syndactyly of the second, third, and fourth web spaces inhibits independent digital motion, particularly abduction, and therefore reduces the span of the hand. • Syndactyly between digits of unequal length causes tethering of the longer digit, which deviates toward the shorter digits and may also cause a flexion contracture at the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) that progresses with
- 11. Surgical contra indication • include mild incomplete syndactyly without functional impairment • medical conditions that preclude surgery, or complex • syndactylies that risk further functional impairment with attempted separation. • In complicated complex – there are insufficient components in the fused mass to produce independent, stable, and mobile digits . • This situation typically arises in central brachysyndactyly or synpolydactyly, and separation risks reducing function.
- 12. Surgical factors to be taken into account • timing of the procedure or procedures • staging the releases of multiple web space syndactylies • creation of a commissure • techniques of separation and resurfacing of the digits • postoperative dressing and aftercare.
- 13. Timing of surgery • Syndactyly release has been performed in the neonatal period or during infancy, or it has been delayed until childhood. • Longterm reviews by Flatt and Ger have shown better outcomes with release after 18 months, although early surgery may be dictated by progressive skeletal deviation or deformity. • The goal is to complete all the releases by school age • . In multiple staged release - the first procedure can be combined with isolated release of the fingertips and distal phalangeal fusions of all the digits to reduce the tethering effect between surgical procedures
- 14. Surgical anatomy • cleeland's ligament: - coalesce in interdigital space forming a dorsal roof over digital vessels and nerves as well as forming a septum between them; - digital nerves and arteries may not be available for both digits; - vessels may be entwined, or absent w/ in the bridge; - aberent anatomy is more common w/ more complex deformities; - nerves should be teased apart using magnification;
- 15. Surgical steps • (1) separation of the digits • (2) commissure reconstruction • (3) resurfacing of the intervening borders of the digits. • (4) Paronyhcial fold formation
- 16. Seperation of digits • Release of syndactyly requires careful planning to optimize use of the available skin and to allow surgical exposure for separation of digits and structures. • Separation of the digits requires division or excision of fascial interconnections between the digits, with care taken to identify and preserve the individual neurovascular bundles and the venous plexus on the dorsum of the digits and of the commissure flap • . Bifurcation of the common digital nerve and artery may be distal to the planned position of the web space. • In this situation, the digital artery can be ligated provided the other side of the digit is unoperated or the contralateral digital artery is known to be intact Cronin and Skoog –dorsal and volar triangular flap with matched zig zag incision Somarlad open finger technique
- 17. Different skin incision technique depicted below
- 18. Commissure reconstruction • A basic tenet of syndactyly release is reconstruction of the interdigital commissure with a local skin flap. • Incision design must be placed such that inevitable scar contraction will avoid joint or web space contracture • For 1st web space: Other options include a transposition flap from the index finger, a combination of transposition flaps from the radial and ulnar borders of the index and thumb, respectively, or a “V-to-Y” advancement of the central web. Butterfly flap for web deepening 4 flap Z plasty for1stweb space
- 19. Resurfacing of the digit • Resurfacing the digits is achieved with the palmar and dorsal flaps raised from the conjoined digits supplemented with skin grafts. • Full-thickness skin grafts are preferred over split thickness skin grafts to lessen secondary graft contracture • Resurfacing the digits without skin graft may require some reduction of digital diameter by excising the subcutaneous fat of the digit while preserving the dorsal venous system
- 20. Graftless syndactyly release technique
- 21. Paronychial fold formation • Release of a complete syndactyly, particularly when associated with distal phalangeal fusion, requires the formation of a paronychial fold. • The distal phalangeal tufts may be covered using the technique described by Buck-Gramcko. • Laterally based long narrow triangular flaps are raised from the hyponychium of the conjoined digital mass and folded around to form the lateral nail fold
- 22. Post operative dressing • The dressings must apply gentle compression across the skin graft sites and protect the separated digits. • Nonadherent dressings and moist cotton are placed into the web spaces and reinforced with large amounts of soft gauze. • In young children, the compressive hand dressing is reinforced by above-the elbow plaster or a soft cast to prevent inadvertent removal. • The elbow is positioned in at least 90 degrees of flexion to minimize the chances of the cast sliding off the arm. • The dressings are removed 3 weeks after surgery, and then gentle washing and wound care are needed. The wounds are protected until they are dry and healed. • Normal hand use is allowed after the dressing has been removed. • Once healing has taken place, an elasticized compression glove may be fitted and worn for up to 3 months for scar management. • Scar massage by oil/gel , silicone gel sheets, or elastomere products can be used to treat areas of hypertrophic scarring.
- 23. Complication • Early :vascular compromise, infection, wound dehiscence, and graft loss. • Late : web creep, Joint contractures, beaked nail deformity
- 28. Syndactyly : and its associated syndrome • Acrosyndactyly Poland's syndrome: - hypoplasia of hand and simple syndactyly of fingers on the same side as the absent pectoral muscles (and other chest wall muscles); - Apert's Syndrome: - when all digits are joined, as is common in spoon hand of Apert's syndrome (acrocephalosyndactyly), it is important to release border digits-thumb and small finger-first; - remaining 3 joined fingers can be managed by removing middle digit, thus creating a three-fingered hand with a thumb and sufficient skin for closure; - Chromosomal Syndromes: - trisomy of 13, 18, or 21; - deletion of short arm of chromsome 5; - Craniofacial Syndromes: - Aglossia adactylia - Mobius Syndrome - Oculomandibulofacial syndrome
- 29. Acrosyndactyly: • Classification: - Type I: - conjoined finger tips with well formed webs w/ normal depth; - treatment involves separation and contouring of the tips of the digits; - partial digit ablation may be required; - Type II: - tips of digits are joined and web formation is incomplete; - treatment involves separation of tips of digits and deepening of web space; - Type III: - absent web spaces, sinus tracts, joined digit clefts; - as in simple syndactyly border digits are reconstructed first •
- 30. Apert syndrome • Acrocephalosyndactyly – craniosynostosis with acrosyndactyly and symphalangism and clinodactyly of thumb • M:F – 1.5:1 • AD/AR • 1:2,00,000 • Single gene mutation
- 31. Upton classified into I spade , mitten and rosebud appearance respectivity Type 1-3
- 34. Radial thumb clinodactyly • Dao recommended a release of the abnormal abductor pollicis brevis tendon insertion into the distal phalanx and reinsertion the proximal phalanx, excision of the metacarpal head ulnar prominence, and pinning of the interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints. • Oishi and Ezaki proposed that the thumb be reconstructed by releasing the abnormal abductor pollicis brevis insertion, opening or closing wedge osteotomy of the proximal phalanx, and a V-Y advancement flap on the radial side of the thumb.
- 35. First web space release
- 36. THANK YOU
