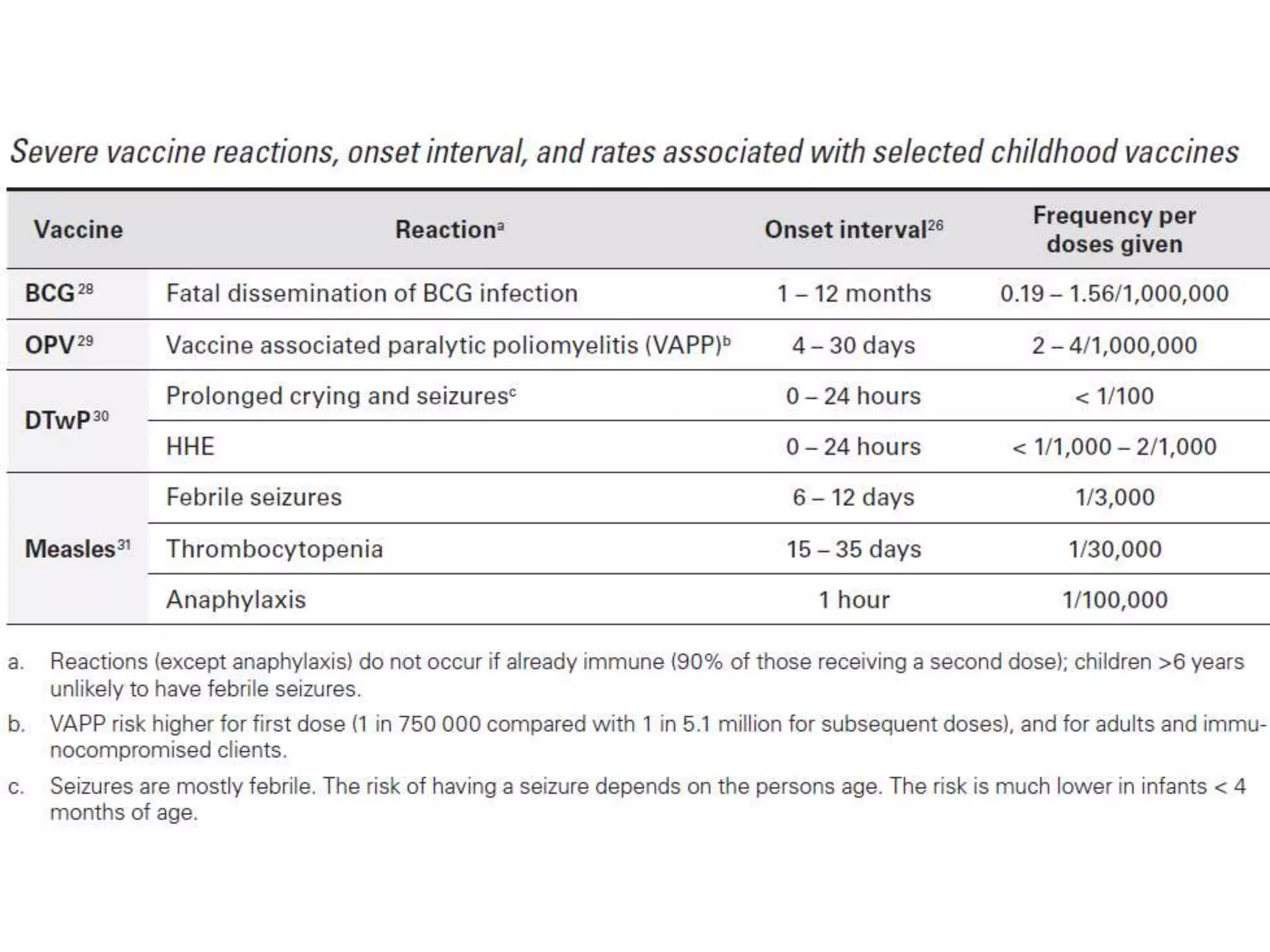
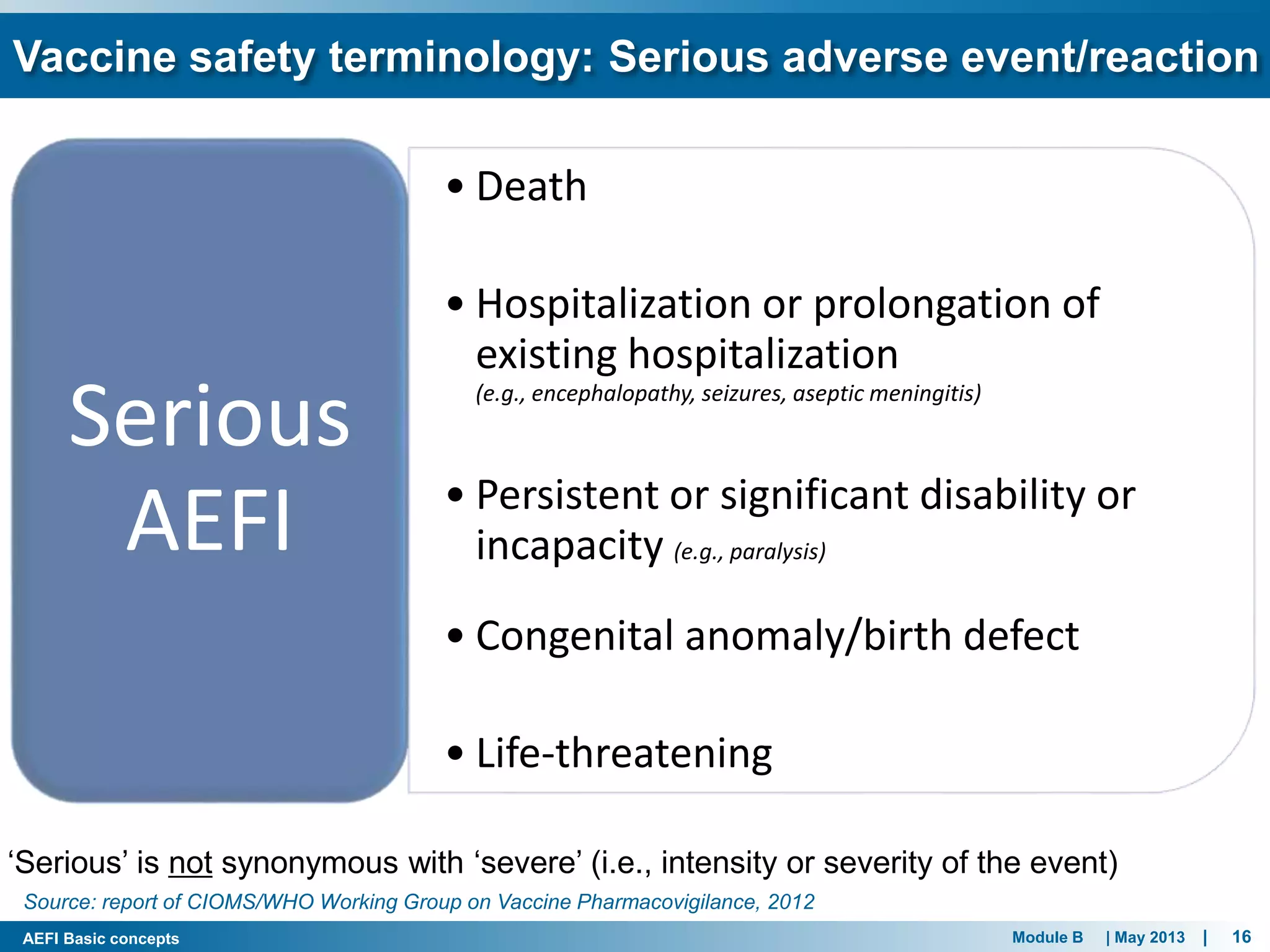
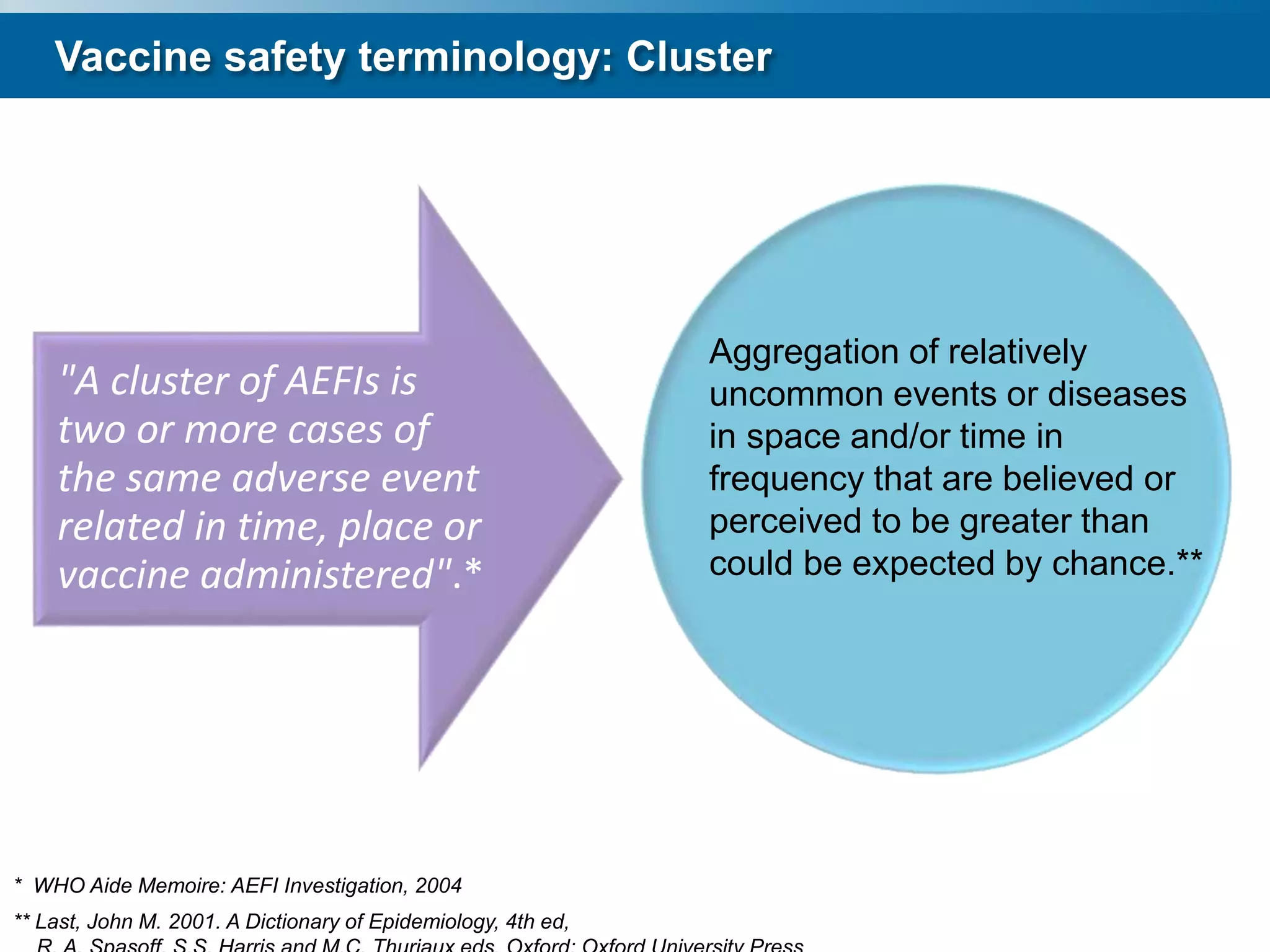
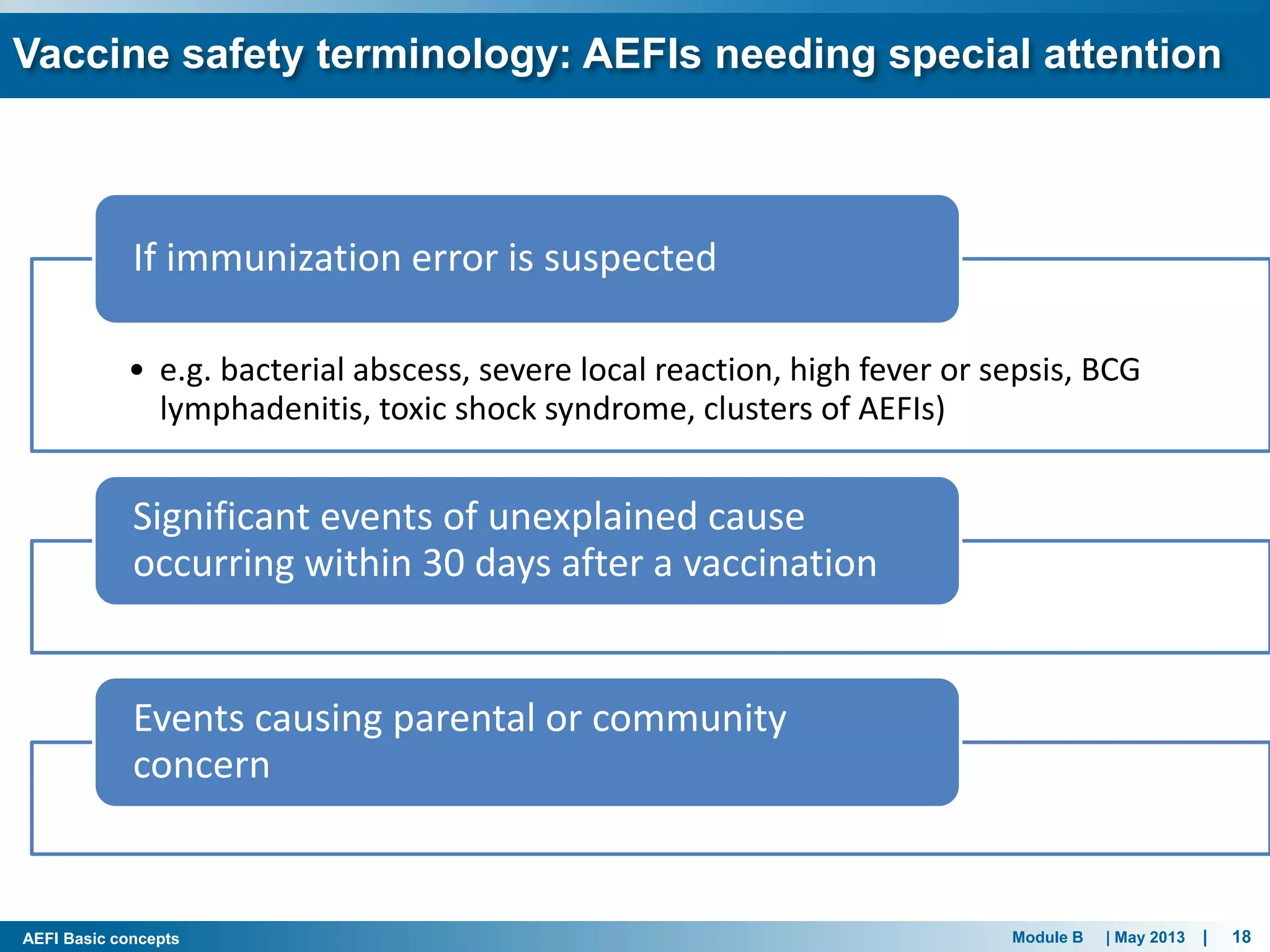
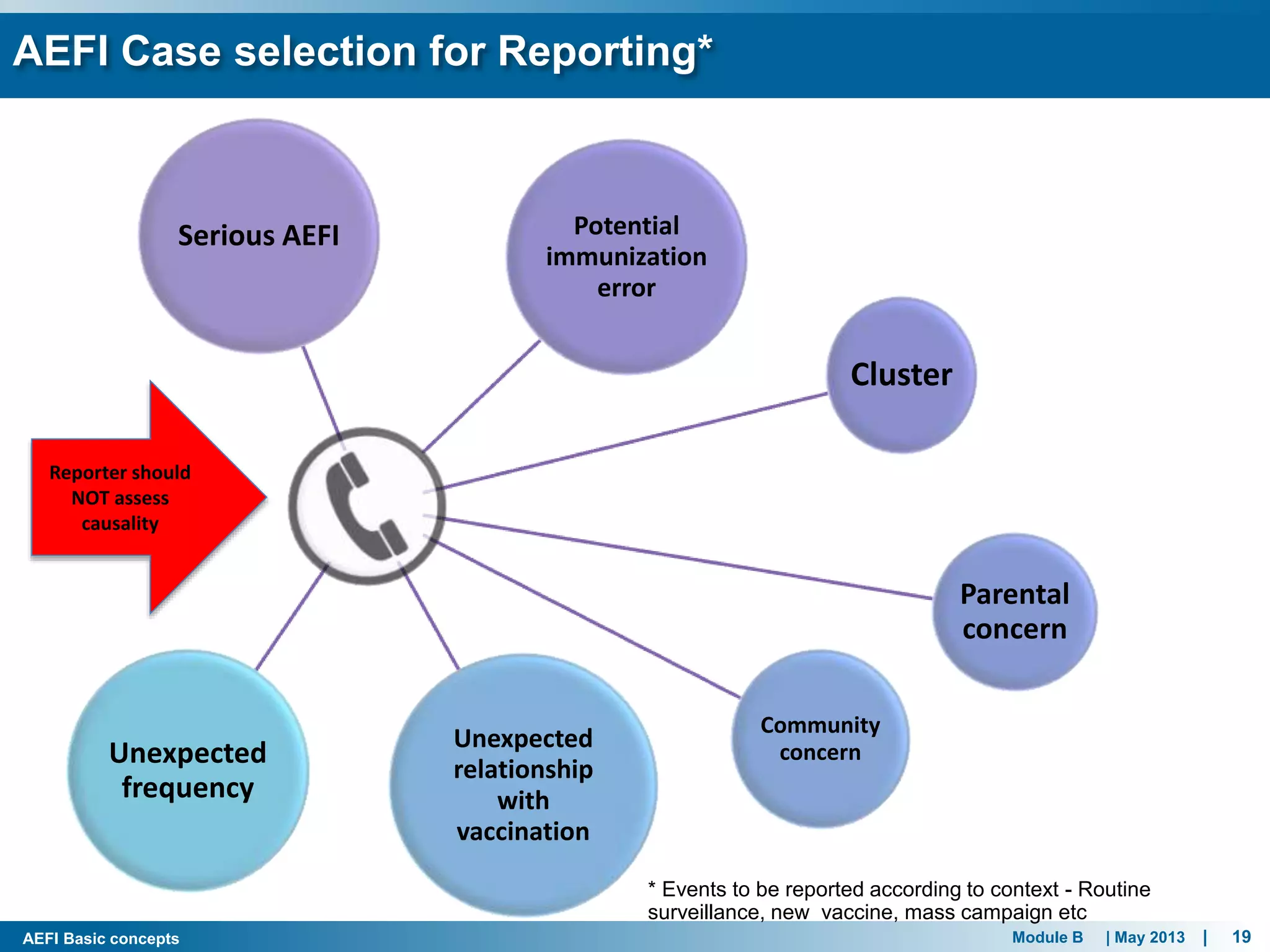
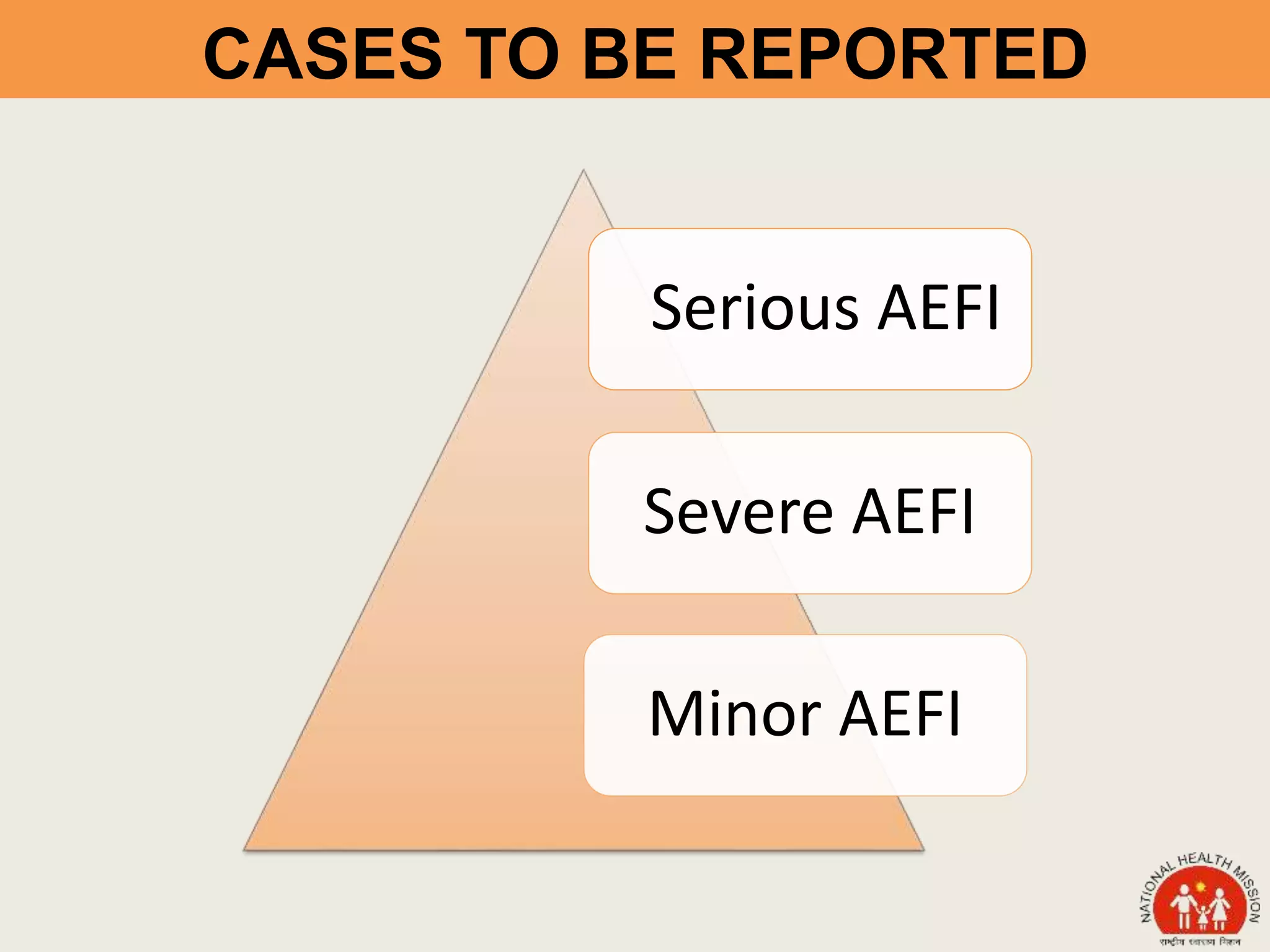
