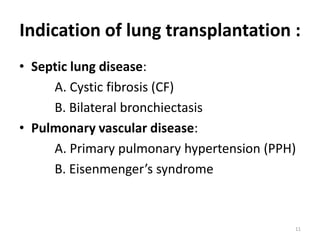
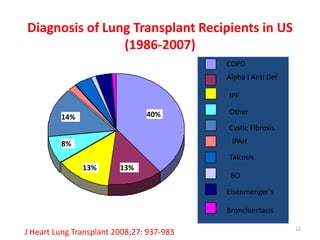
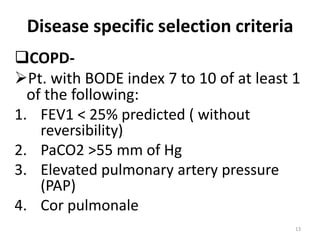
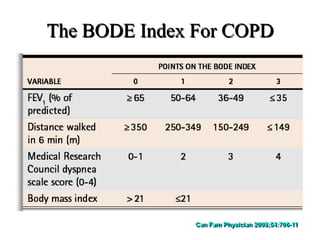
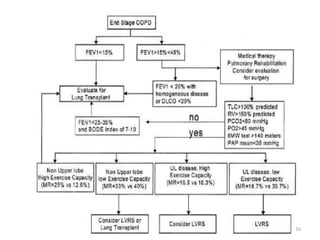
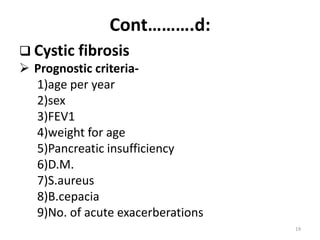
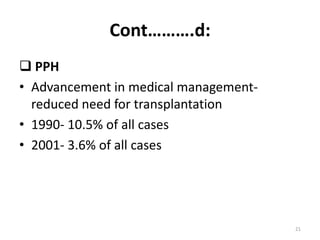
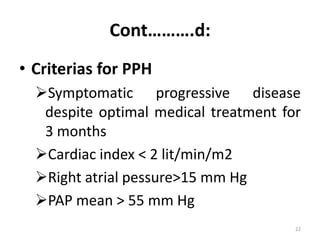
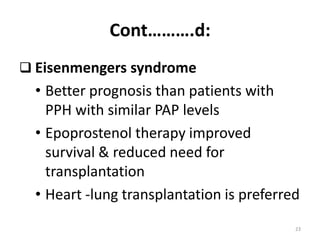
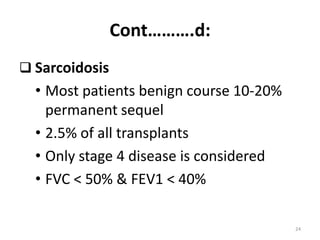
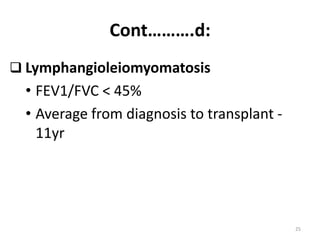
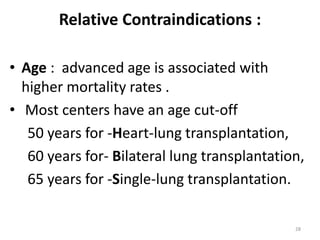
Lung transplantation involves removing diseased lungs and replacing them with healthy donor lungs. It is used to treat end-stage lung diseases like COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, and cystic fibrosis. Candidates undergo evaluation including lung function tests and imaging. Donor lungs must be disease-free and match the recipient's size. The surgery connects the donor lungs to blood vessels and airways. Patients are monitored closely after for bleeding, infection, and organ rejection. Long term immunosuppression is required to prevent rejection and complications include infections and chronic lung allograft dysfunction.