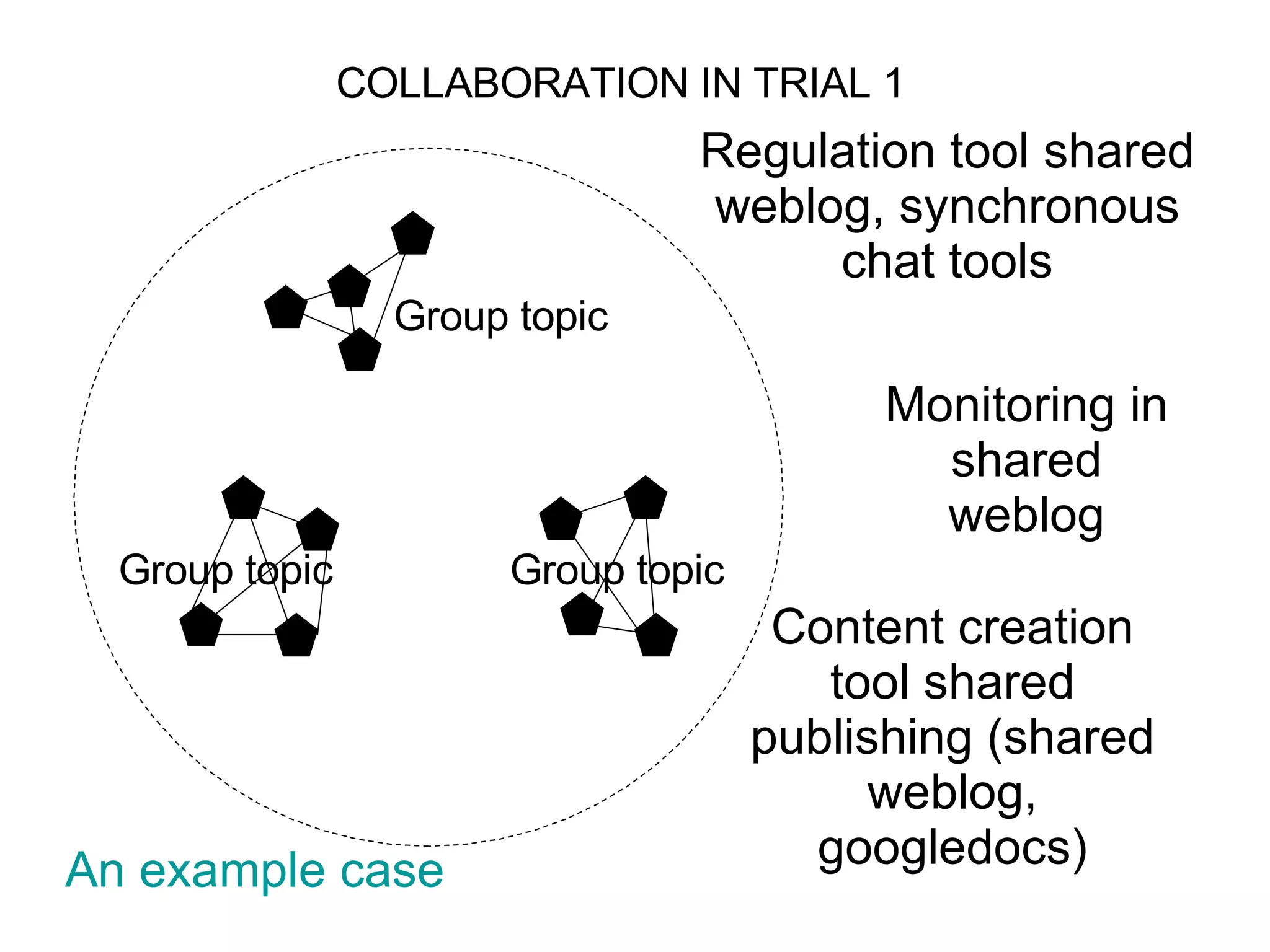
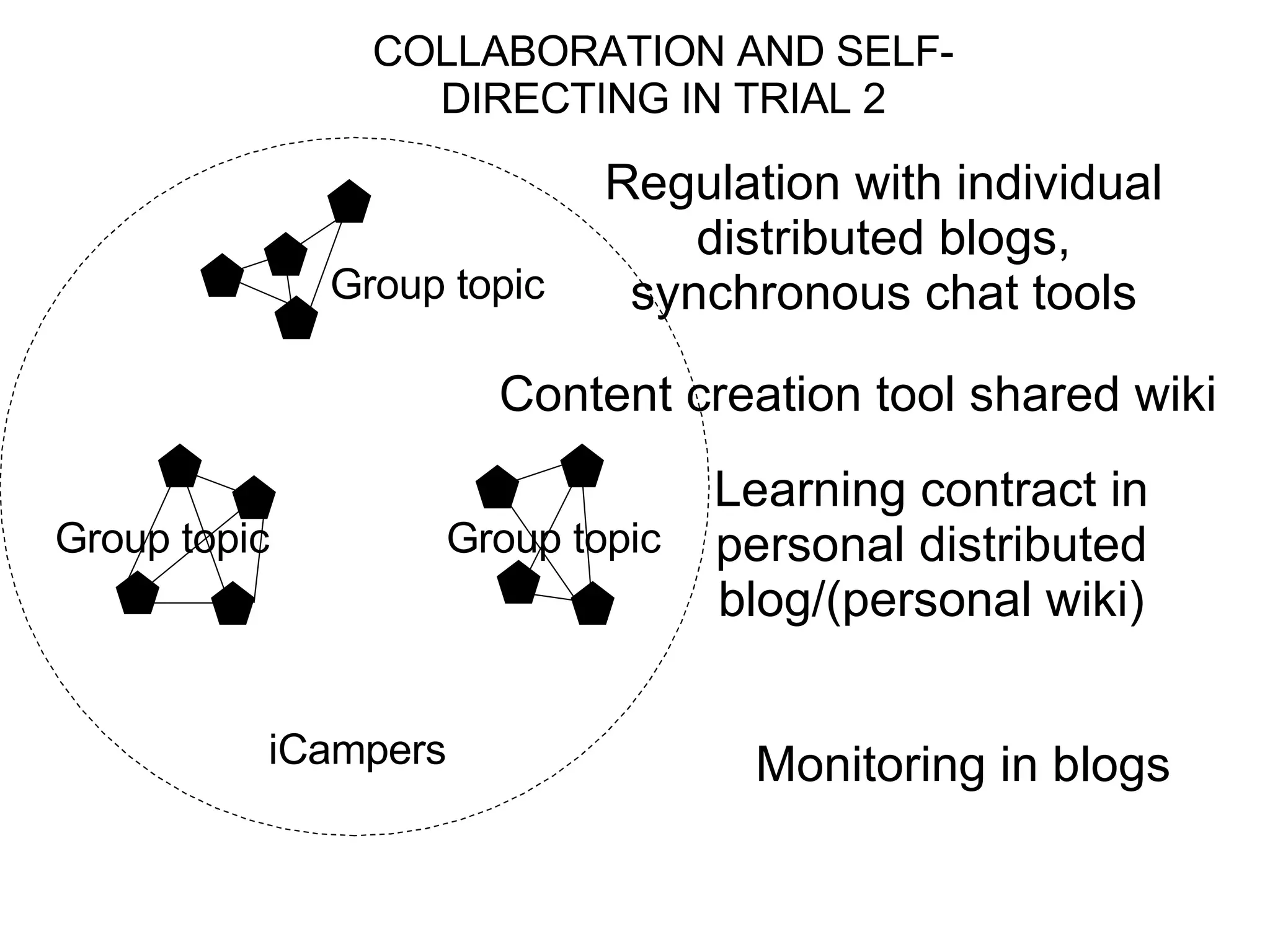
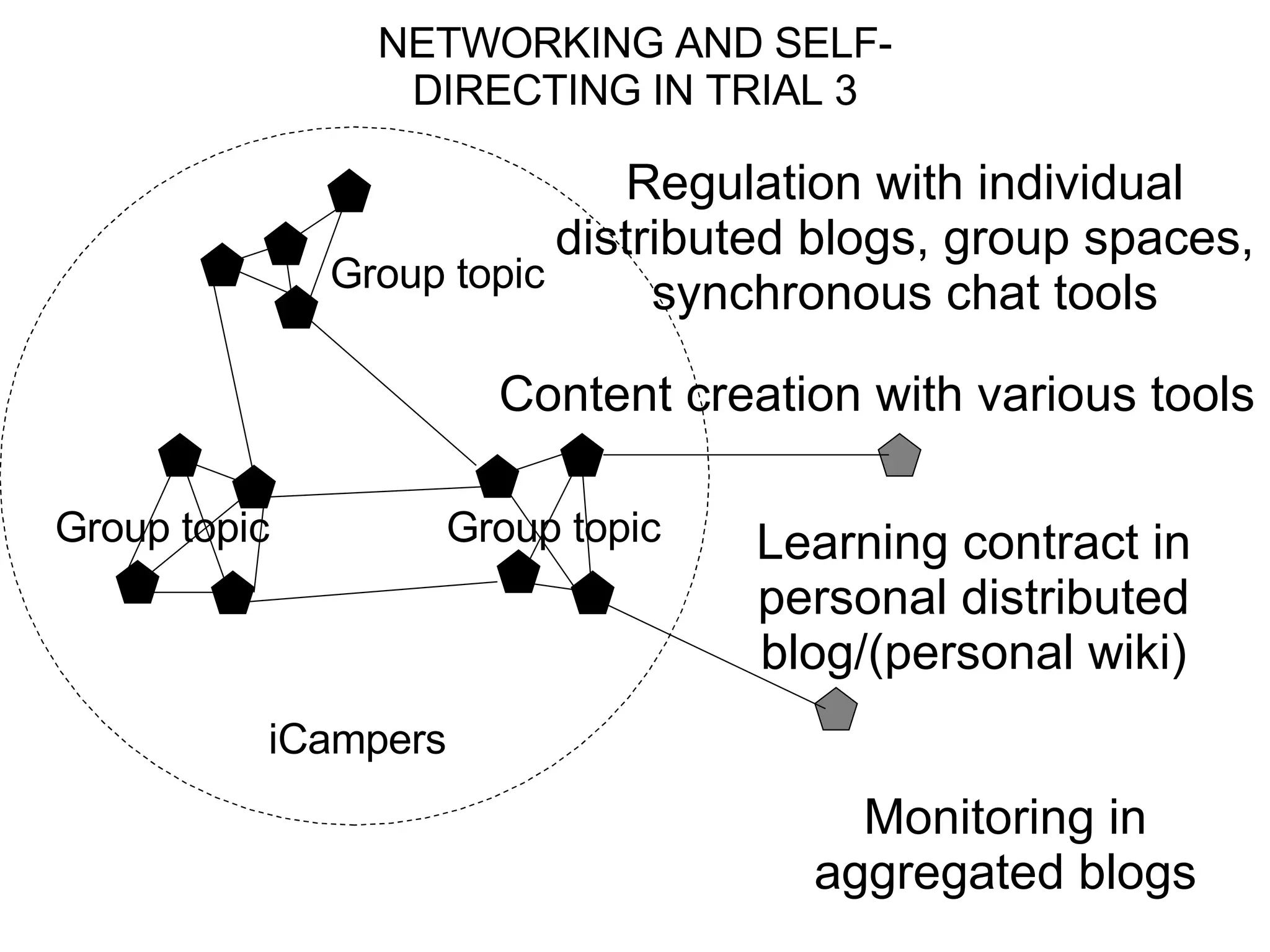
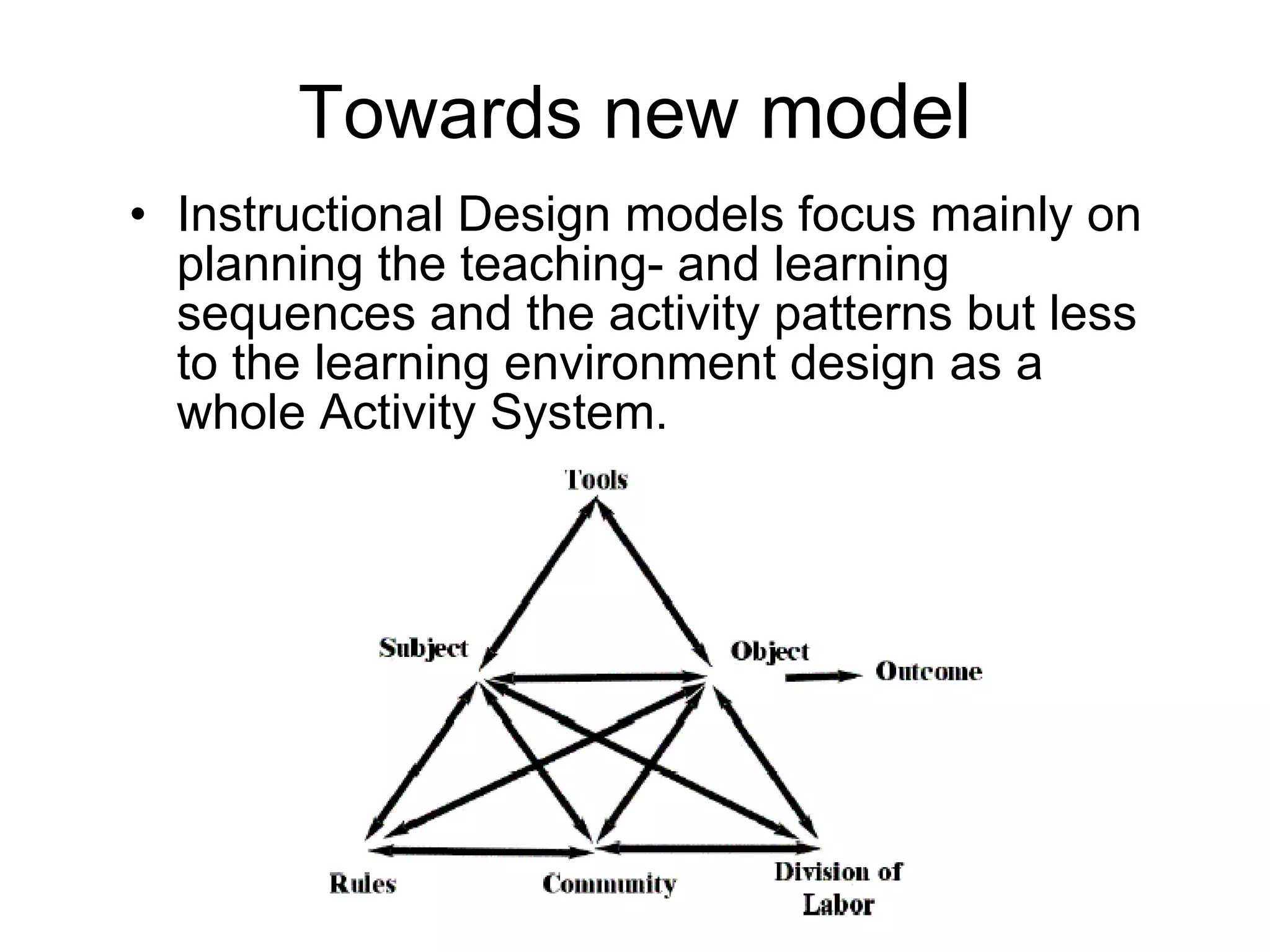
