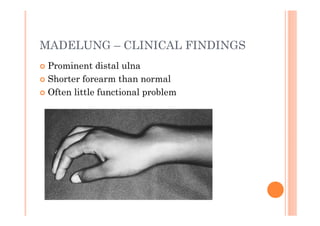
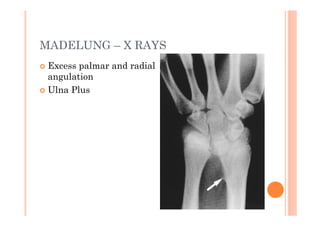
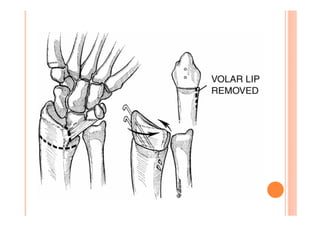
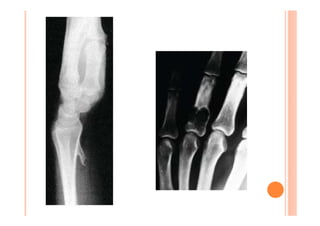
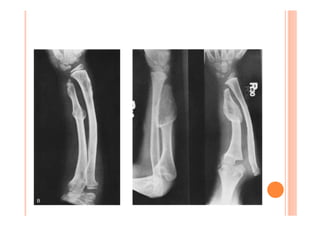
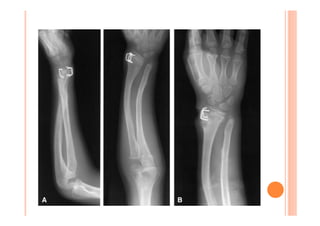
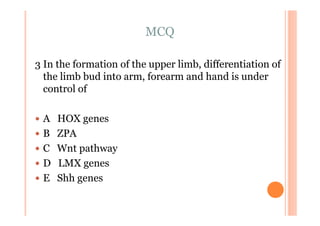
The document discusses Madelung deformity, a forearm and wrist deformity due to multiple hereditary exostoses characterized by excessive radial and palmar angulation of the distal radius. It outlines the clinical features, radiographic findings, treatment options, and differentiates hereditary multiple exostoses from other conditions. Additionally, it includes multiple-choice questions related to congenital hand deformities and their classifications.