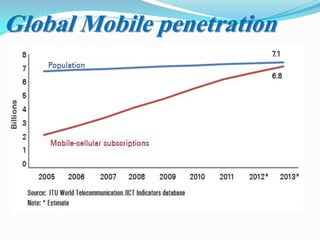
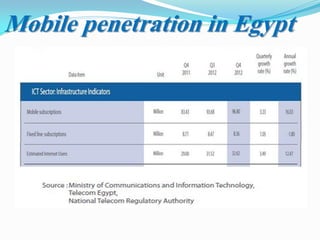
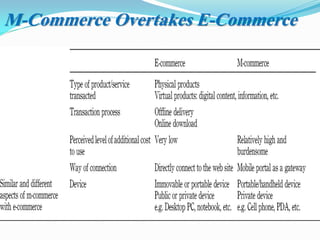
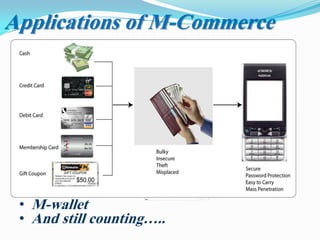
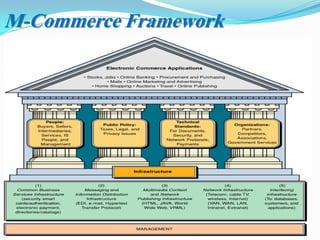
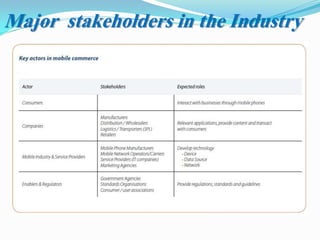
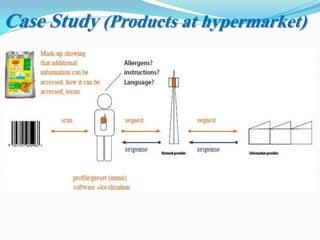
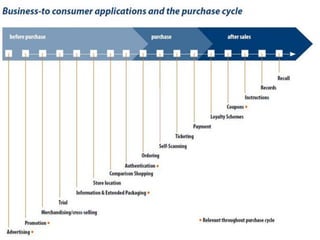
The document presents an overview of mobile commerce (m-commerce), detailing its definition, growth factors, applications, and challenges. It highlights the rapid increase in mobile phone penetration and the shift from e-commerce to m-commerce, driven by technological innovations and user accessibility. The future of m-commerce appears optimistic, with increasing consumer demand for mobile money transfer services and potential for new business opportunities.