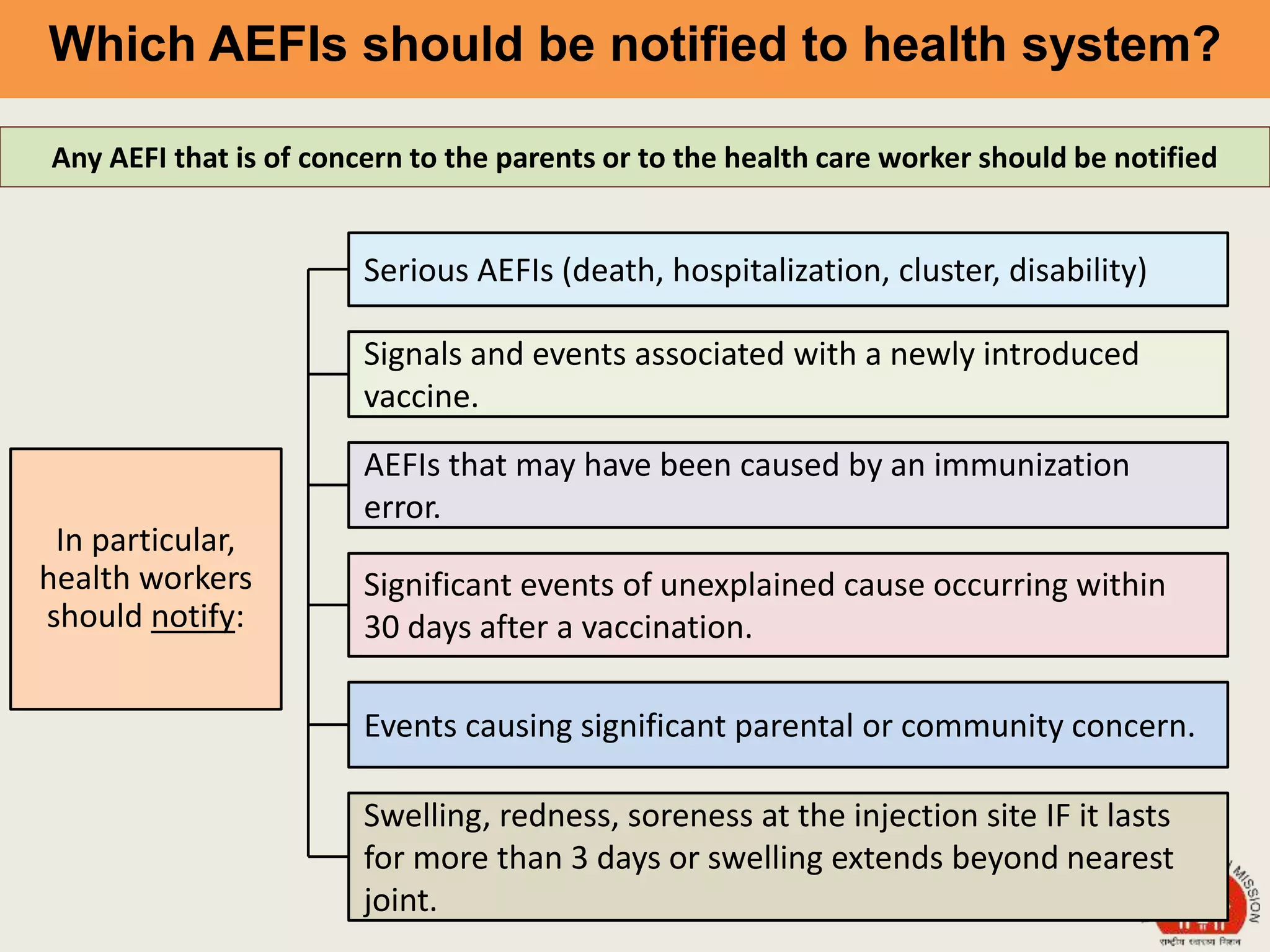
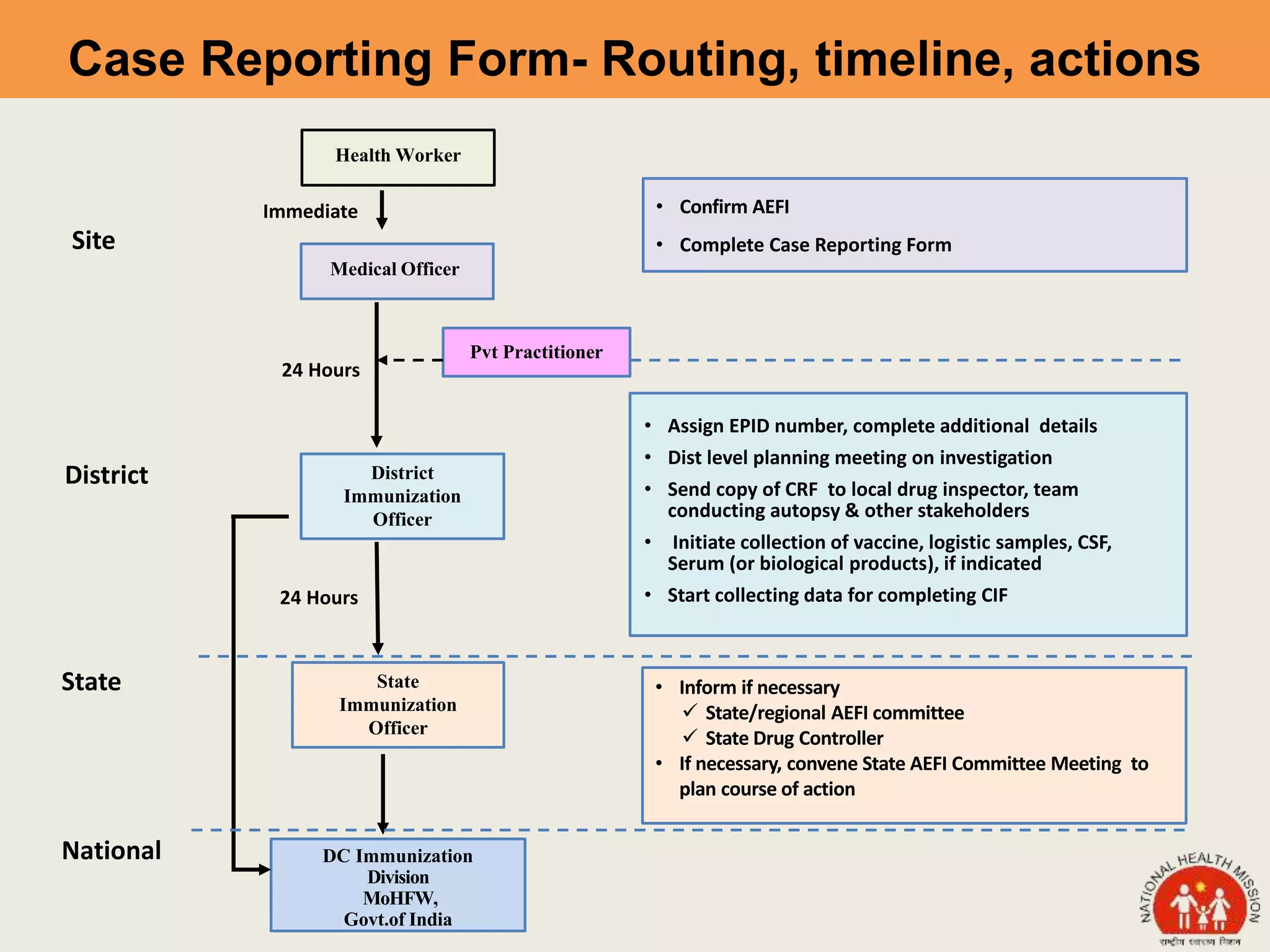
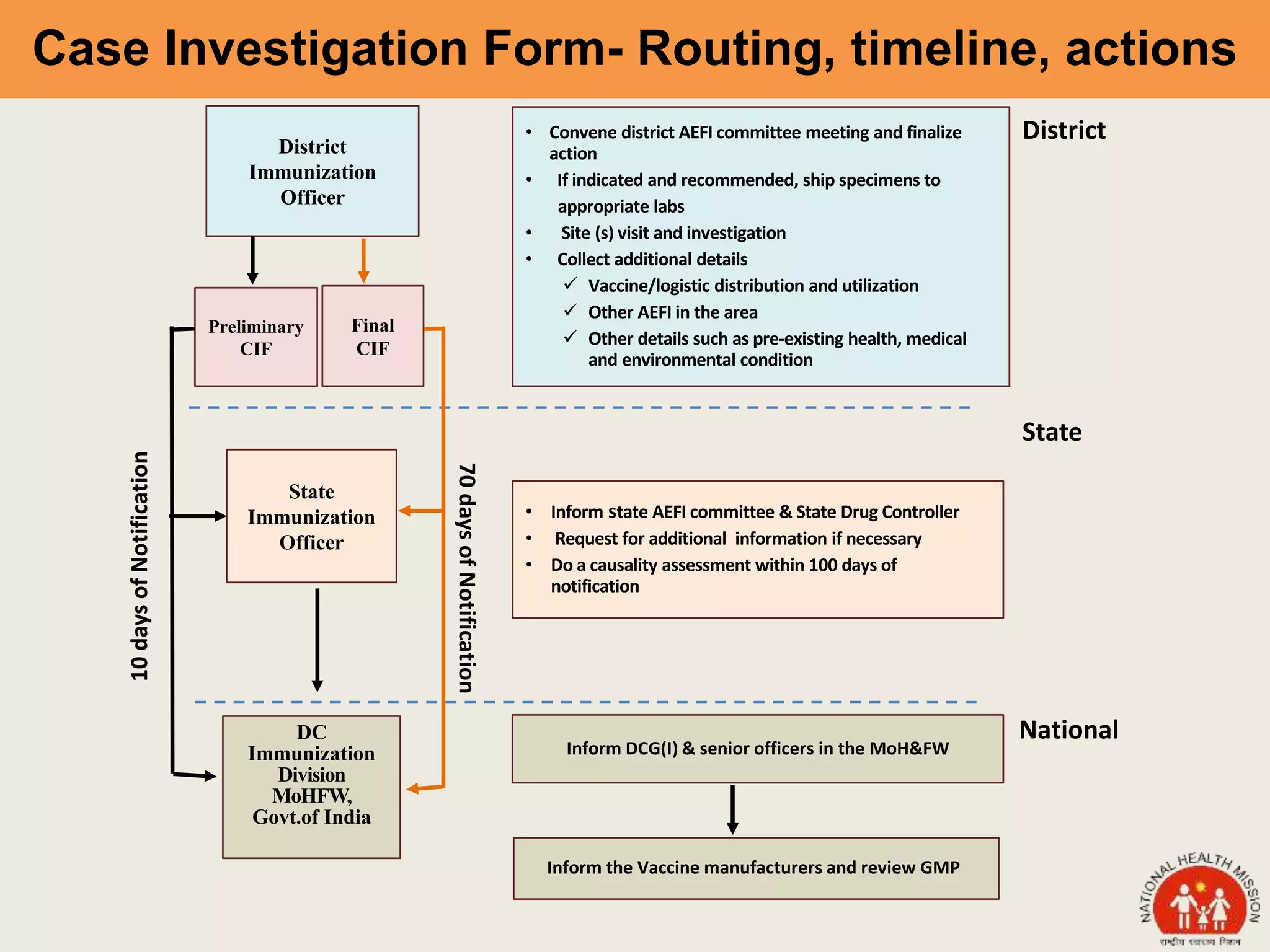
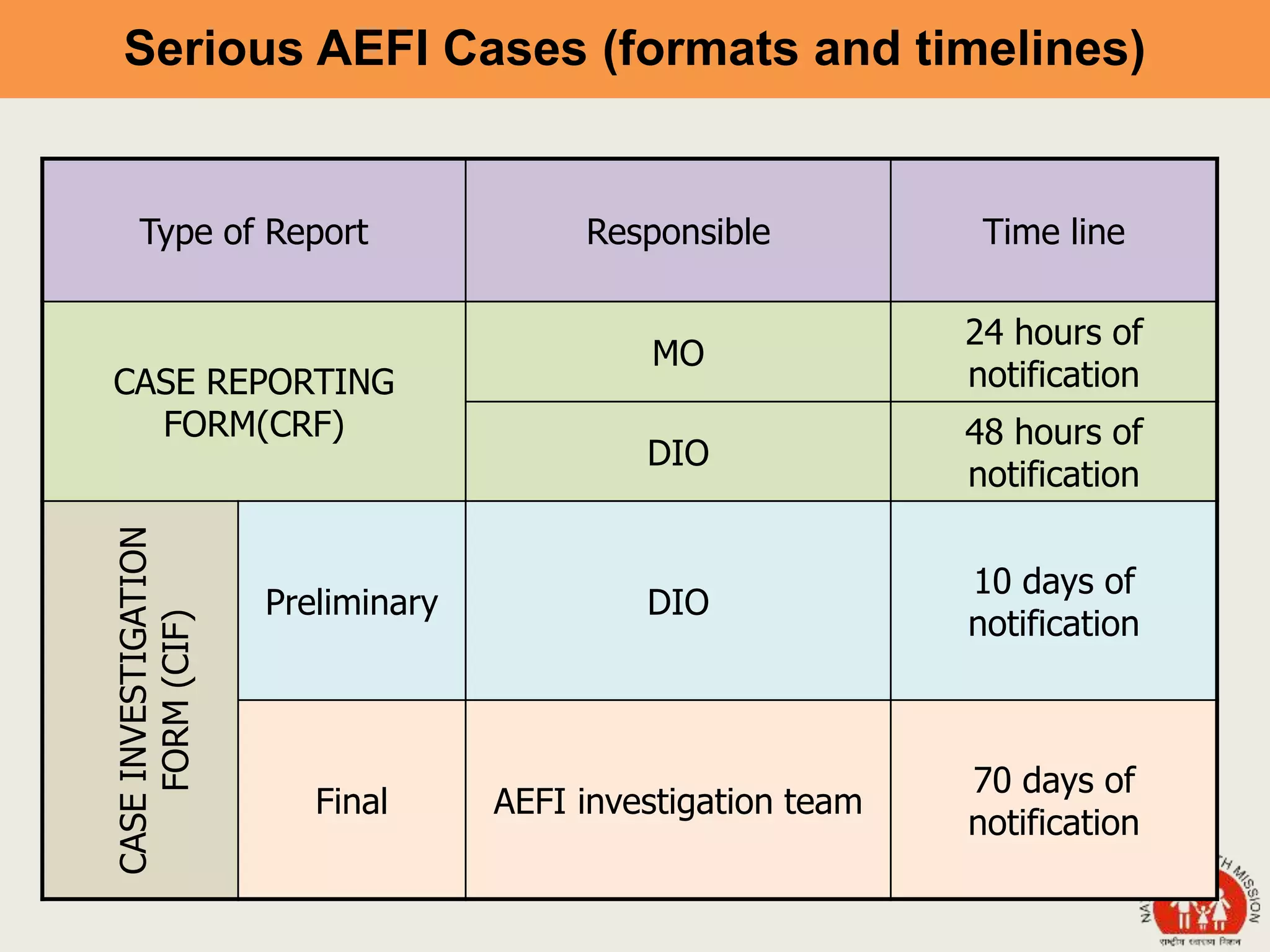
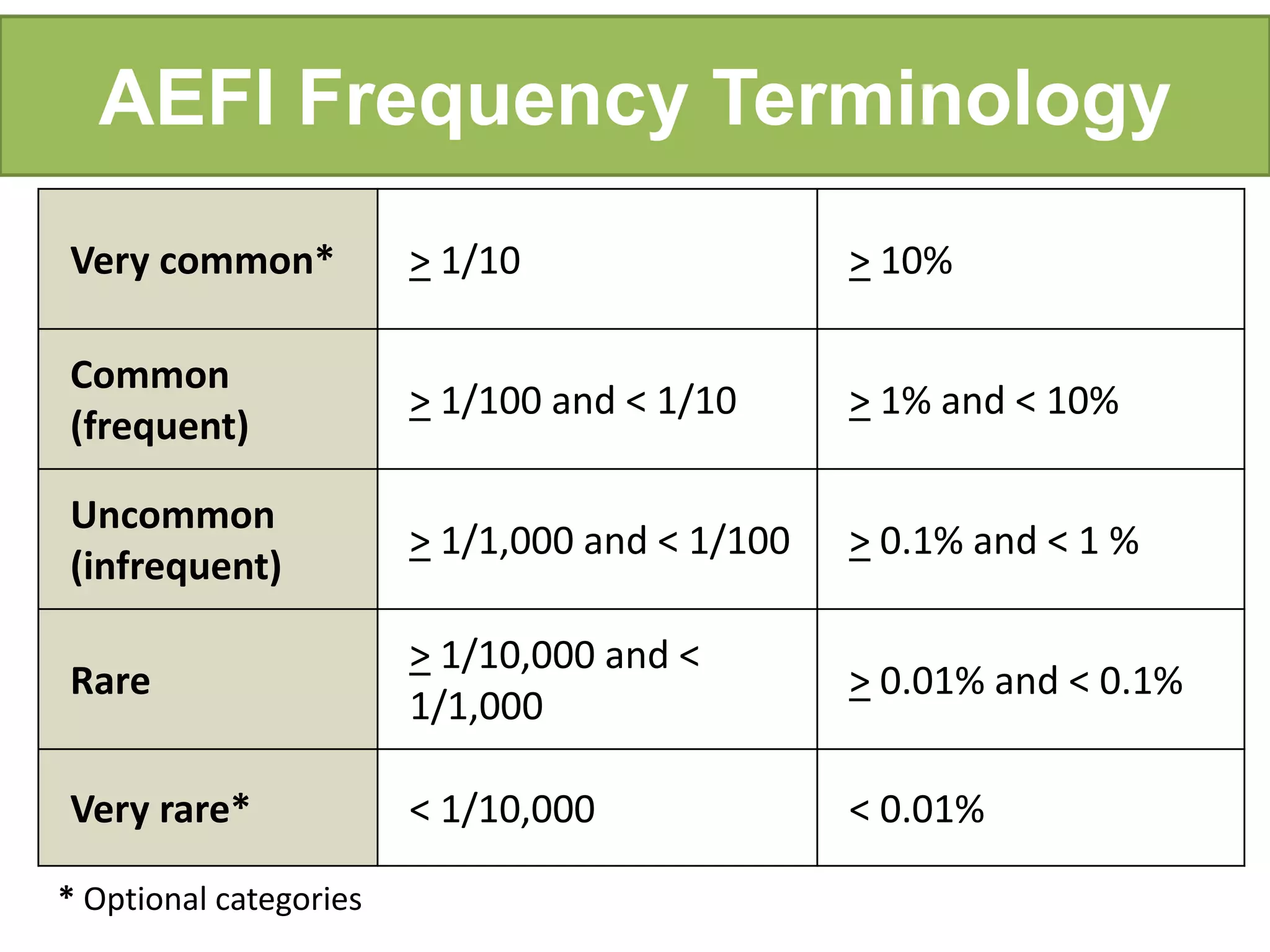
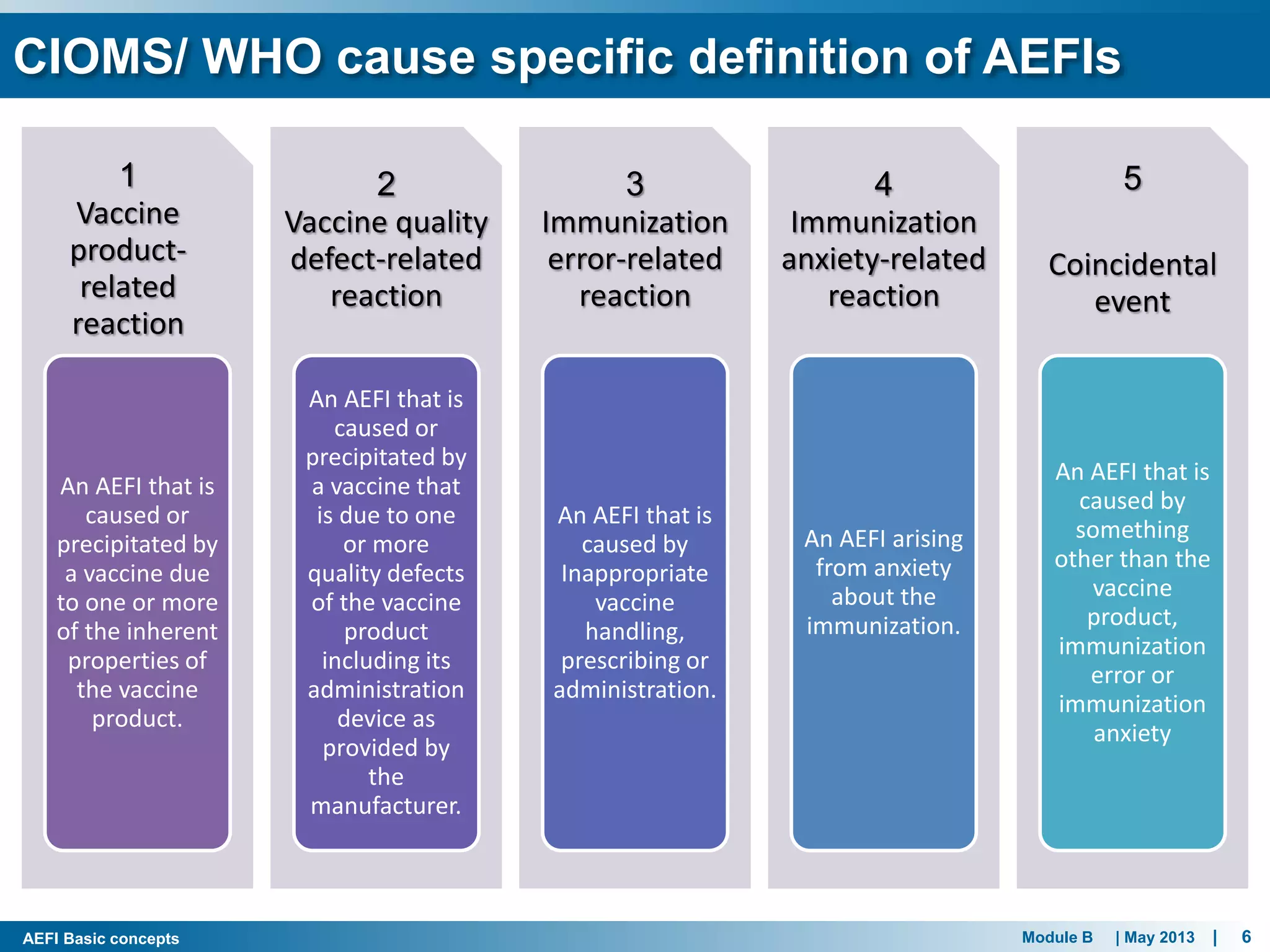
