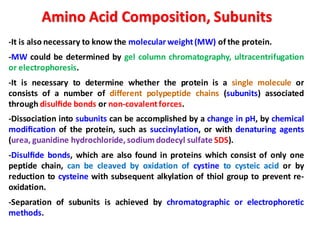
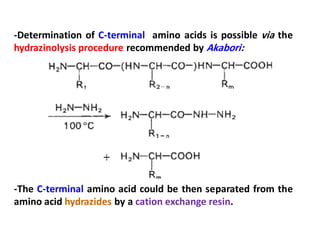
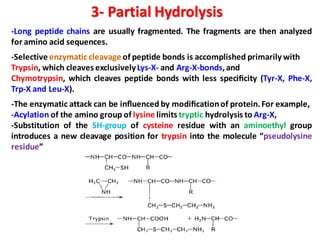
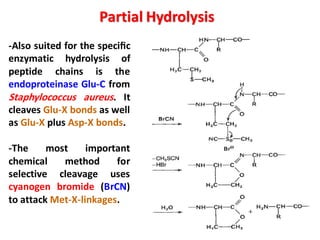
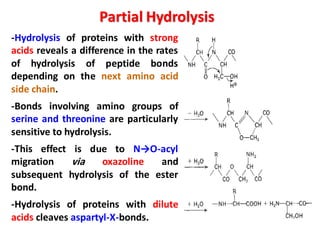
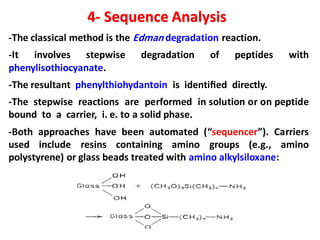
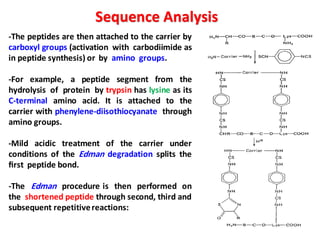
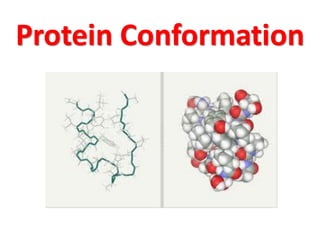
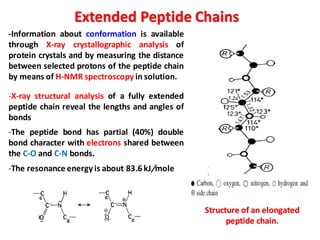
The document discusses the structure of proteins at different levels:
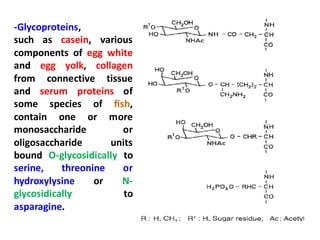
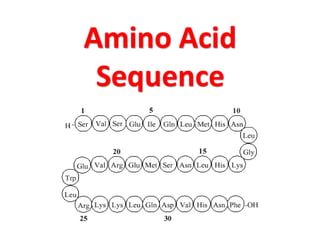
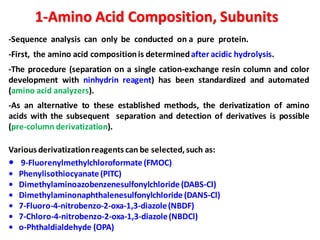
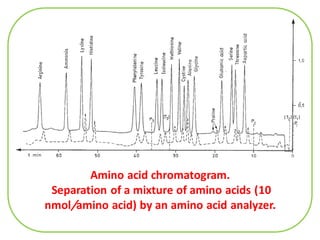
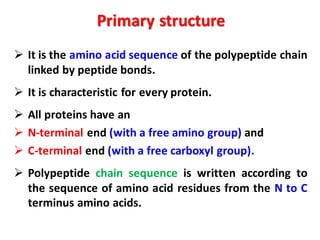
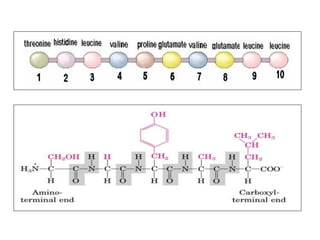
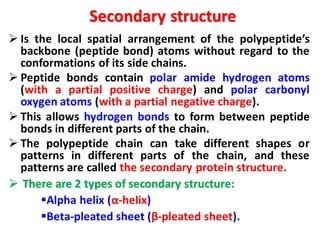
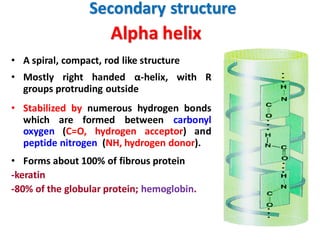
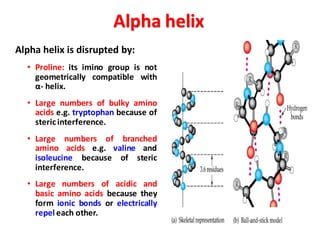
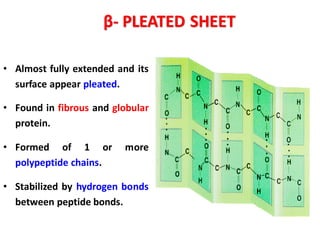
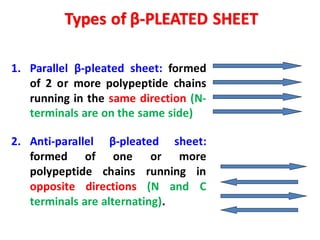
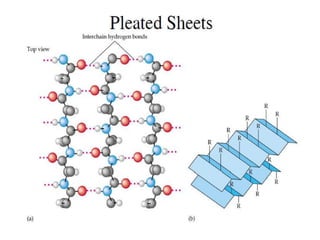
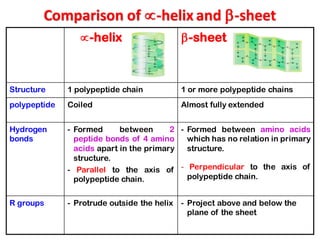
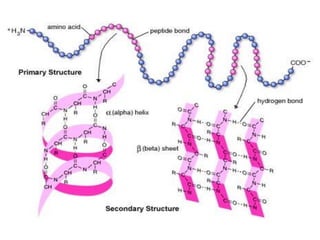
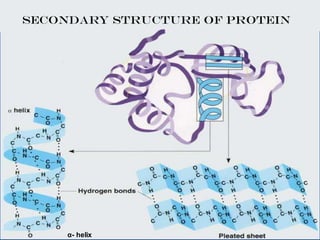