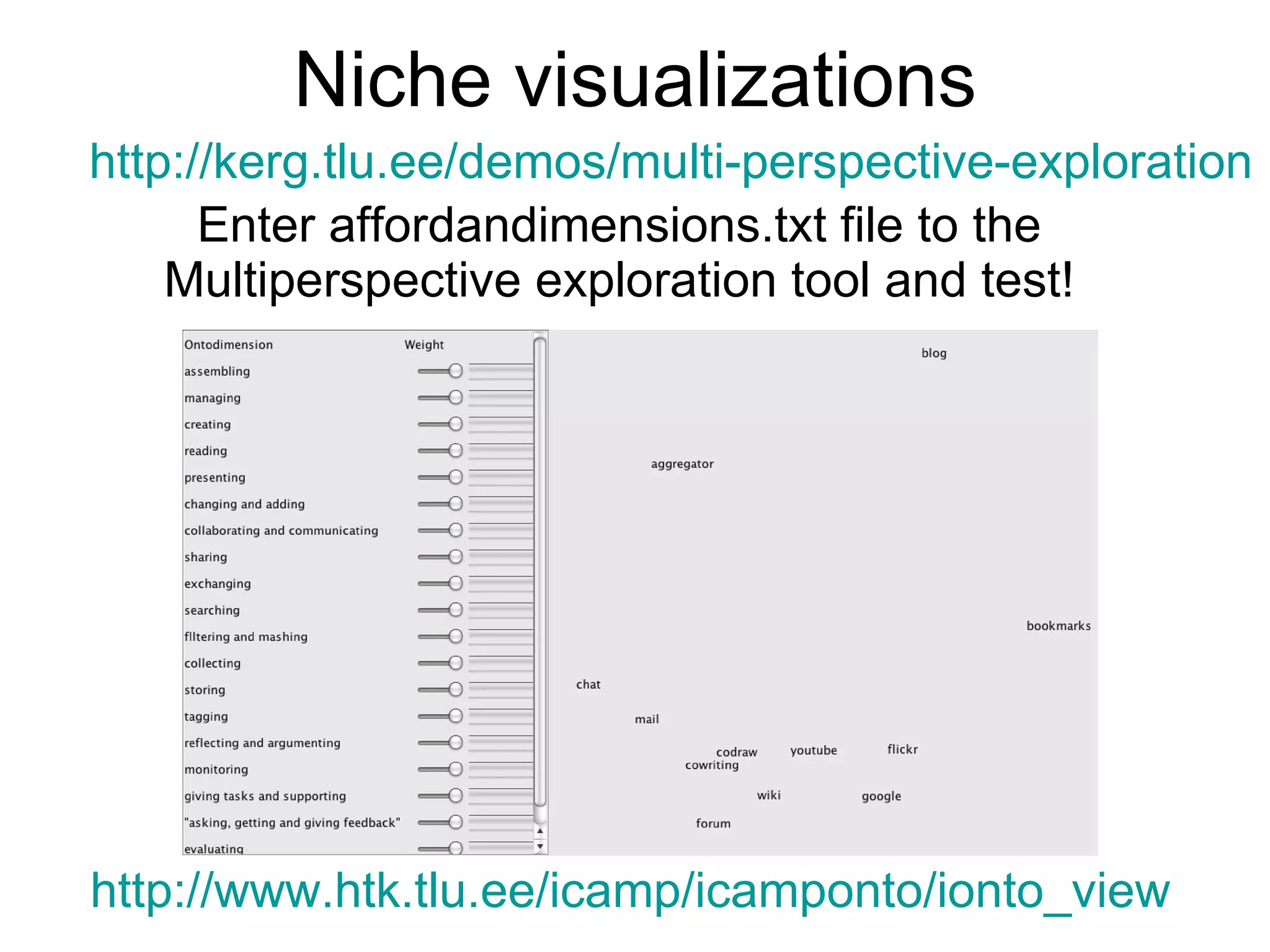
The document discusses the iCamp project which aims to design learning experiences to develop soft skills through innovative and interactive learning environments. It describes trials conducted using tools like blogs, wikis and social networking sites to support self-directed learning, social networking and collaboration across borders. It recognizes challenges in balancing individual and collaborative work, and forming shared workspaces. It proposes moving from traditional instructional design models to an ecological model where learning niches are defined by affordances rather than specific tools.














