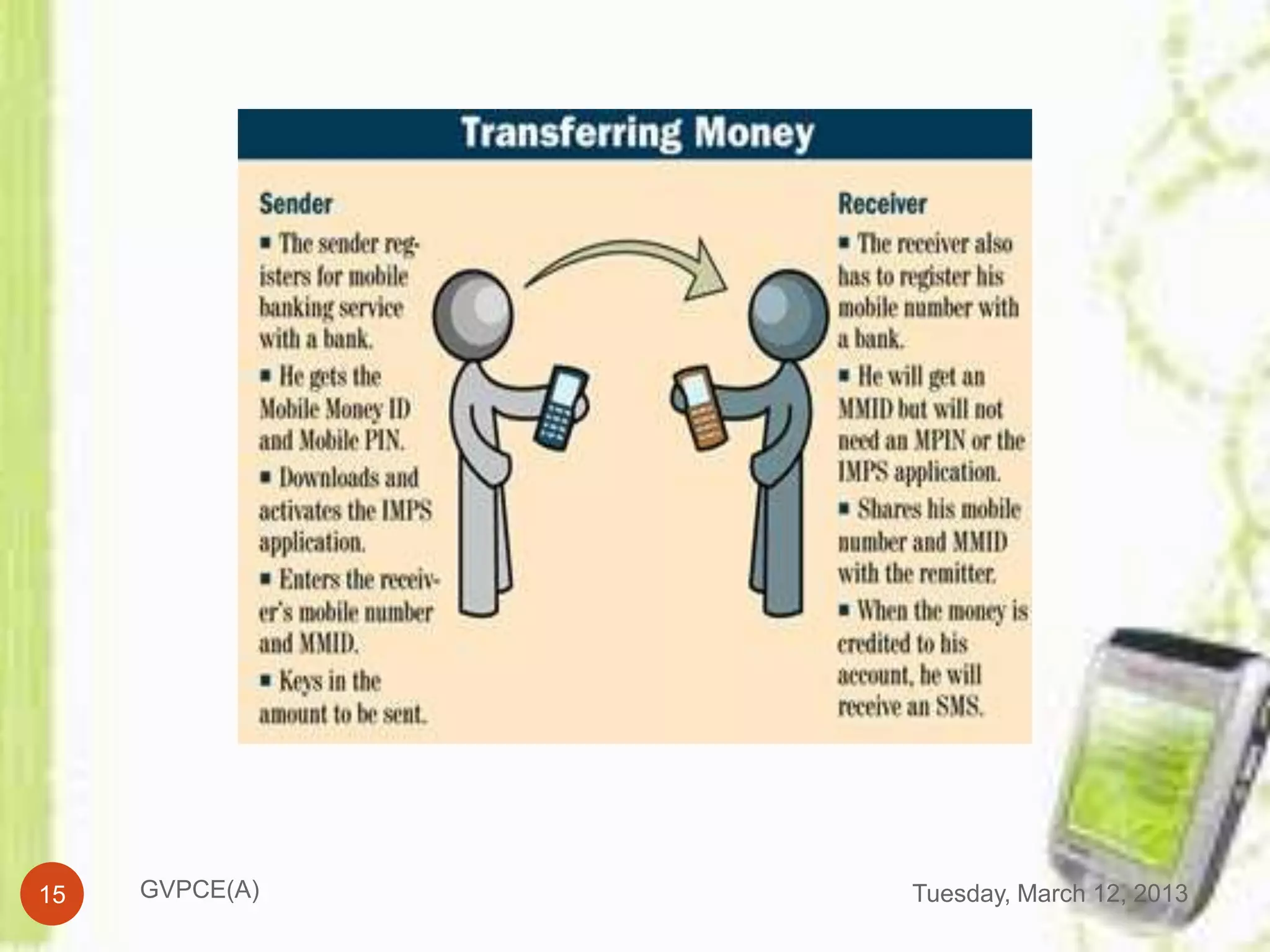
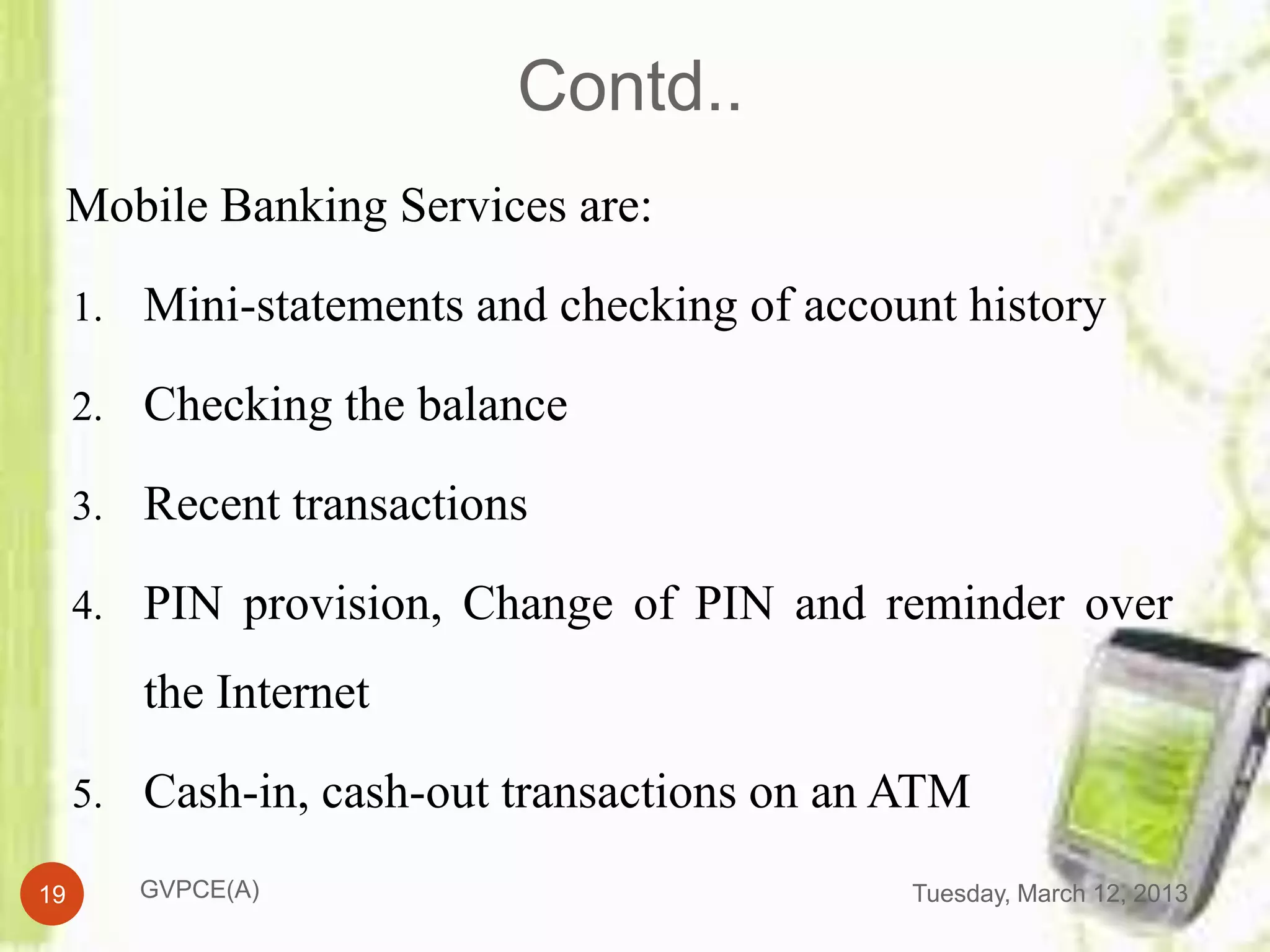
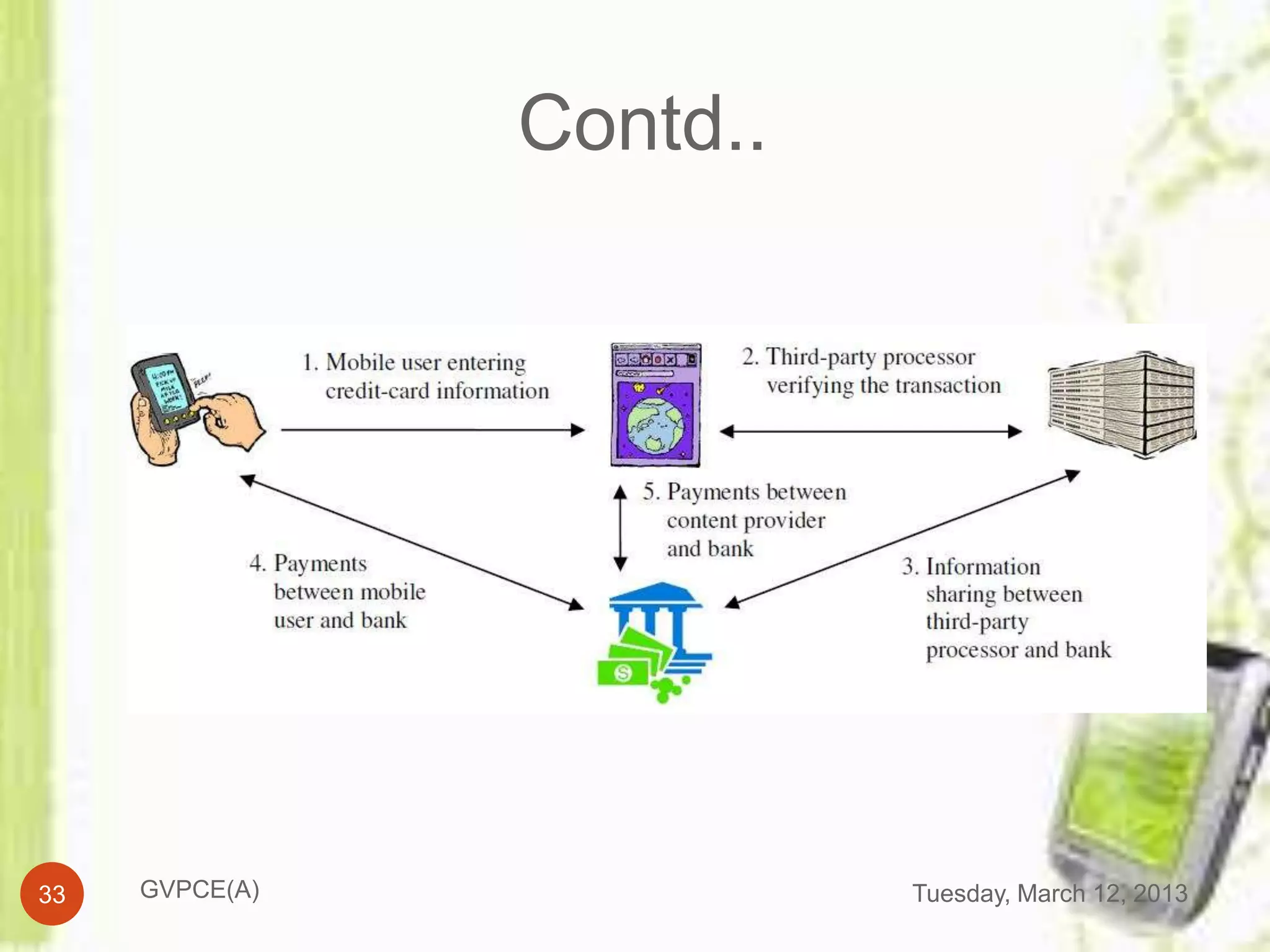
