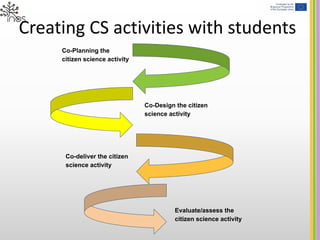
The document outlines strategies for integrating citizen science (CS) activities into higher education, emphasizing co-design and collaboration with students and external stakeholders. It highlights the importance of planning CS as long-term, interdisciplinary tasks that build active citizenship competencies and open science practices. Key recommendations include using digital tools effectively, fostering participant agency, involving mentors, and incorporating policy discussions to ensure a meaningful impact.