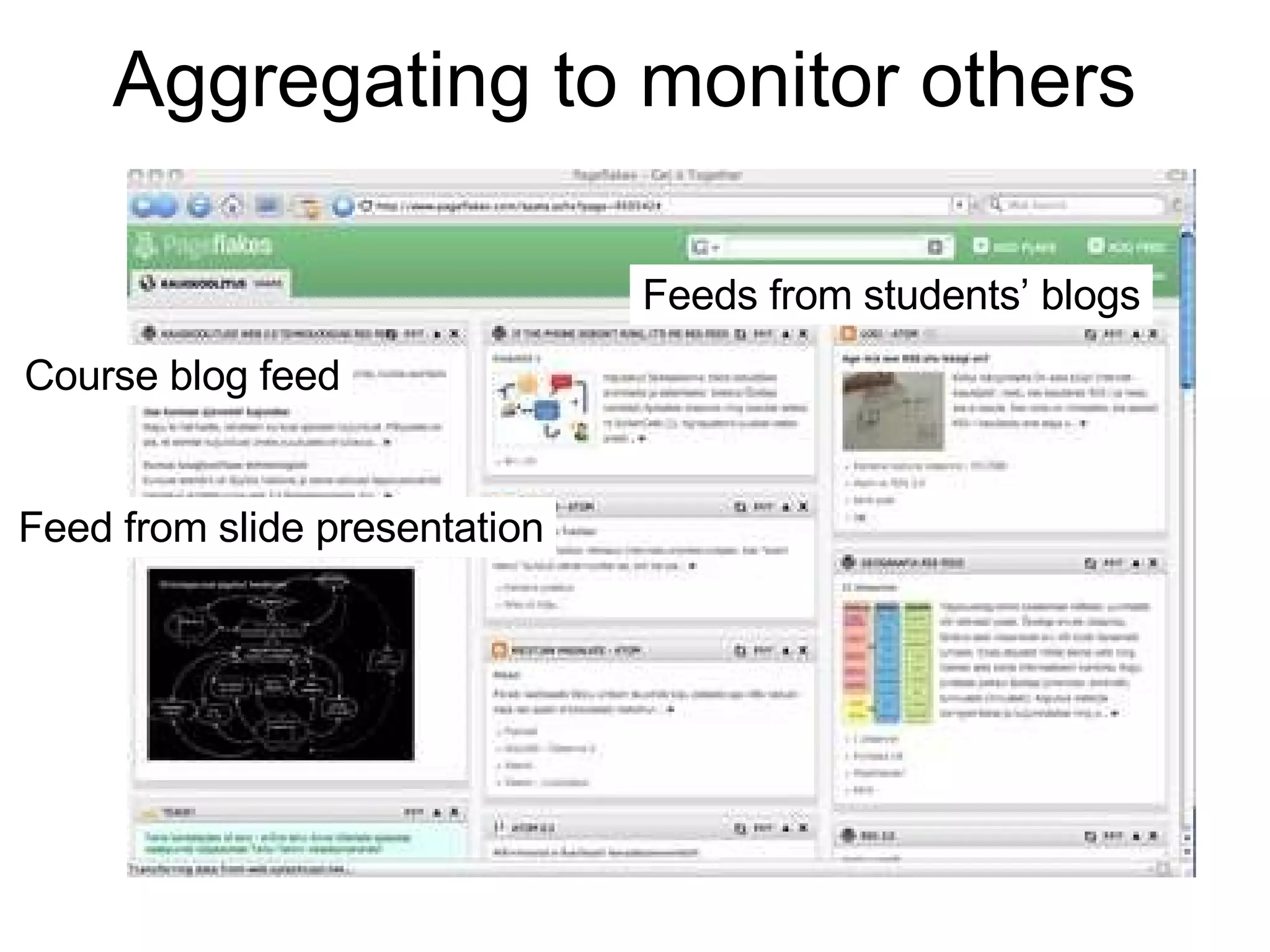






















![Contact me: [email_address] Or read my ideas: http://tihane.wordpress.com Most of iCamp experimental data are still waiting an in-depth analysis, read about our progress in: http://www.icamp.eu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/macedoniaicamp-1213348256707217-9/75/Macedonia-Icamp-47-2048.jpg)