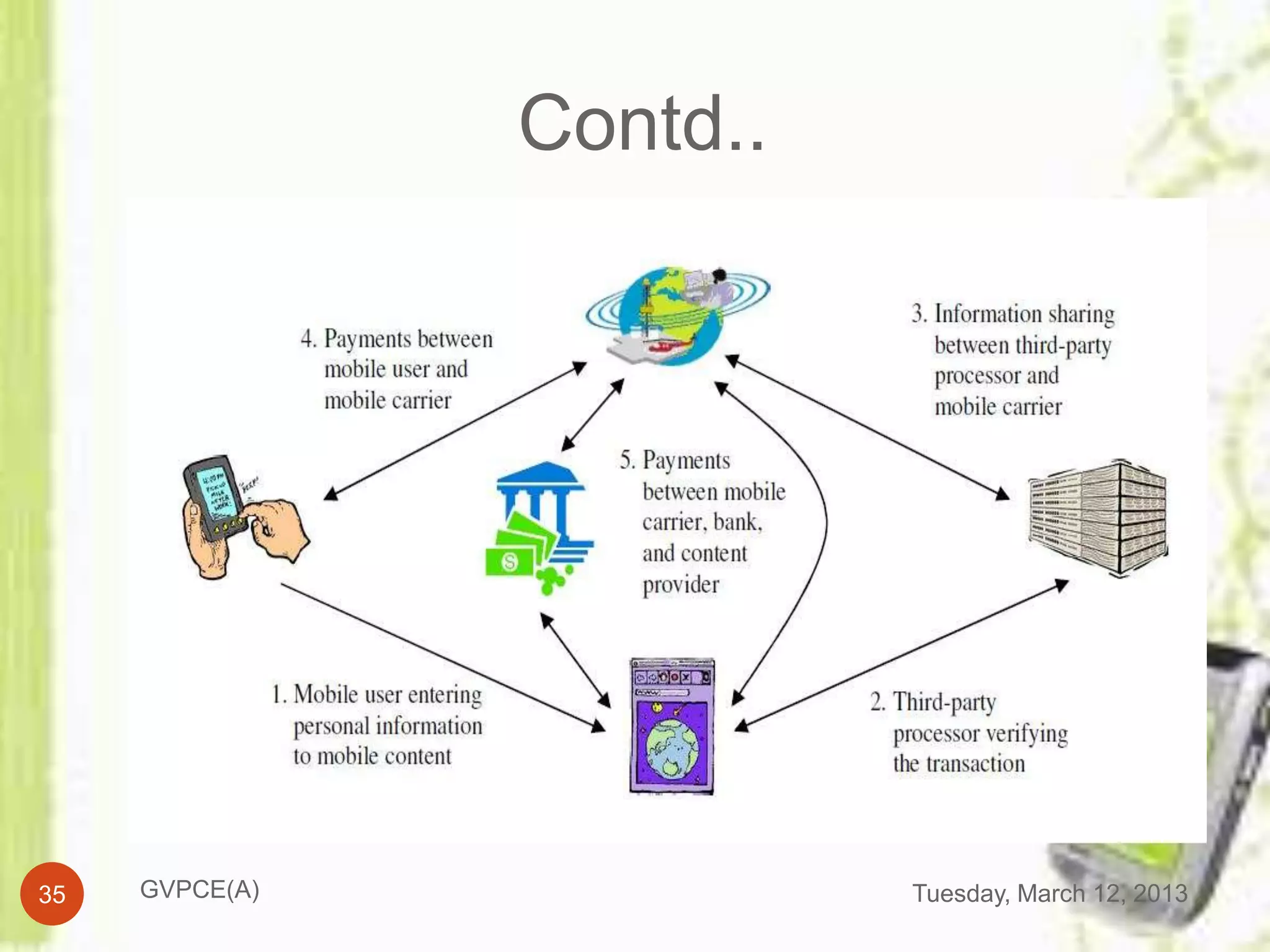
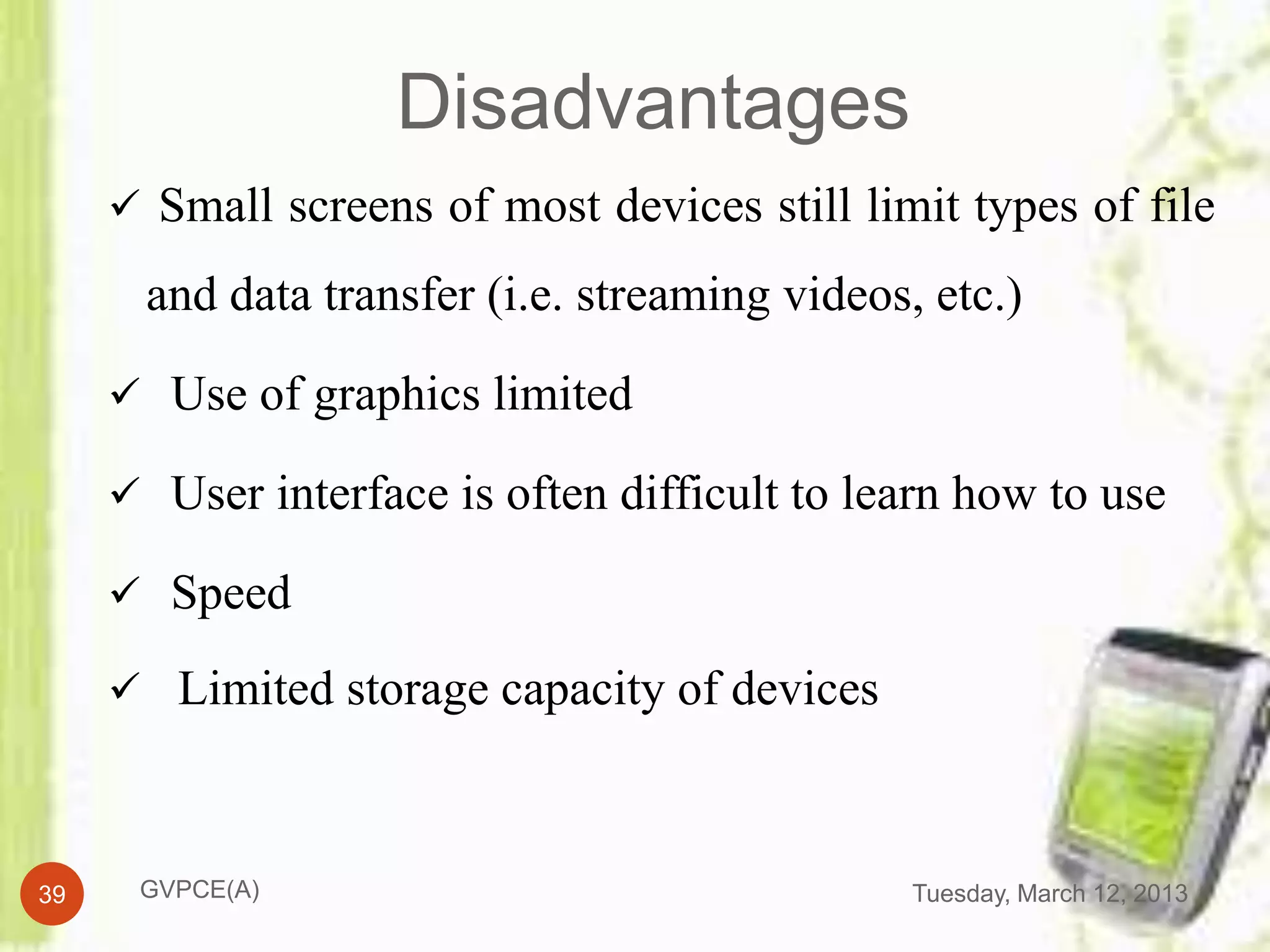
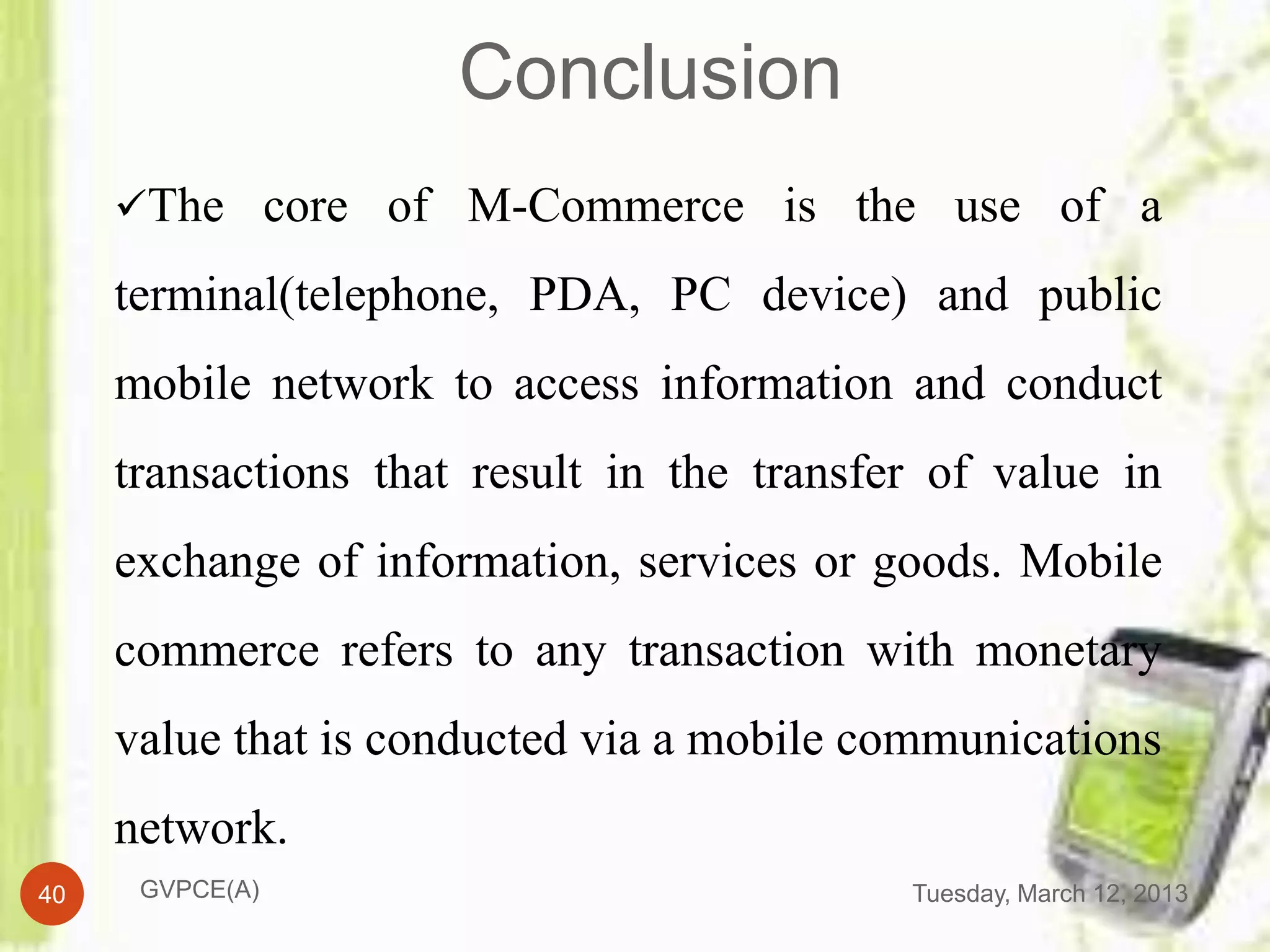
This document discusses e-commerce in mobile computing. It begins with an introduction that defines commerce, e-commerce, and mobile commerce. It then provides a brief history of mobile commerce beginning in 1997. The bulk of the document covers various aspects of mobile commerce such as services and applications like mobile ticketing, payments methods including mobile wallets, and advantages and disadvantages. It concludes with references for further information.