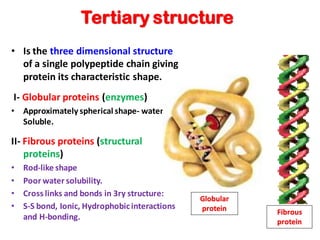
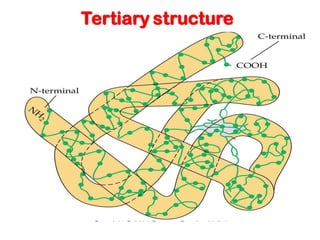
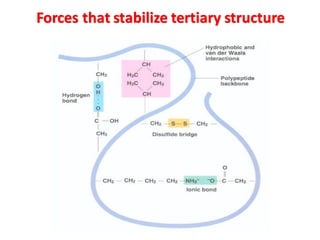
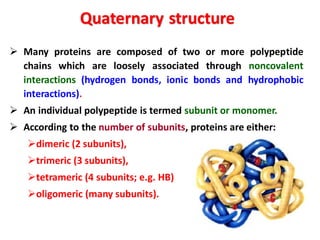
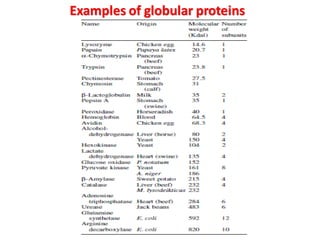
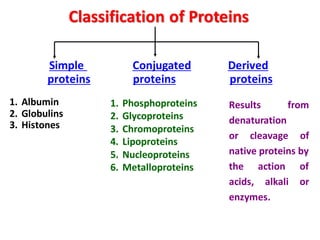
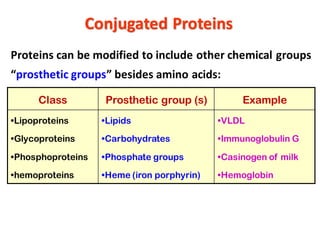
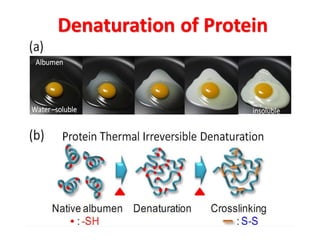
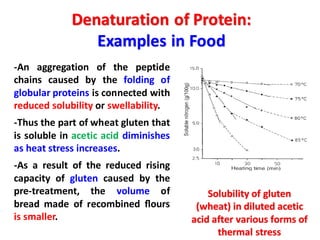
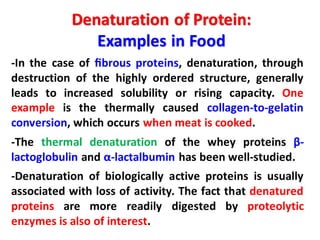
- Primary structure refers to the amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chain. Secondary structure involves hydrogen bonding that forms alpha helices or beta pleated sheets. Tertiary structure describes the overall 3D shape of the folded polypeptide chain. Quaternary structure involves the interactions between multiple polypeptide subunits. The document outlines the forces that stabilize protein structures such as disulfide bonds, hydrogen bonding, and hydrophobic interactions. Proteins are classified based on their composition, which can include modifications like glycoproteins, lipoproteins, or metal-binding groups.