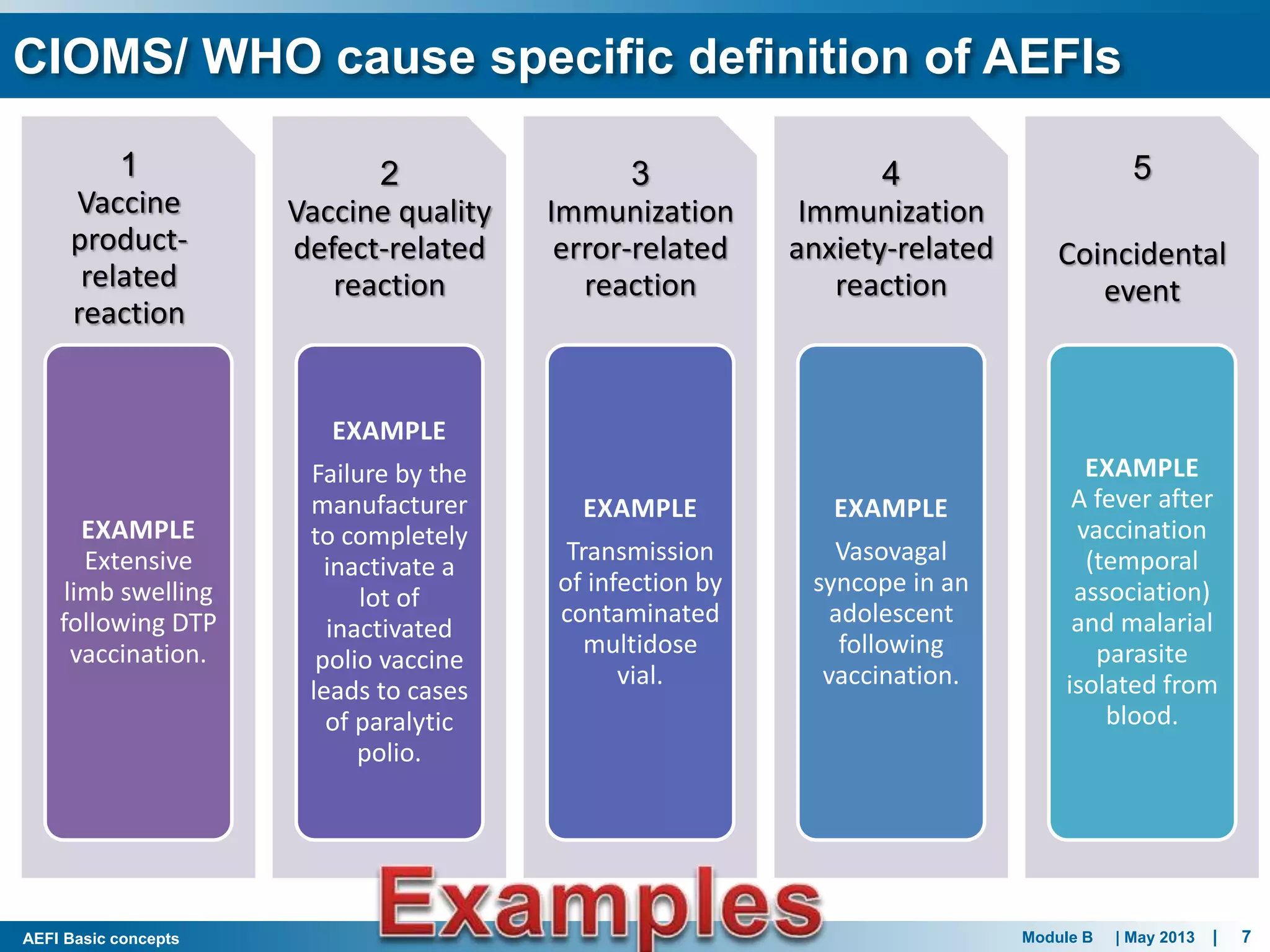
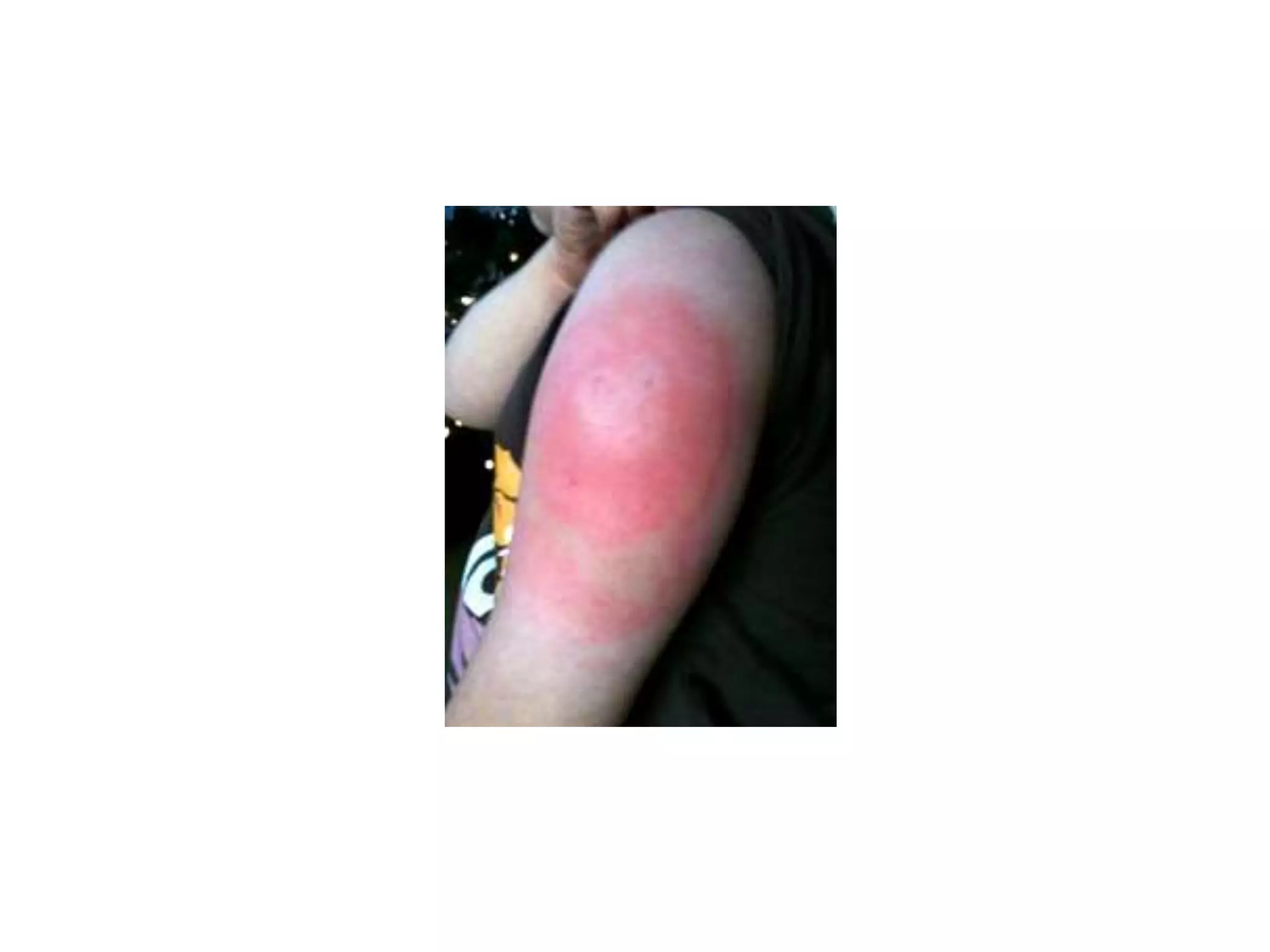
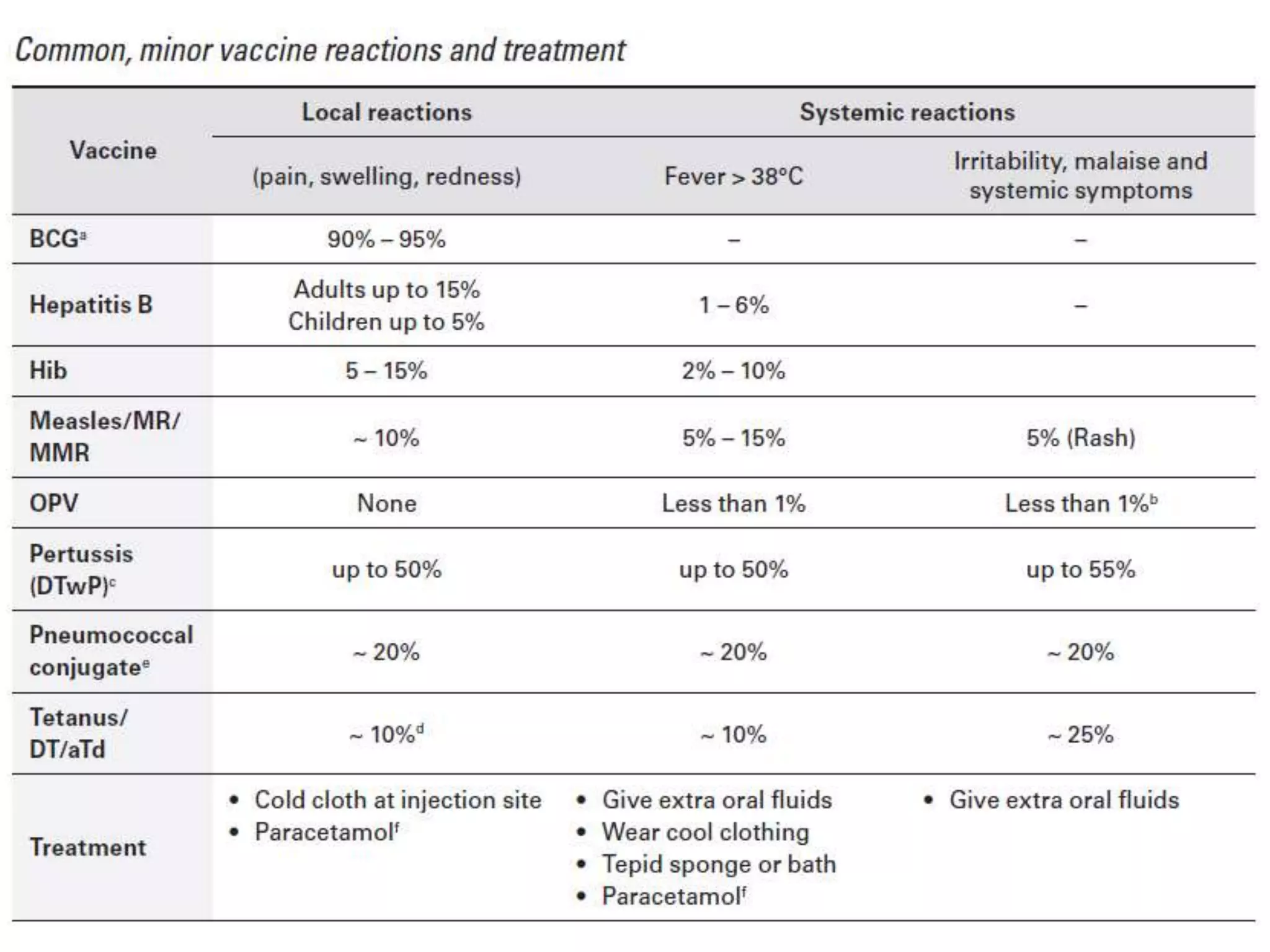
This document discusses adverse events following immunization (AEFI). It defines AEFI as any untoward medical occurrence that follows immunization