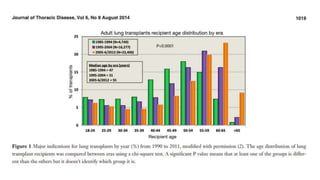
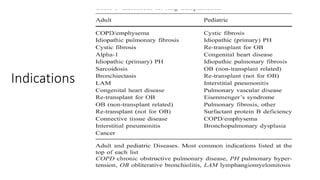
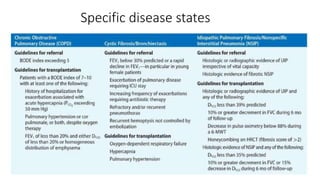
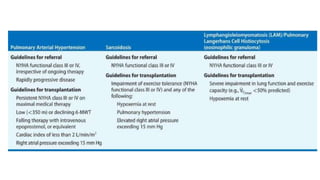
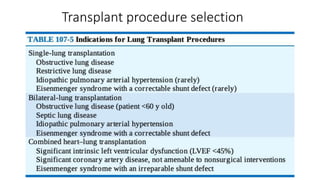
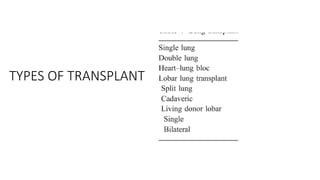
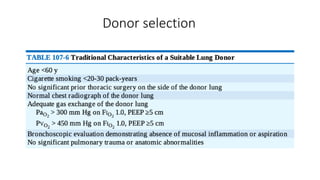
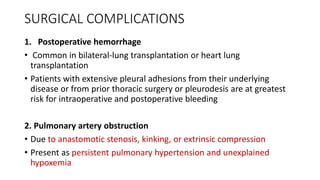
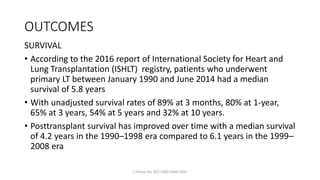
Lung transplantation involves removing diseased lungs and replacing them with healthy donor lungs. It is an accepted treatment for end-stage lung diseases that do not respond to medical therapy. While outcomes have improved since the first lung transplant in 1963, complications include rejection and infections. Post-transplant, patients experience greatly improved quality of life and lung function, though survival rates decline over time due to chronic lung allograft dysfunction.