but does not necessarily have a causal relationship to the vaccine. AEFIs are classified based on whether they are related to the vaccine product, a vaccine quality defect, an immunization error, immunization anxiety, or are coincidental. Serious AEFIs that require reporting include death, hospitalization, disability, and life-threatening events. AEFI reporting and surveillance procedures in India involve using a case reporting form within 24-48 hours and a preliminary and final case investigation form within 10 and 70 days respectively.




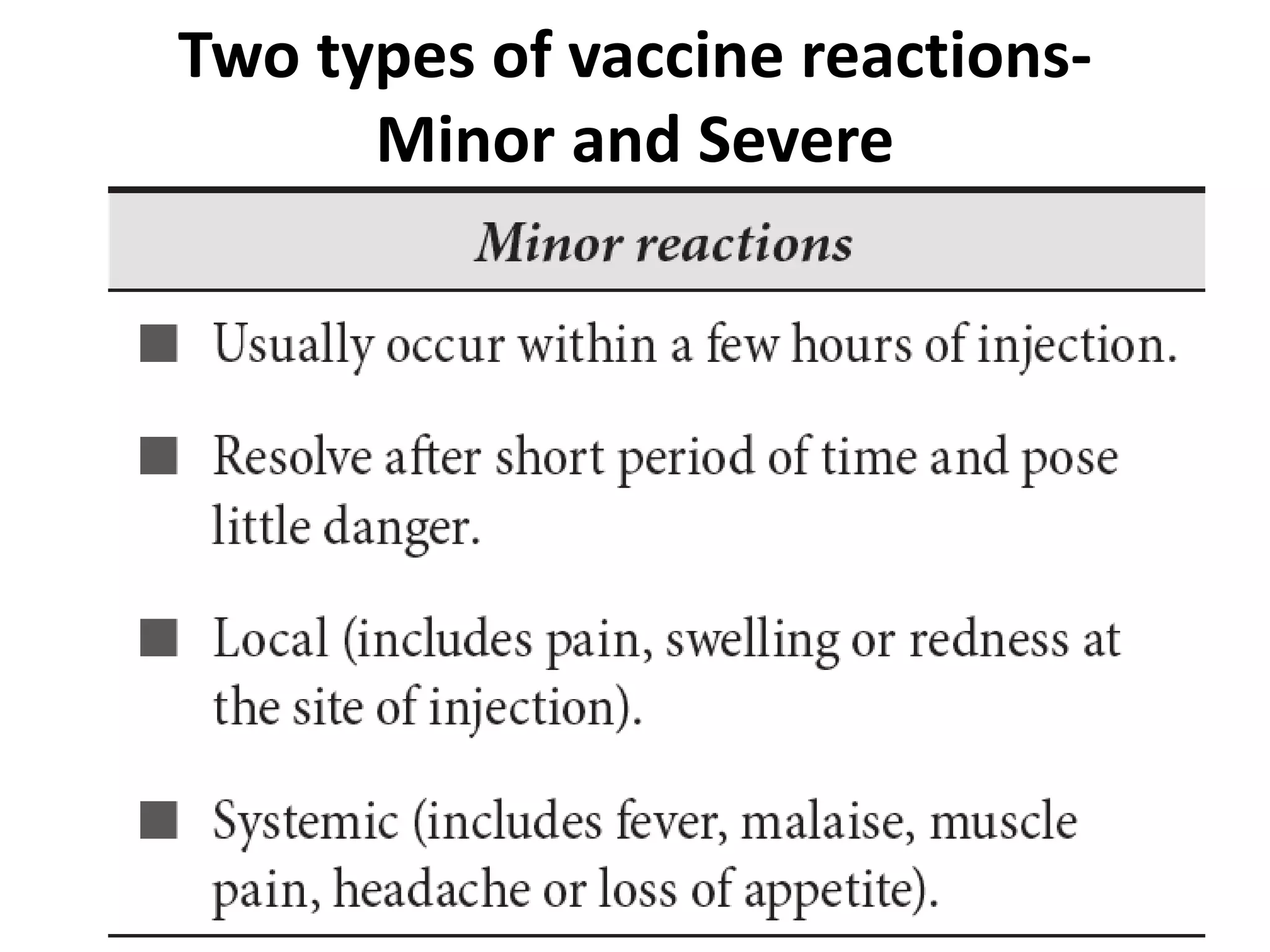

![Two types of vaccine reactions-
Minor and Severe
Antigen
[Live, Killed,
Purified,
Inactivated
toxin]
Stabilizers
(help the vaccine maintain its
effectiveness during storage)
[MgCl2, MgSO4]
Adjuvants
(improve the immune response to
vaccine antigens, most often in
killed vaccine)
[Aluminium
salts]
Antibiotics
(to prevent bacterial
contamination of the tissue
culture cells in which the viruses
are grown)
[Neomycin]
Preservatives
(added to multidose vaccines to
prevent bacterial and fungal
growth)
[Thiomersal,
Formaldehyde]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aefi-150419102834-conversion-gate01/75/Adverse-Events-Following-Immunization-AEFIs-13-2048.jpg)